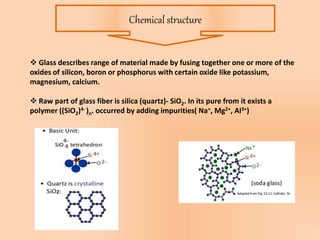
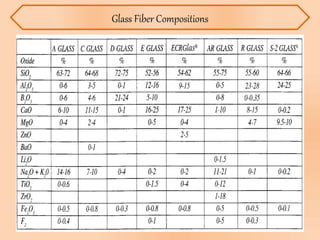
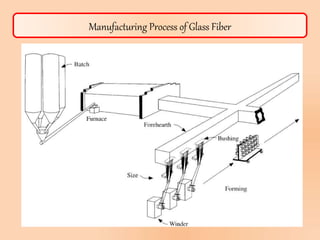
This document summarizes information about glass fiber, including its history, manufacturing process, properties, applications, and end products. Glass fiber is made of extremely fine glass fibers and is produced through a process of heating and drawing glass into fibers. It has good strength, durability, and electrical resistivity. Major applications of glass fiber include composites for transportation, electronics, construction, infrastructure, aerospace, and medical products. Glass fiber has comparable mechanical properties to carbon fiber but is cheaper and less brittle. It has a bright future due to its unique physical properties.