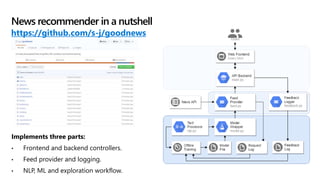
The document details a news recommendation system utilizing machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) to understand user interests and provide tailored news content. It covers the architecture, training processes, and various NLP techniques including text processing, clustering, and topic modeling. The document also highlights the application's potential for personalized recommendations and ongoing advancements in the field.















![1. LDA considers two things:
• Each document in a corpus is a weighted combination of several topics, e.g.,
doc1-> 0.1 finance + 0.2 science + 0.5 * technology,…
• Each topic has its collection of representative keywords, e.g.,
technology -> [‘computer’, ‘microsoft’, ‘google', ...]
3. Topic Modeling: LDA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/goodnews-190308075349/85/No-more-bad-news-18-320.jpg)












