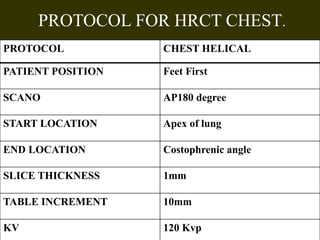
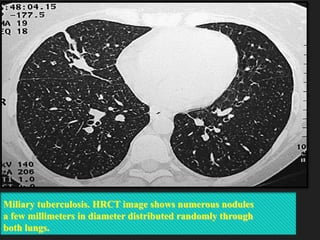
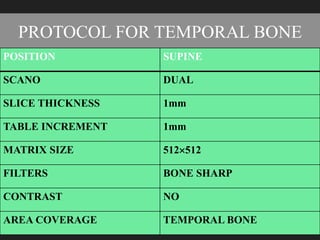
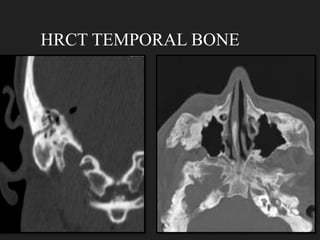
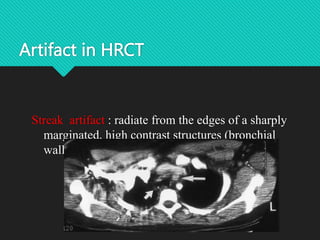
The document outlines the technical aspects and protocols for high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), focusing on its application in diagnosing lung and temporal bone diseases. It details patient preparation, different scanning positions, technical specifications, and potential artifacts. HRCT is significant for assessing various lung conditions, providing improved visualization while noting increased radiation exposure and image noise as disadvantages.