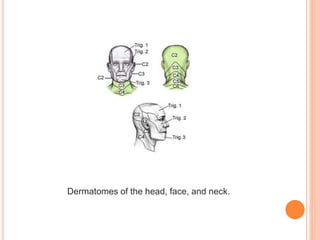
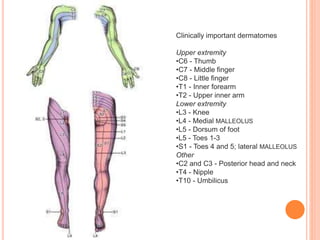
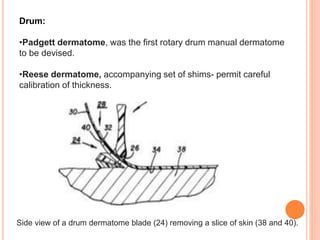
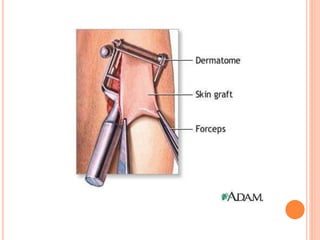
A dermatome is a surgical instrument used to harvest thin skin slices for grafting, primarily for treating grade 3 burns or trauma. It can be manually or electrically operated, with various types including knives, drum, and air dermatomes, each having distinct advantages and disadvantages. The document also outlines the anatomy of dermatomes and their clinical significance in identifying sensory nerve areas in the skin.