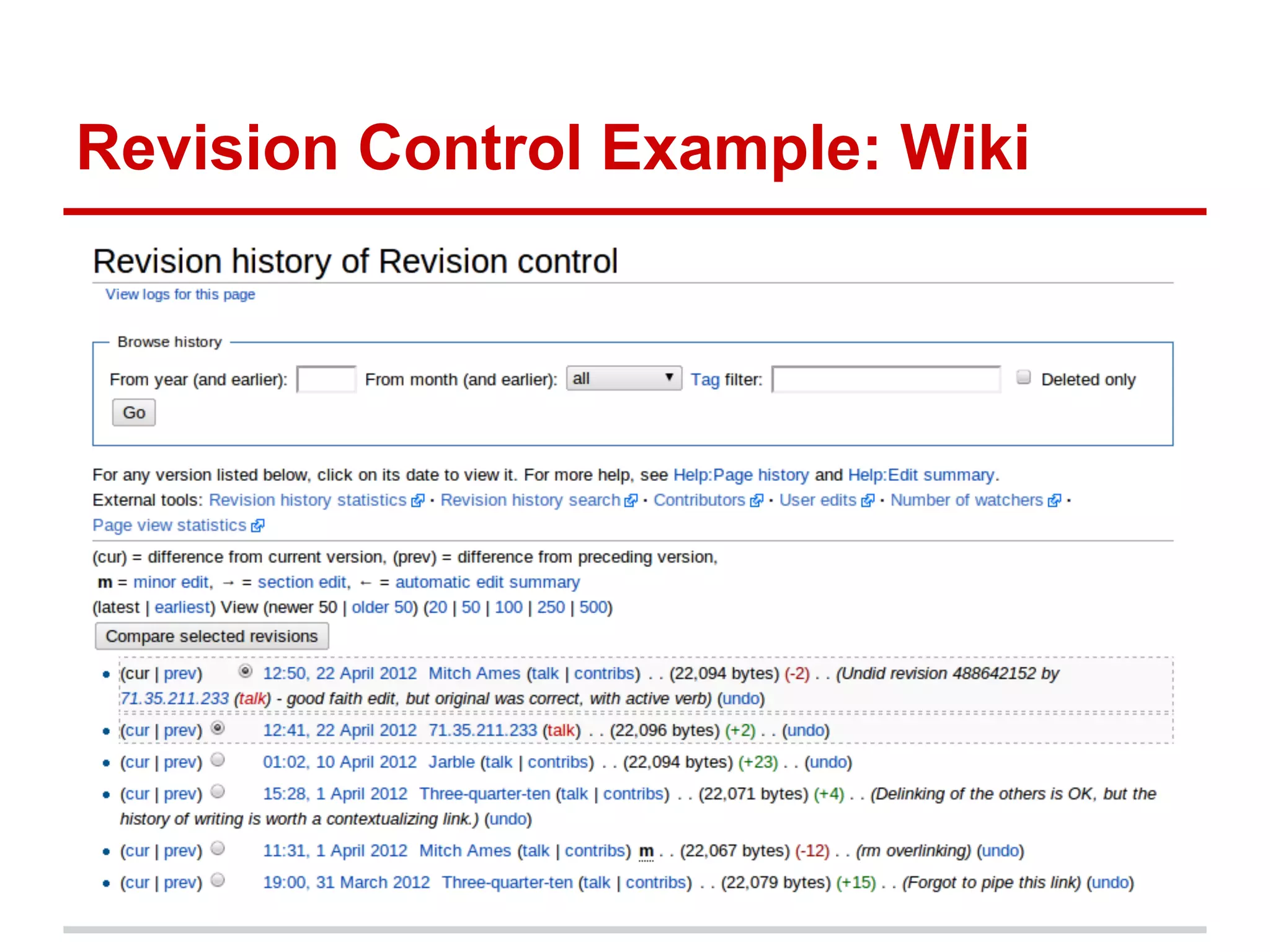
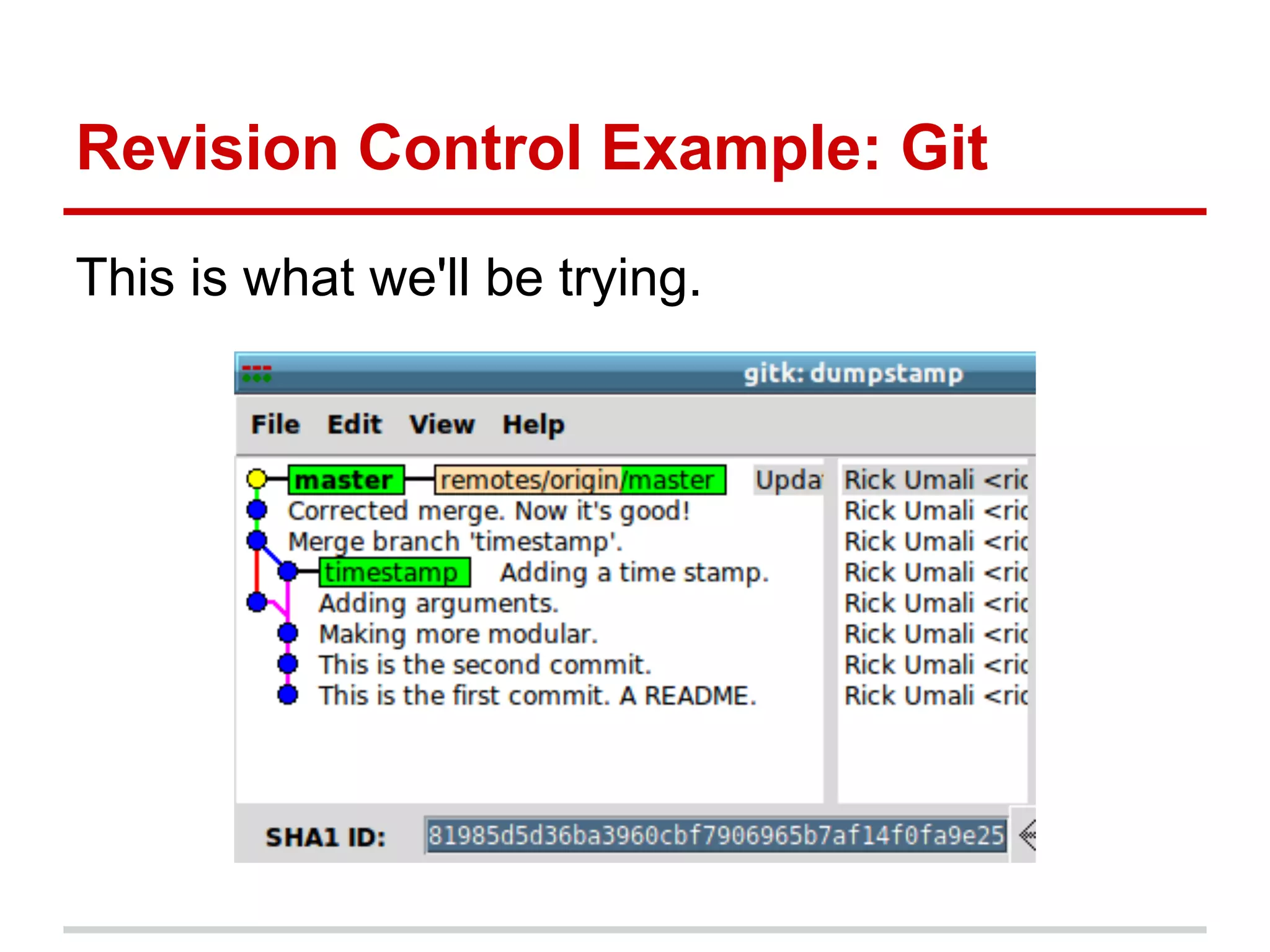
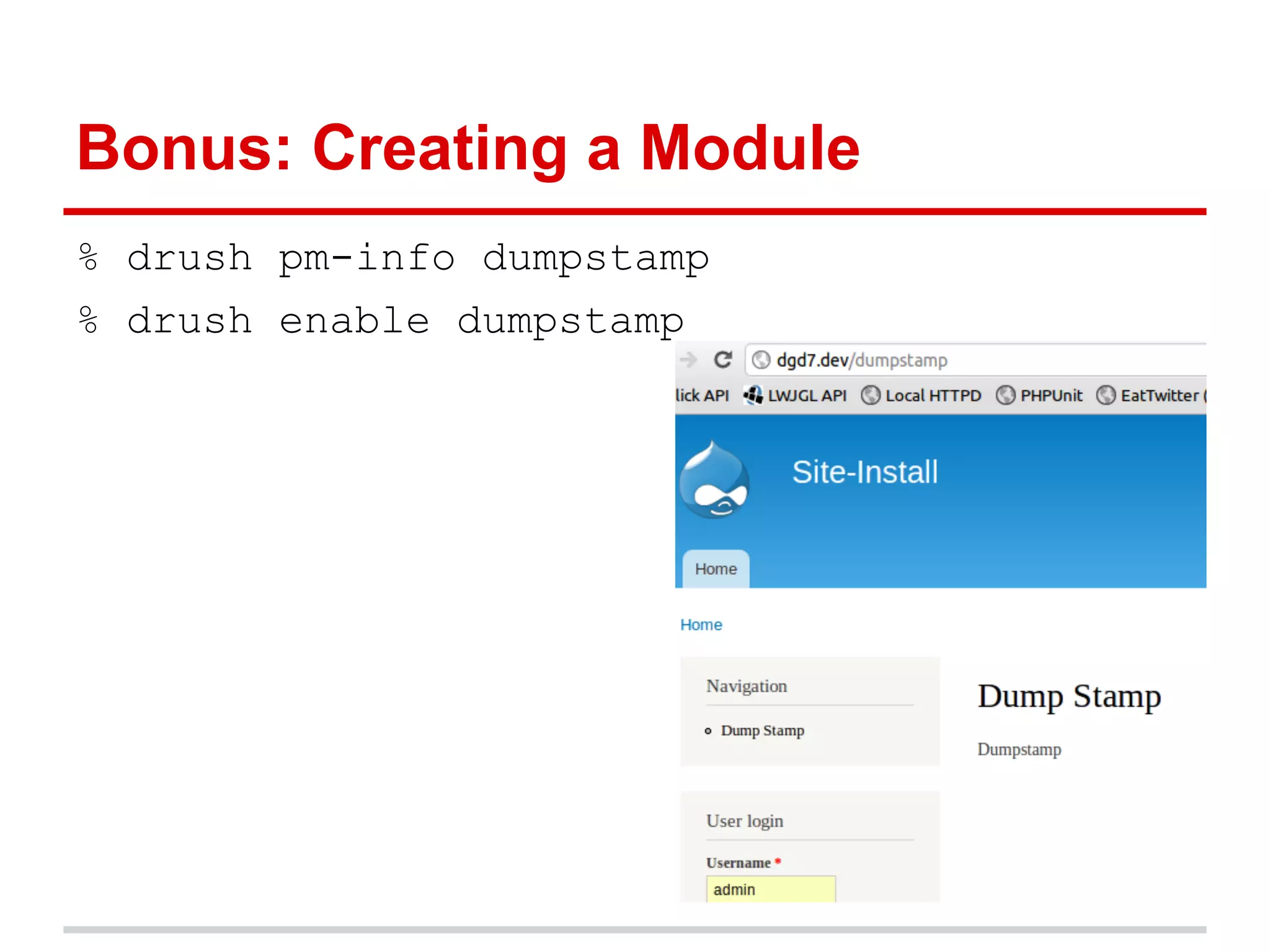
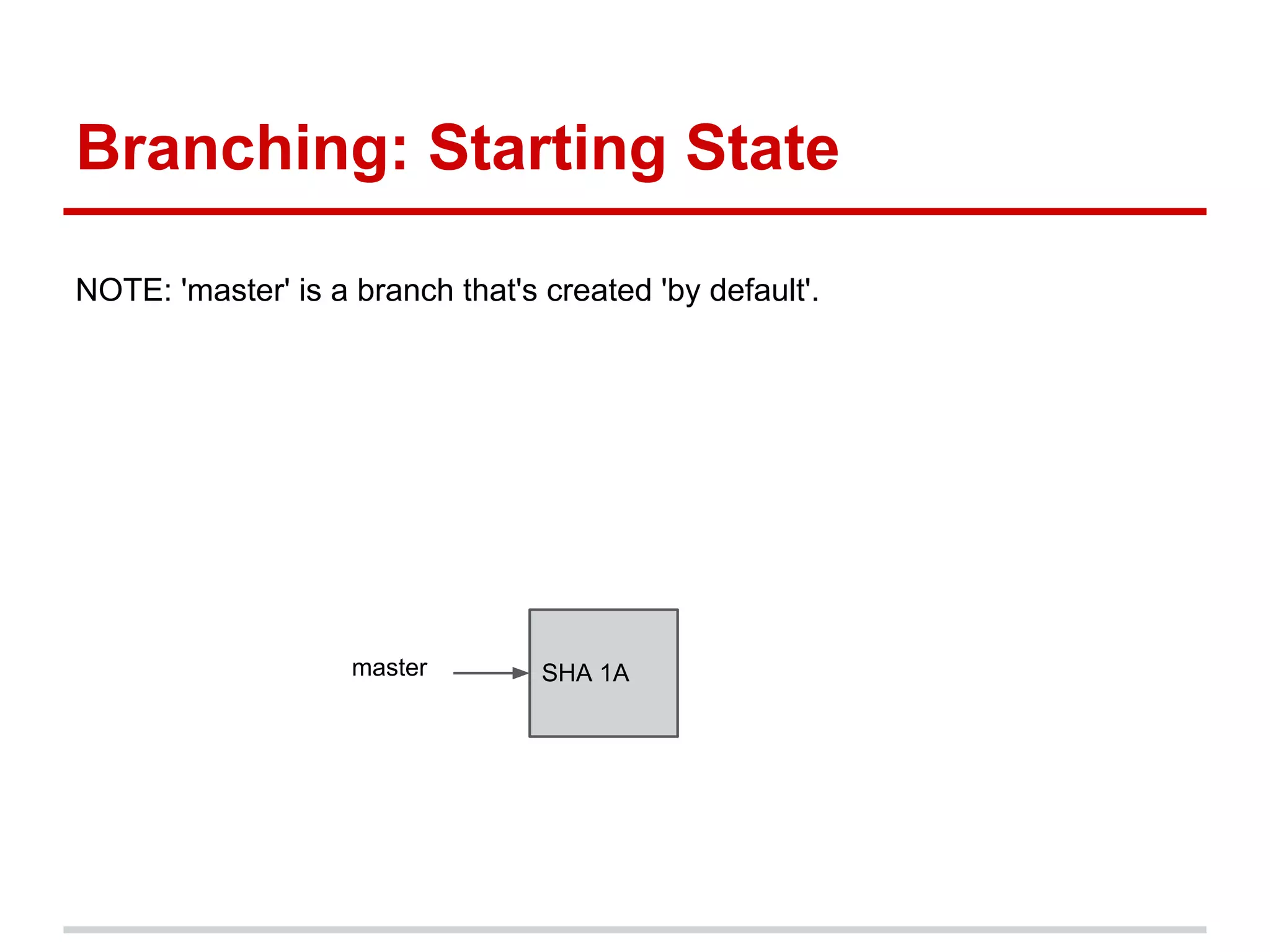
