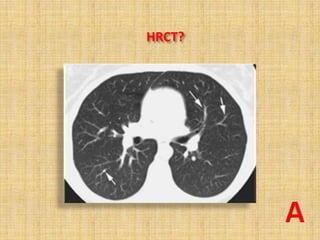
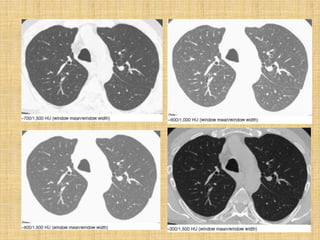
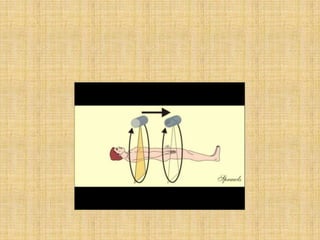
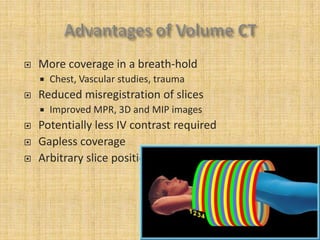
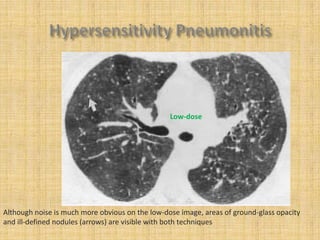
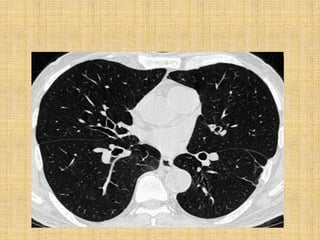
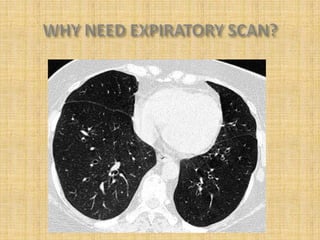
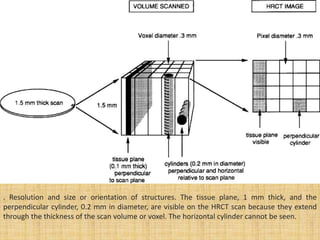
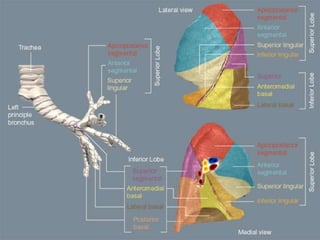
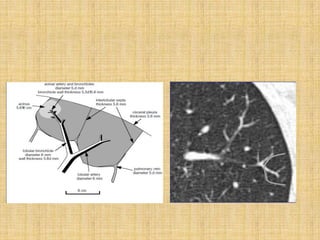
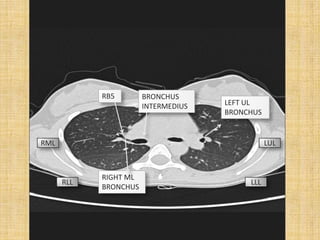
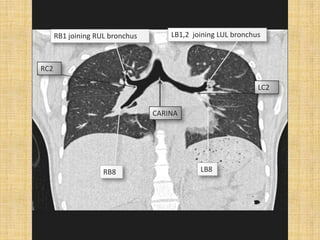
HRCT uses thin collimation and high-frequency reconstruction algorithms to maximize spatial resolution. This allows visualization of small structures. A routine HRCT uses 1mm collimation, 120-140 kVp, 200-300 mAs, and the shortest possible scan time to reduce noise while minimizing motion artifacts. Reconstructing with a sharp algorithm enhances detail but also noise. Increasing kVp and mAs reduces noise at the cost of increased radiation. MDCT allows whole-lung imaging in one breath-hold with improved multiplanar review compared to spaced HRCT scans. Low-dose HRCT can identify most abnormalities but with reduced image quality.