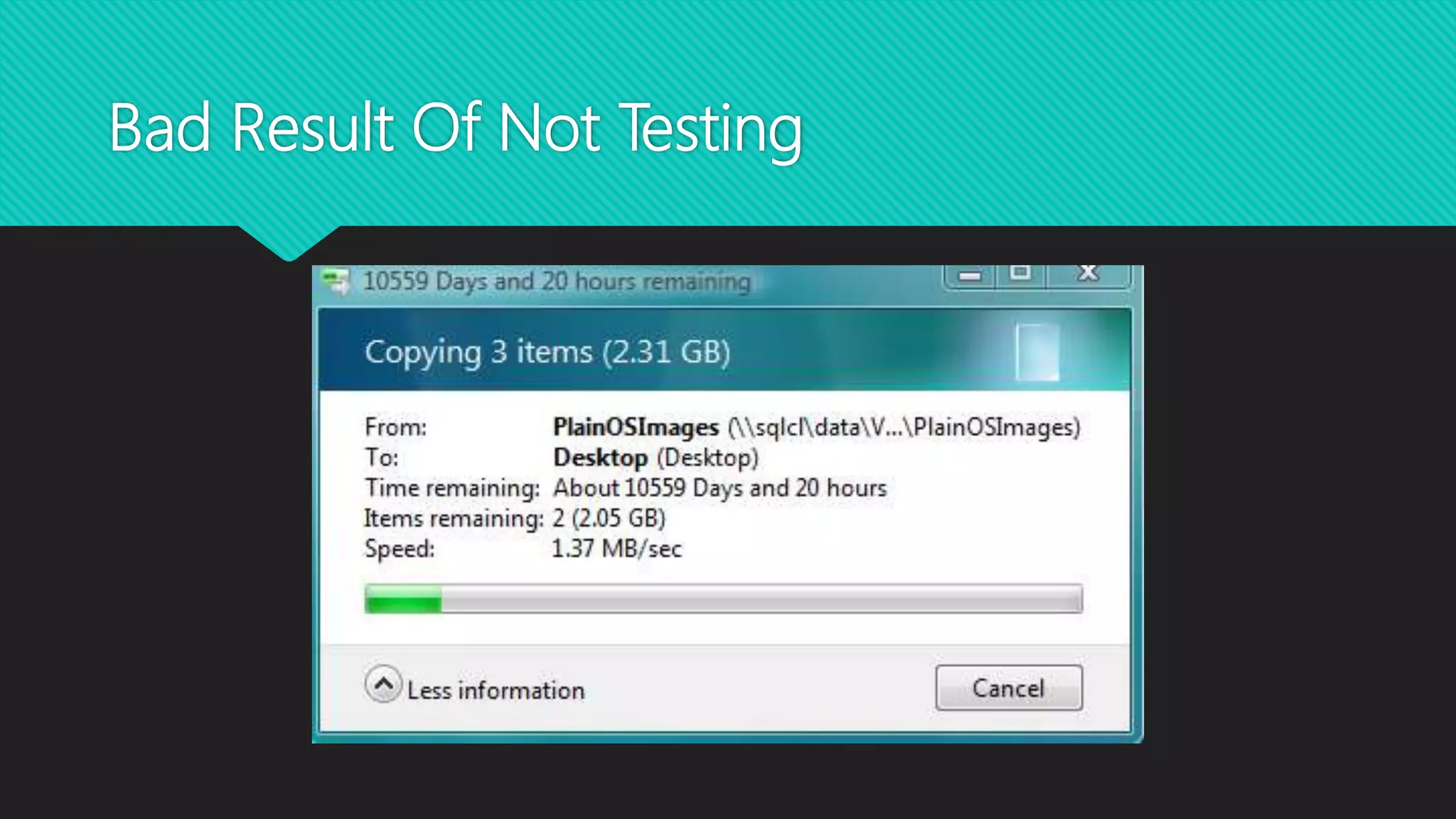
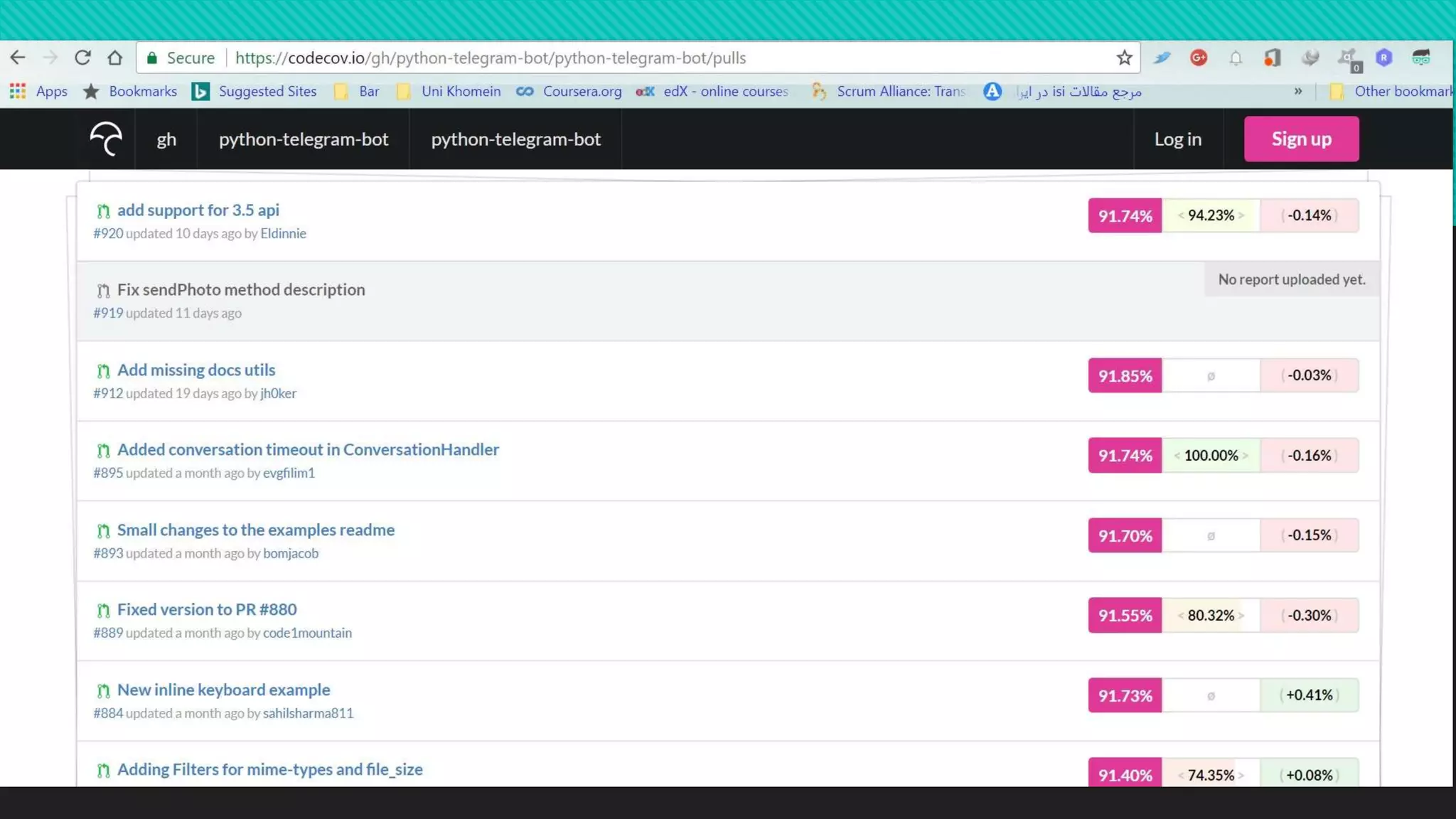
The document discusses various types of software testing. It defines software testing as executing a program to find bugs and ensure it meets requirements. There are different types of tests like unit, integration, system, and acceptance. Unit tests check individual code units work as intended. Integration tests check multiple units work together. System tests check the full application in a production environment. Acceptance tests check the software meets business needs. The document emphasizes the importance of testing for quality, flexibility, and avoiding expensive failures. Thorough testing helps ensure customer satisfaction and business success.