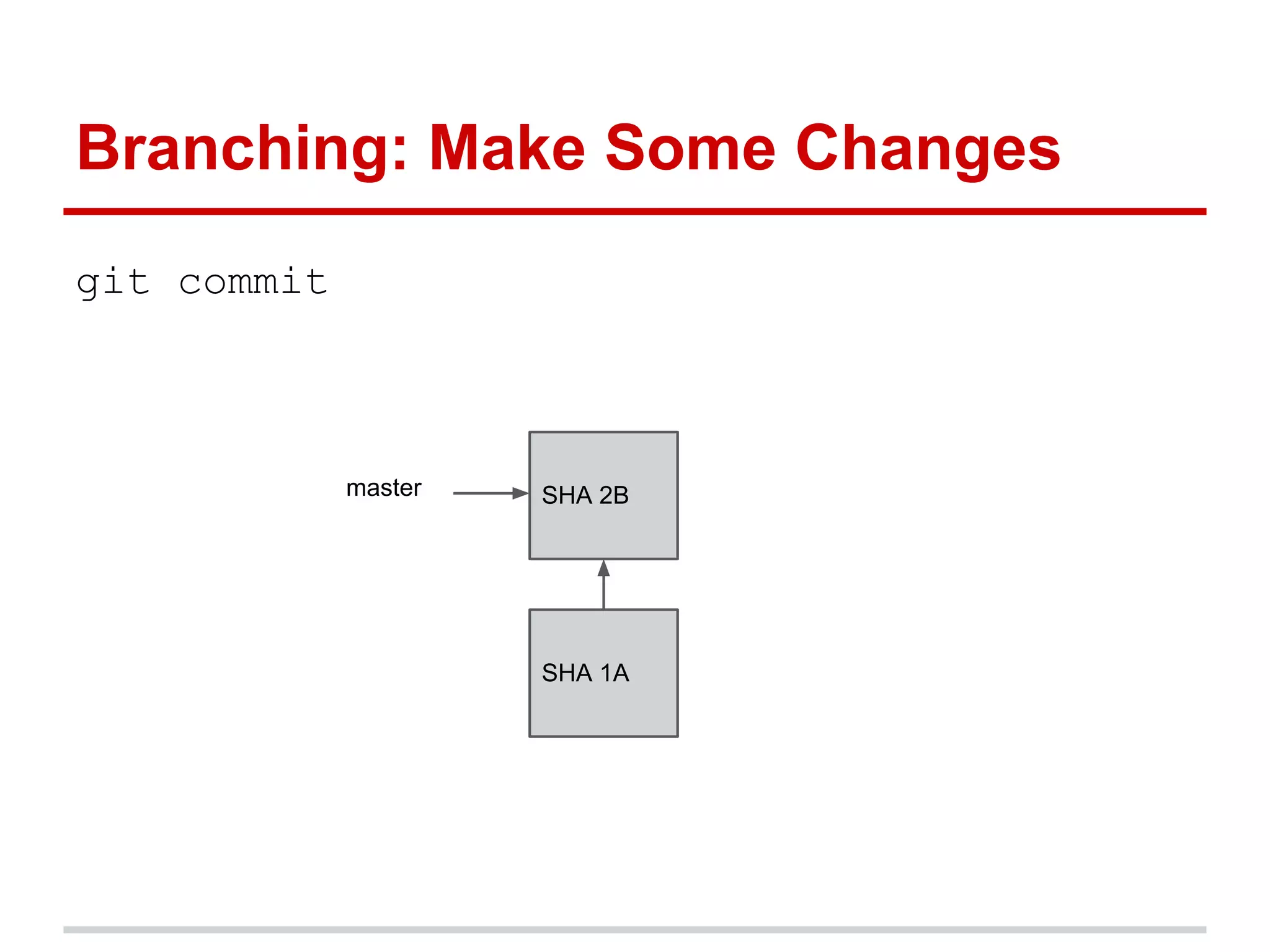
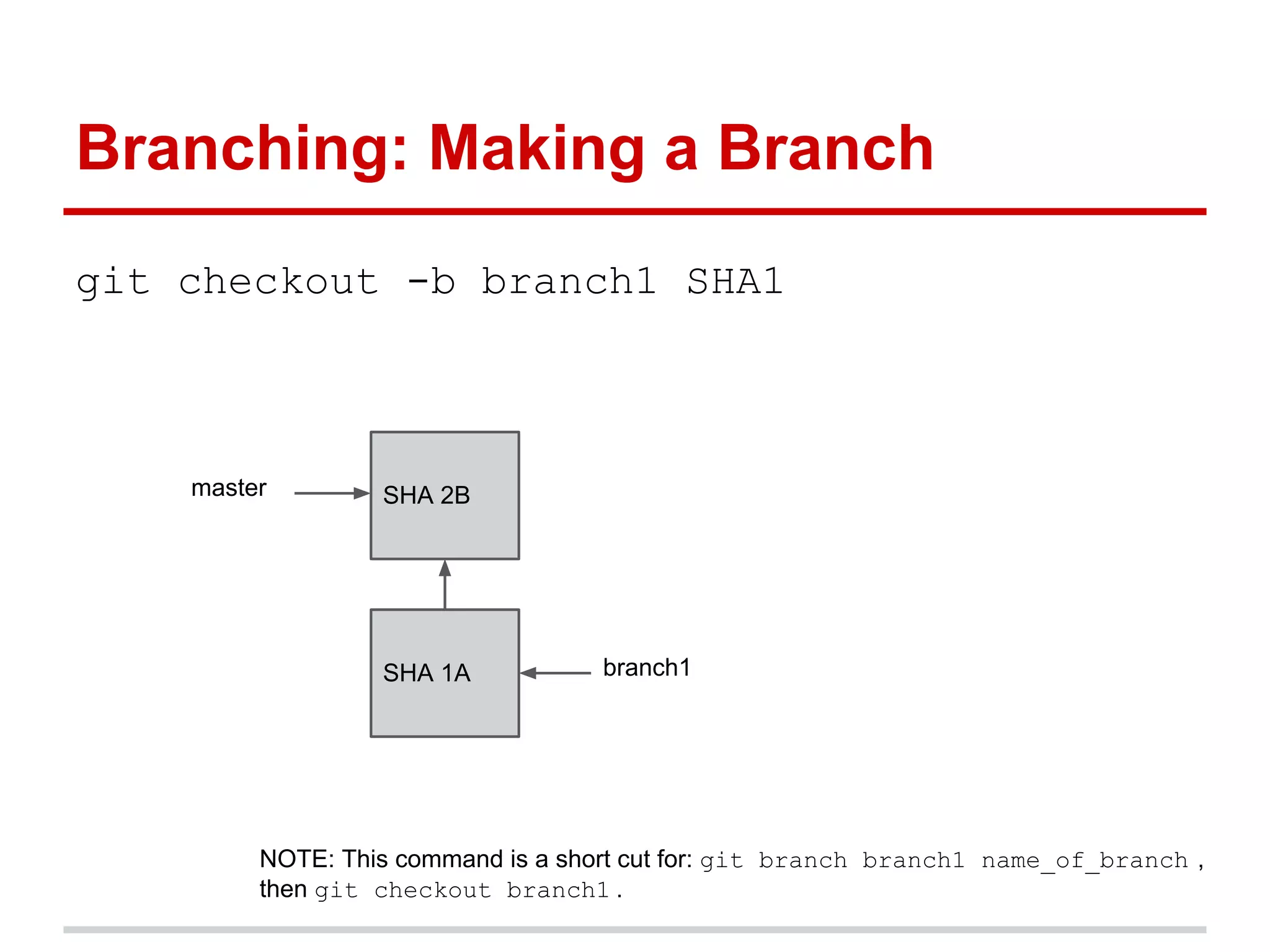
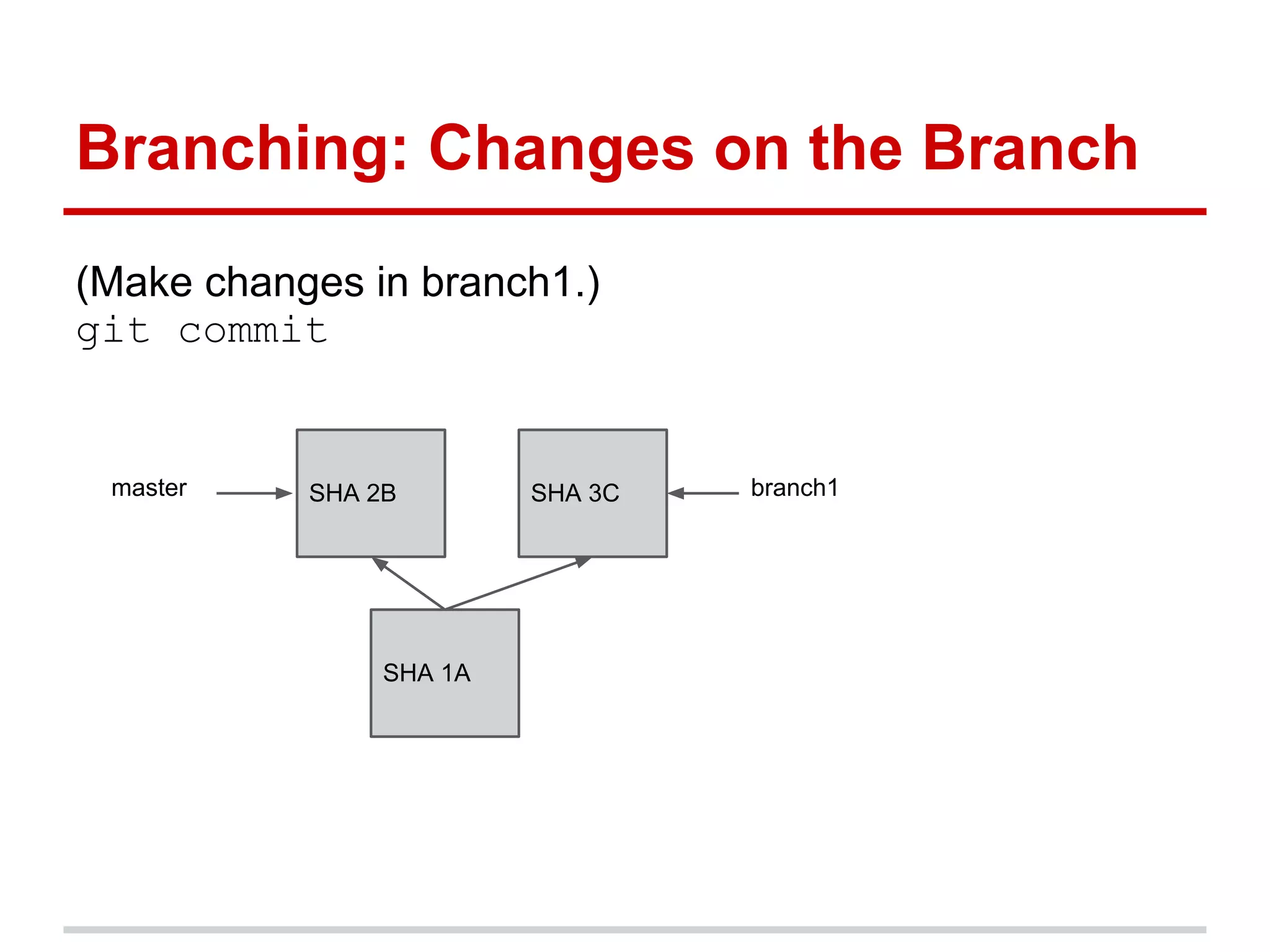
