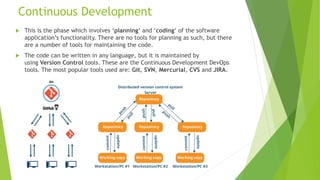
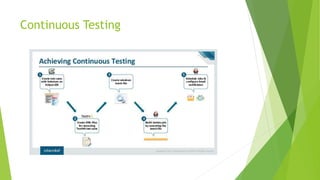
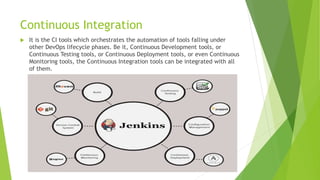
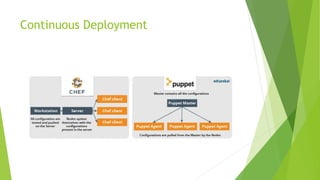
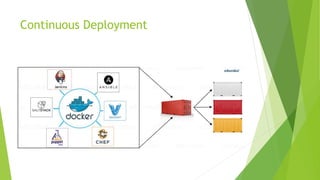
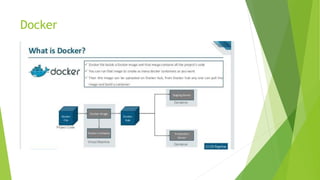
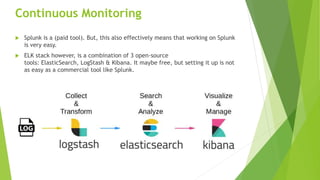
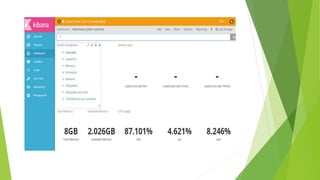
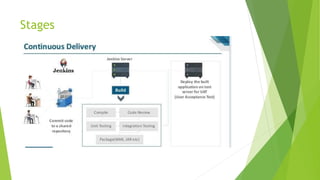
This document discusses DevOps CI/CD practices. It begins by introducing DevOps and contrasting it with traditional Waterfall and Agile methodologies. The document then covers the various stages of CI/CD pipelines including continuous development, continuous testing, continuous integration, continuous deployment, and continuous monitoring. It discusses tools used at each stage like version control systems, testing frameworks, CI servers, configuration management, containers, and monitoring tools. Specifically, it provides details on tools like Git, Jenkins, Selenium, Puppet, Docker, Splunk and the ELK stack.