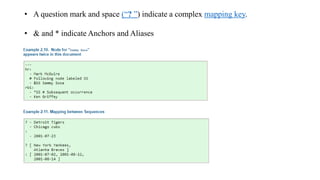
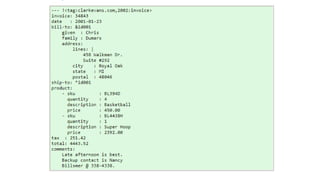
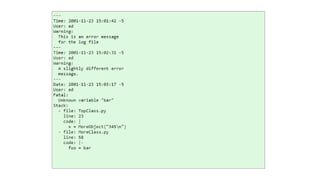
YAML is a data serialization language that is human-friendly and designed for interacting well with programming languages. Unlike XML, YAML aims to be easily readable by humans for config files, logging, and messaging. YAML uses indentation rather than tags to indicate hierarchy. It supports common data structures like lists, dictionaries, and scalar values like strings and integers.