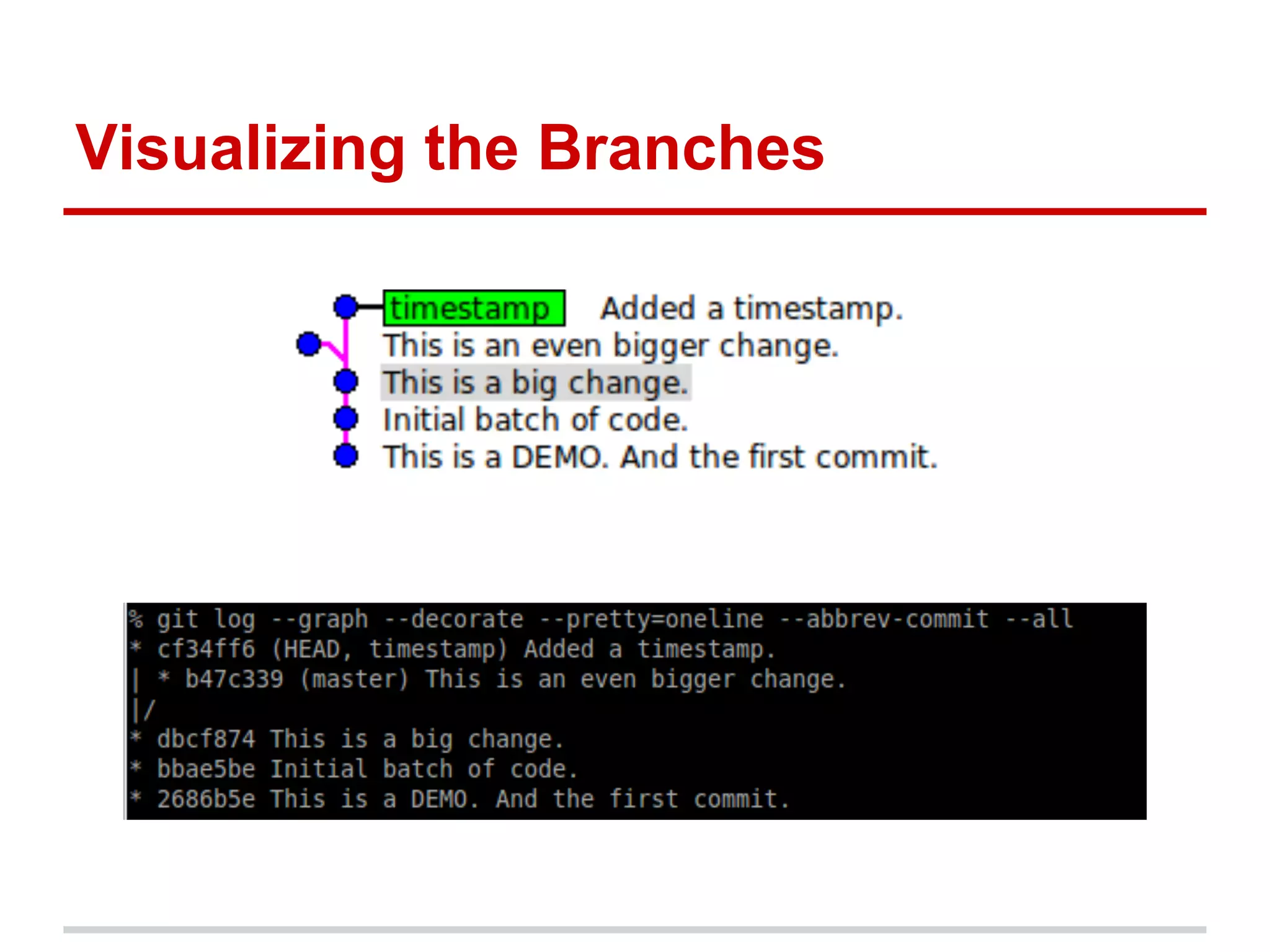
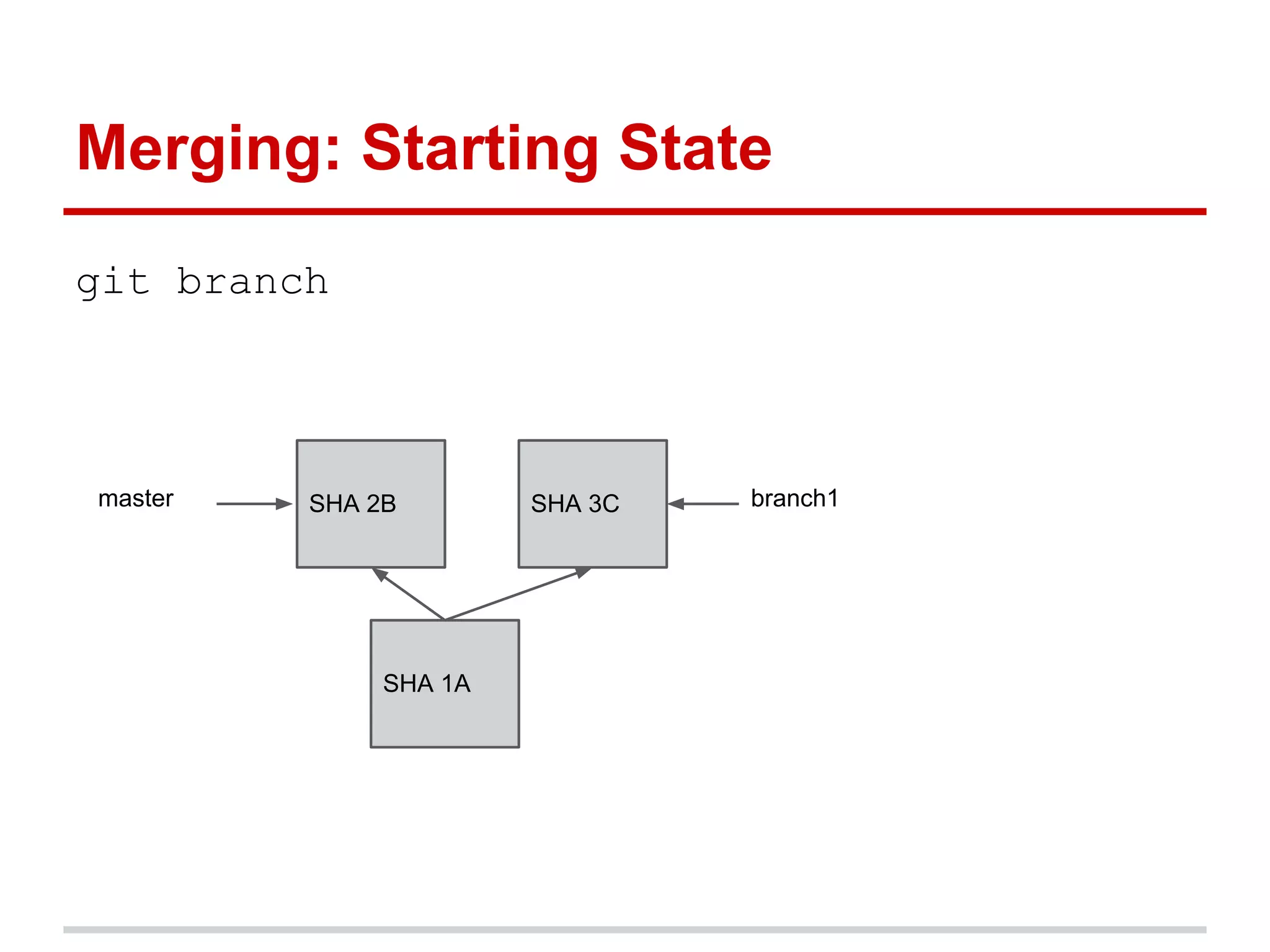
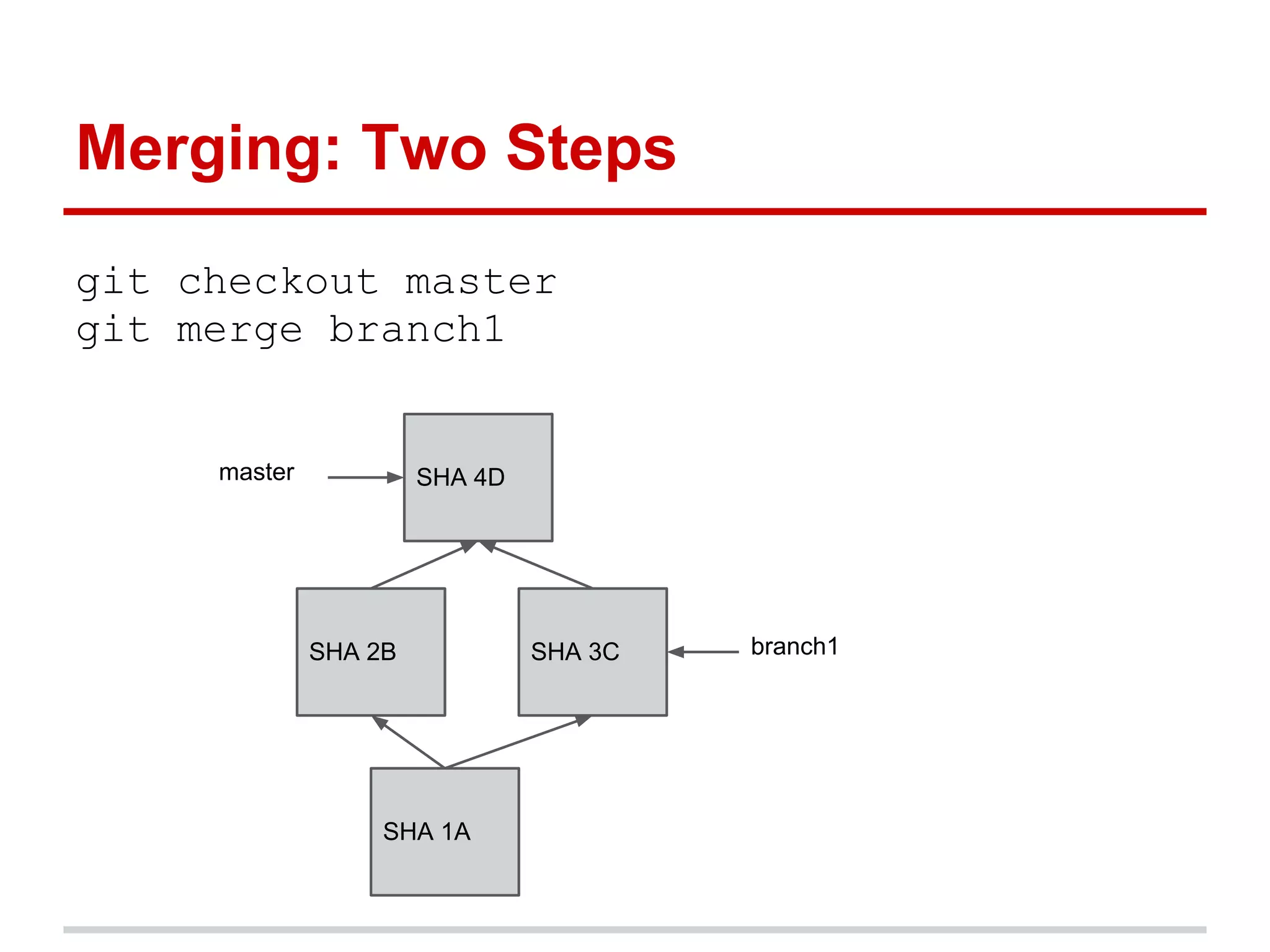
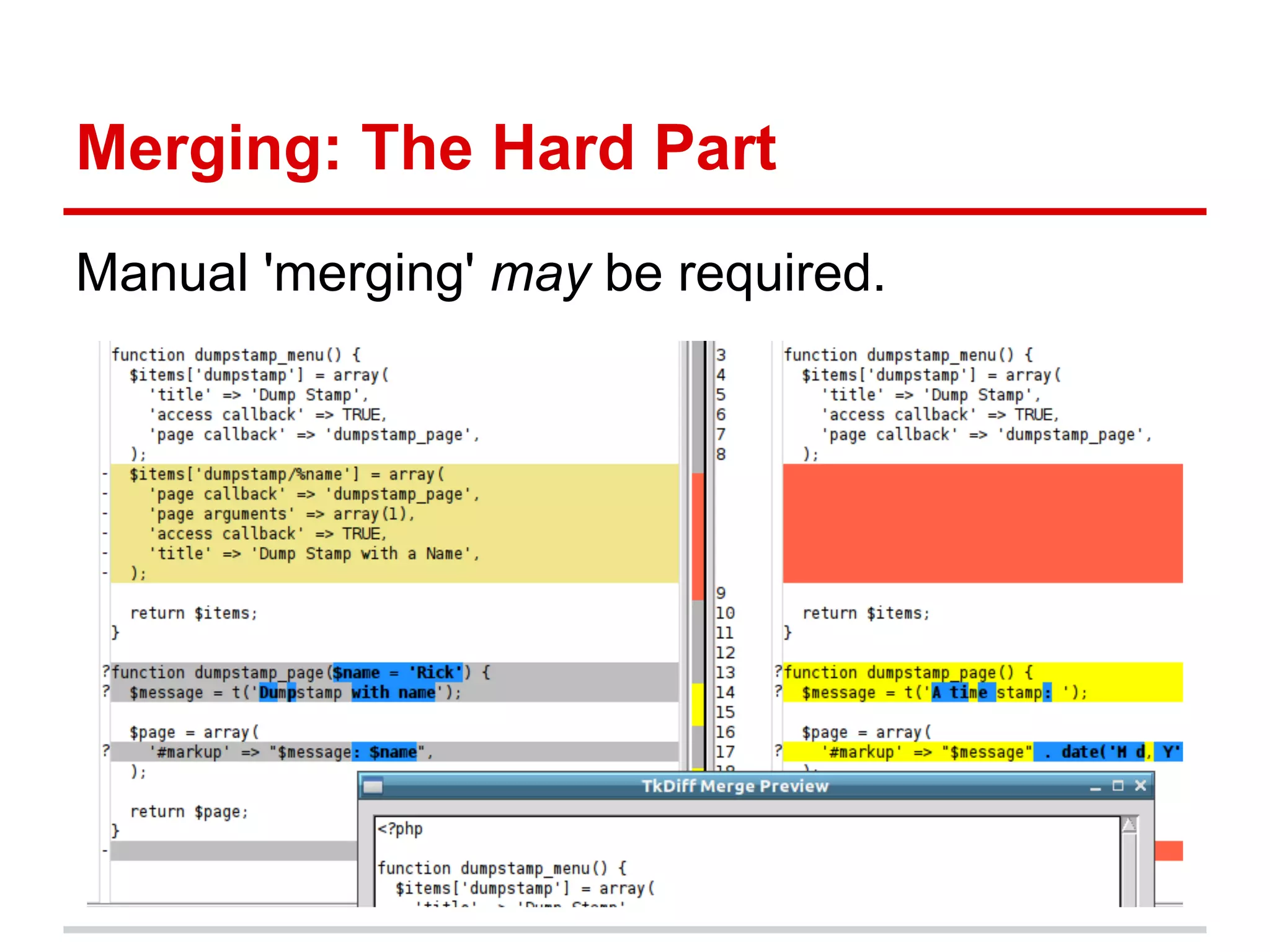
