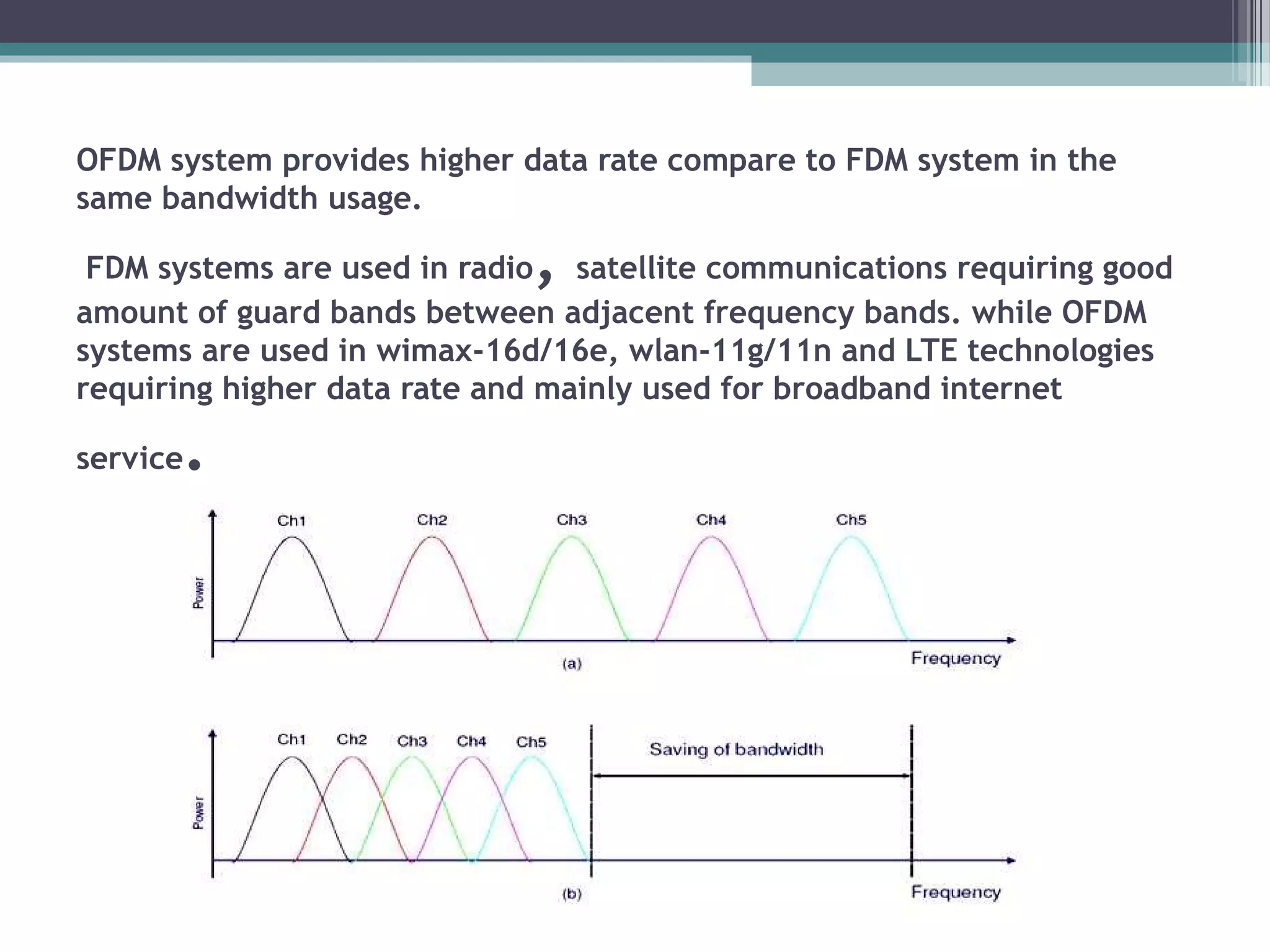
This document discusses Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM). It defines OFDM as a digital multi-carrier modulation technique that uses a large number of closely spaced orthogonal sub-carrier signals to carry data. The document outlines the advantages of OFDM, which include being robust against interference and fading, and its efficient implementation using FFT. Examples of applications that use OFDM are given as digital audio/video broadcasting, ADSL, wireless networking and power-line technology.