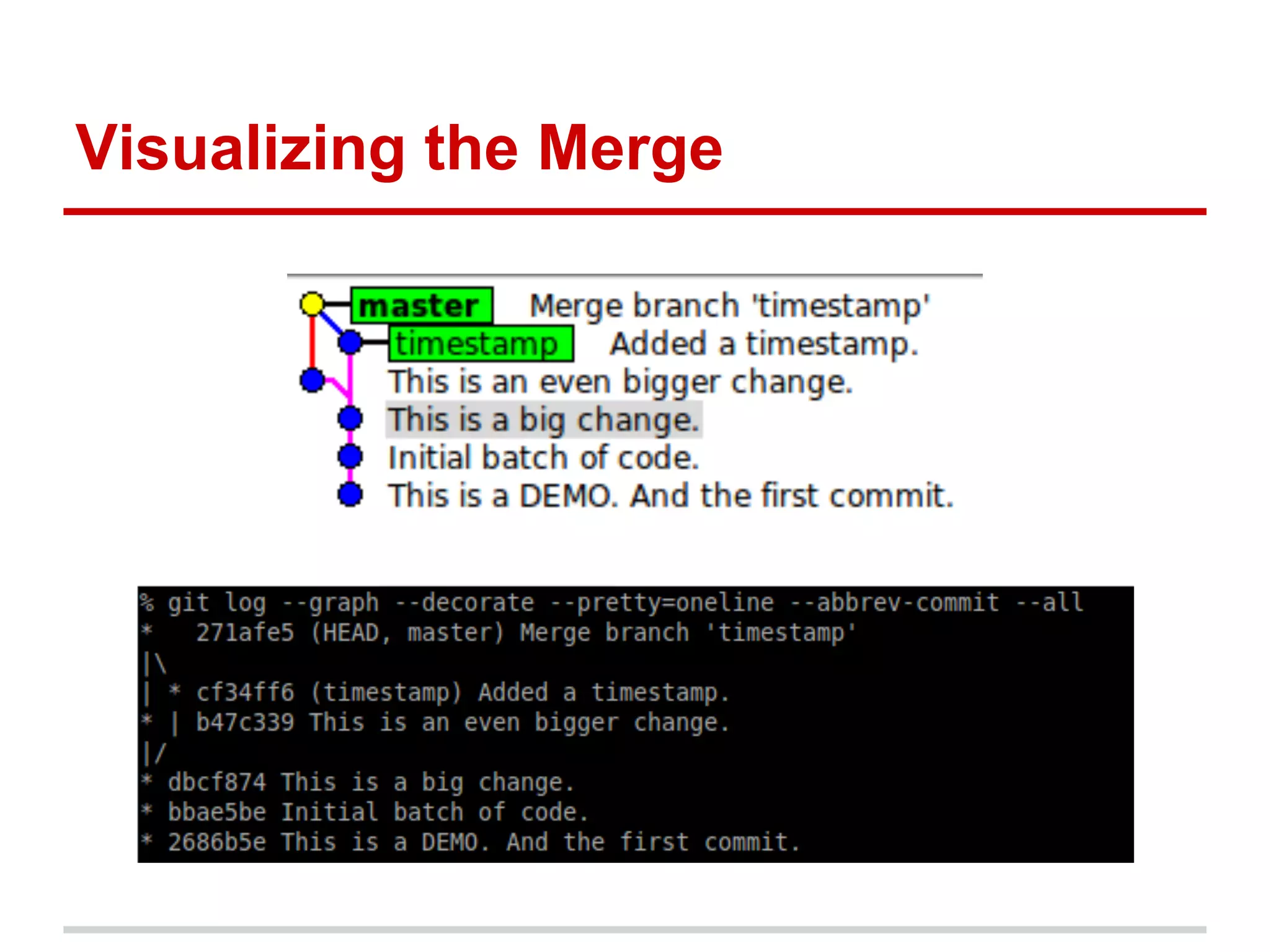
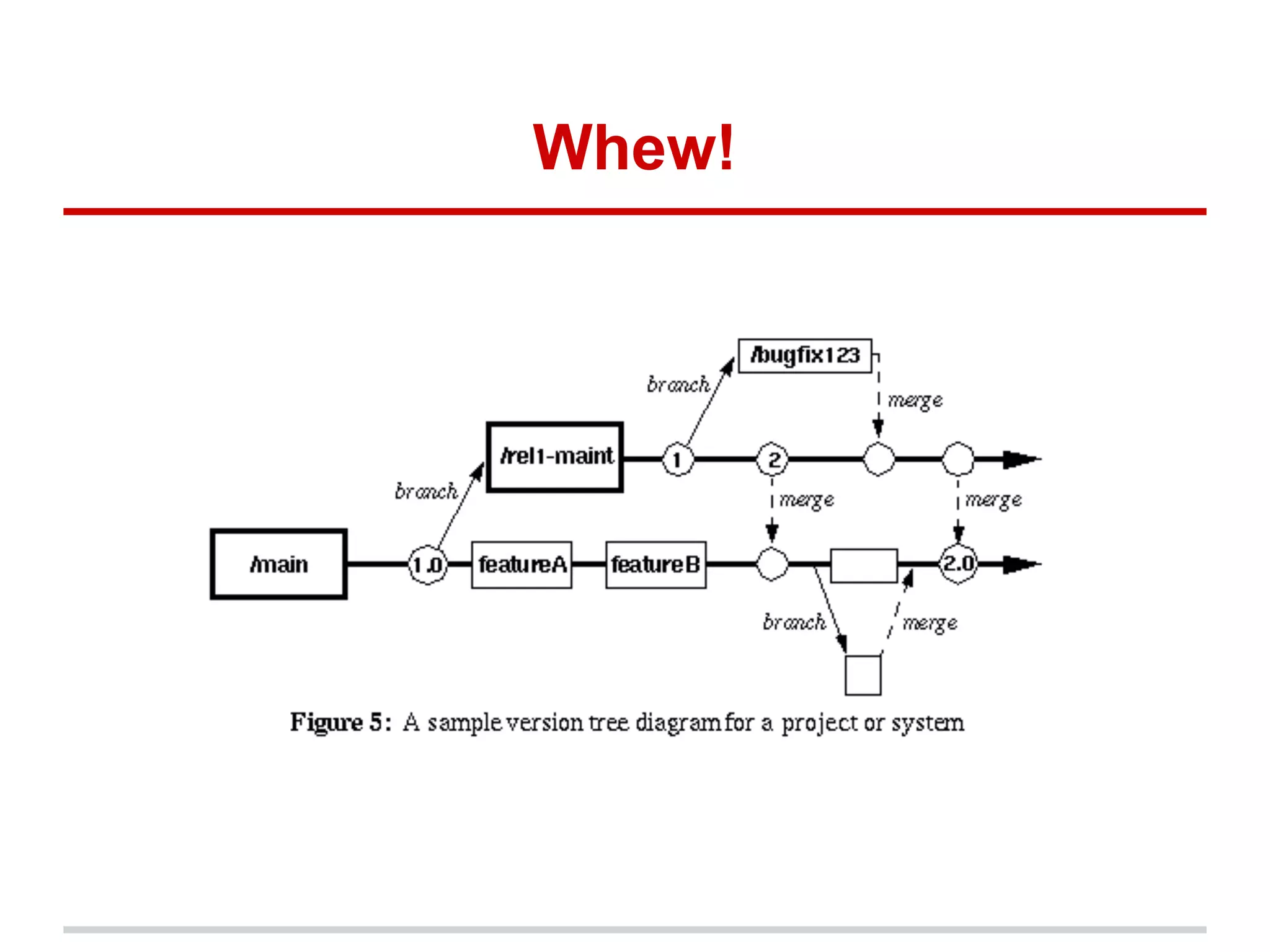
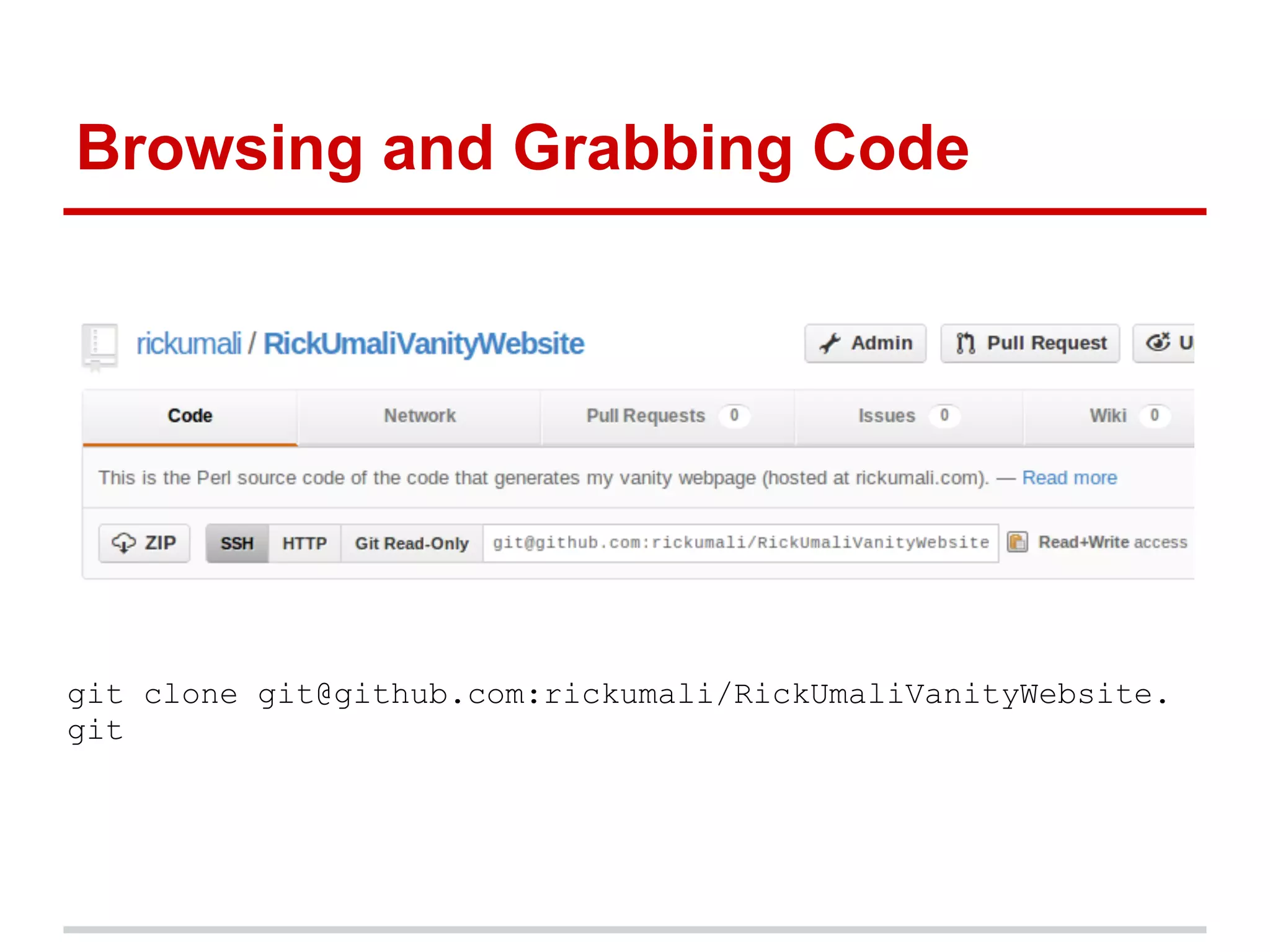
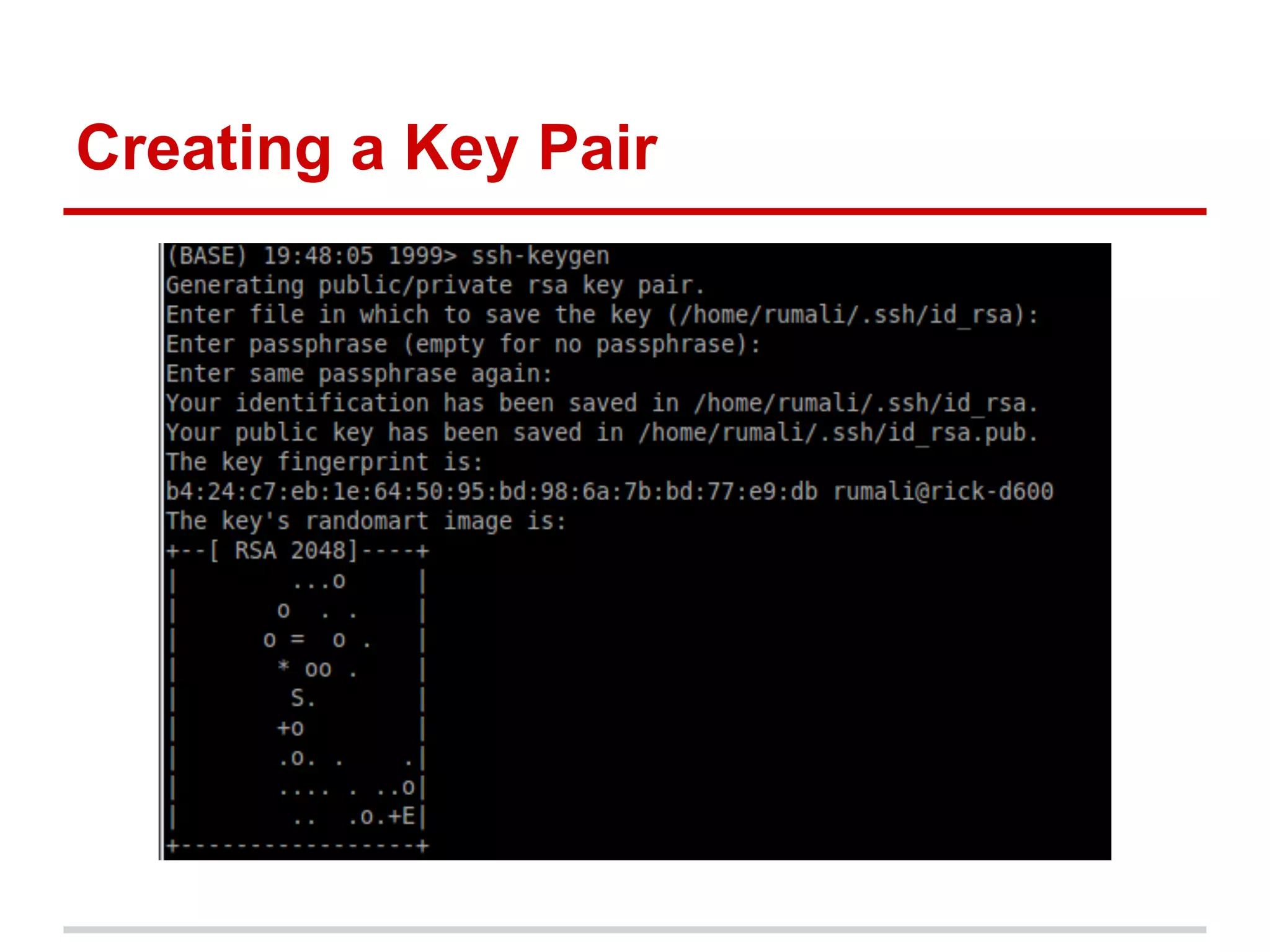
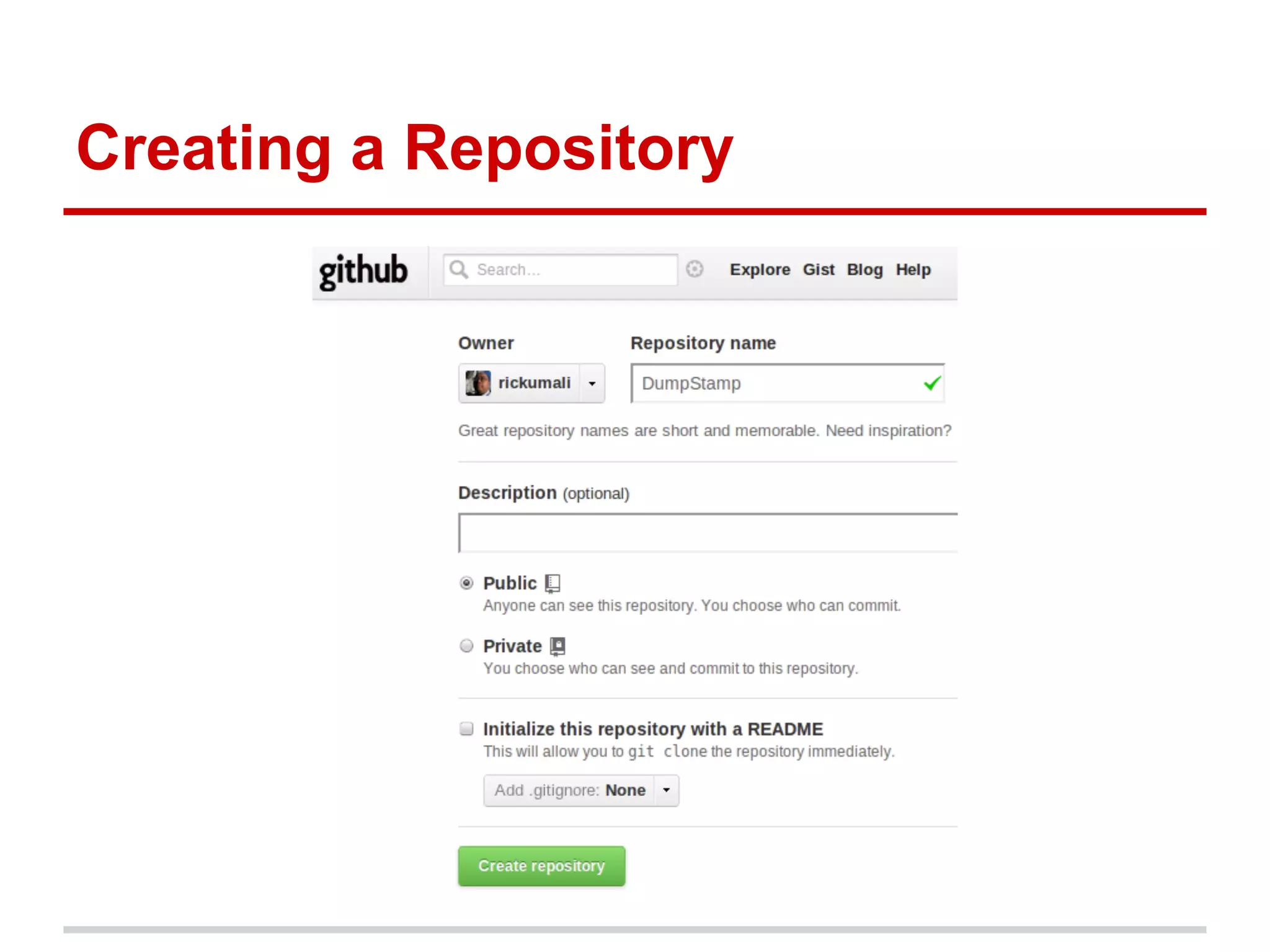
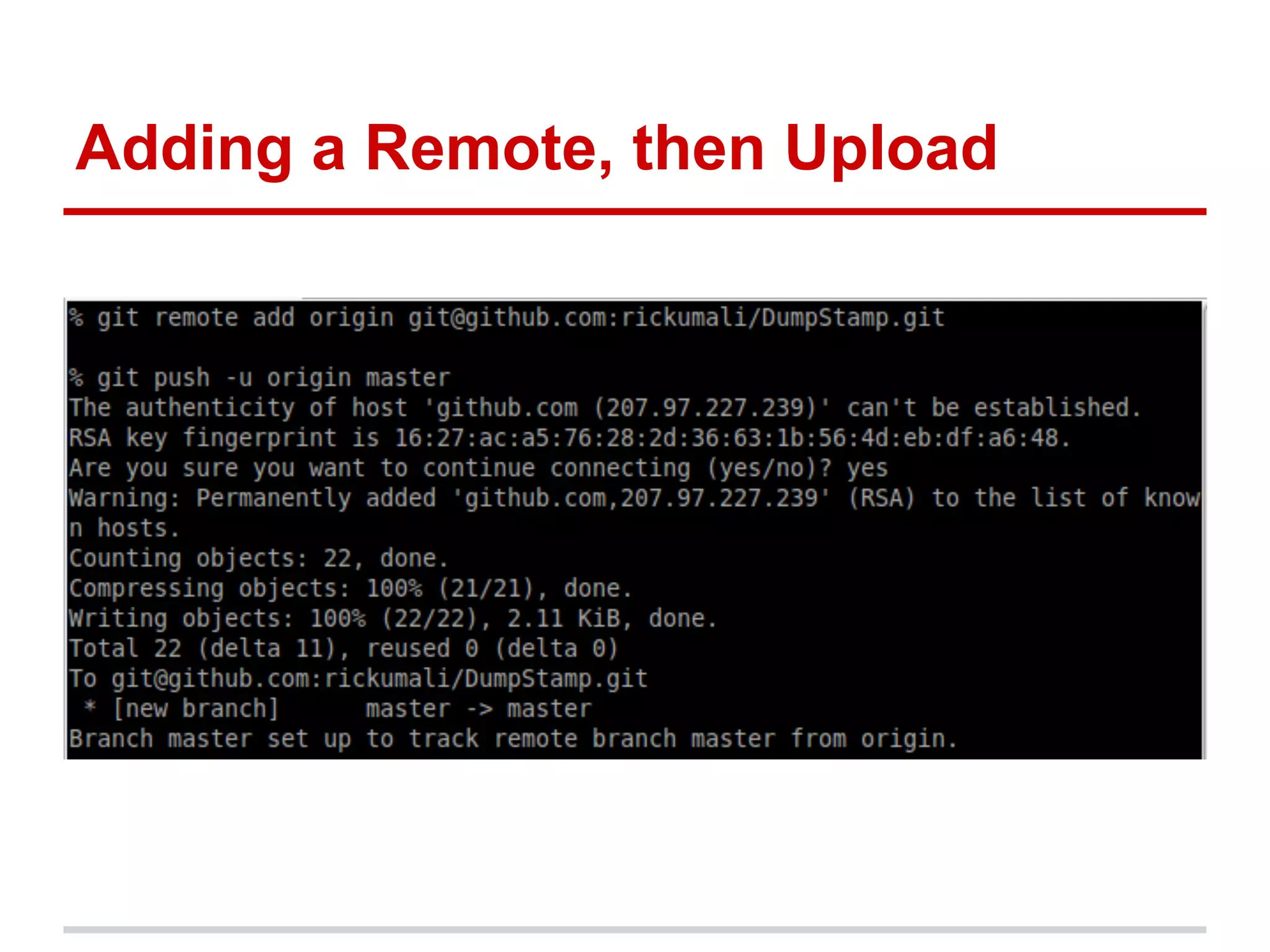
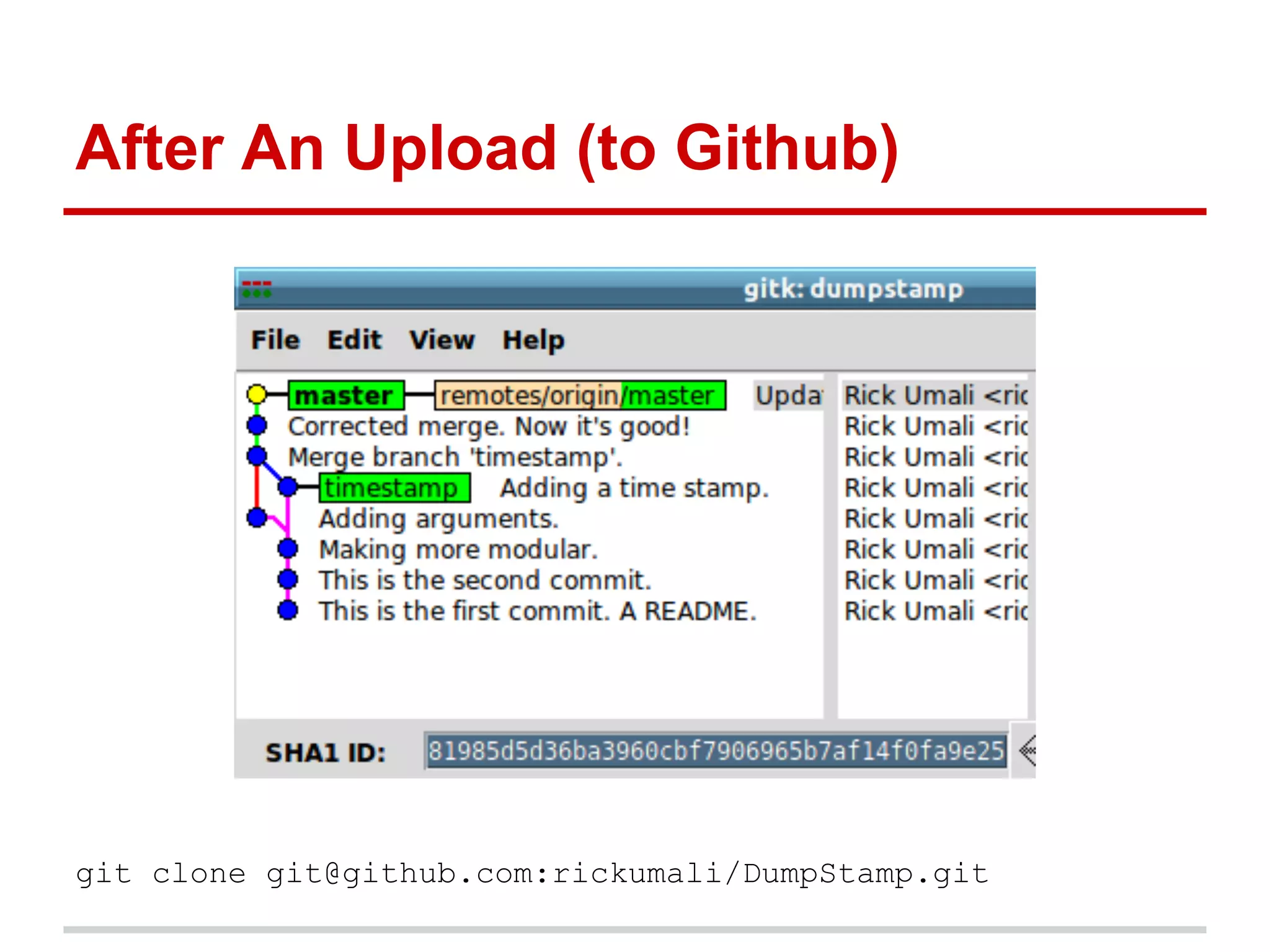
The document provides a comprehensive overview of Git, highlighting its function as a distributed version control system for tracking changes in source code. It covers installation, basic commands, workflows for committing changes, branching, merging, and collaborating with remote repositories. Additionally, it includes resources for further learning and emphasizes the importance of frequent commits and experimentation.