Class test of cost accounting
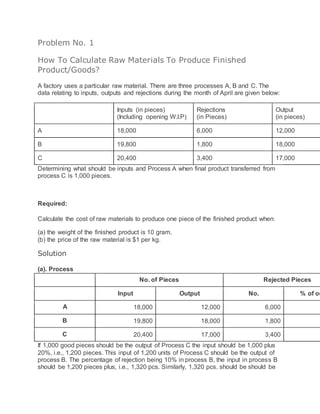
- 1. Problem No. 1 How To Calculate Raw Materials To Produce Finished Product/Goods? A factory uses a particular raw material. There are three processes A, B and C. The data relating to inputs, outputs and rejections during the month of April are given below: Inputs (in pieces) (Including opening W.I.P) Rejections (in Pieces) Output (in pieces) A 18,000 6,000 12,000 B 19,800 1,800 18,000 C 20,400 3,400 17,000 Determining what should be inputs and Process A when final product transferred from process C is 1,000 pieces. Required: Calculate the cost of raw materials to produce one piece of the finished product when: (a) the weight of the finished product is 10 gram. (b) the price of the raw material is $1 per kg. Solution (a). Process No. of Pieces Rejected Pieces Input Output No. % of ou A 18,000 12,000 6,000 B 19,800 18,000 1,800 C 20,400 17,000 3,400 If 1,000 good pieces should be the output of Process C the input should be 1,000 plus 20%, i.e., 1,200 pieces. This input of 1,200 units of Process C should be the output of process B. The percentage of rejection being 10% in process B, the input in process B should be 1,200 pieces plus, i.e., 1,320 pcs. Similarly, 1,320 pcs. should be should be
- 2. the output of Process A. The rejection being 50%, the input of process A should be 1,320 plus 50%, i.e., 1,980 pcs. It can be tabulated as follows: Process Input Rejection % Rejection of output Outp A 1,980 660 50% B 1,320 120 10% C 1,200 200 20% Also Check: Cost Plus Contract (b) Given: weight of the finished product = 10 grams per pc. Assuming that there is no other loss of material, the total material required for 1,980 pcs. of input of Process A shall be: 1,980 pcs. X 10 gms. = 19,800 gms. Rate of Material = $1 per kg. Cost of raw material = (19,800X1) / 1,000 = $19.80 Cost o fraw material per pc.= 19.80 / 1,000 = $0.0198 Problem No. 2 Calculation Of Maximum, Minimum And Reorder Stock Levels. (1). Discuss the consideration that influences the setting of maximum, minimum and reorder stock levels. Illustrate their computation by using the following information for a component ‘ZYP’. Normal usage 50 per week Minimum usage 25 per week Maximum usage 75 per week Re-order quantity 300 units Re-order period 4 to 6 weeks Solution
- 3. (Note: For consideration influencing the stock levels, read the discussion in the previous pages) Re-order level = Max. consumption per day / per week etc. X Max. Re-order period = 75 units X 6 weeks = 450 Units. Maximum Level = Re-order Level + Re-order Quantity – (Minimum consumption per day/per week etc. X Minimum time required to obtain supplies) = 450 units + 300 units – (25 units x 4 weeks) = 750 units – 100 units = 650 units Minimum Level = Re-Order level – (Normal consumption per day/per week etc. X Average Re-order period) = 450 units – (50 units x 5 weeks) = 450 units – 250 units = 200 units (2). Two Components, A and B are used as follows: Normal usage = 50 units per week each Minimum usage = 25 units per week each Maximum usage = 75 units per week each Reorder quantity A: 400 units Reorder quantity B: 600 units Reorder period A: 4 to 6 weeks Reorder period B: 2 to 4 weeks Also Check: How to calculate profit and loss on contracts? Required: Calculate for each component (i) Reorder Level (ii) Minimum level (iii) Maximum level (iv) Average stock level Solution (i) Reorder Level = Maximum consumption per day/per week etc. X Maximum Re- Order Period Component A = 75 units X 6 weeks = 450 units Component B = 75 units X 4 weeks = 300 units (ii) Minimum Level = Reorder Level – (Normal consumption per day/per week etc. X Average Re-order period)
- 4. Component A = 450 units – (50 units x 5 weeks) = 200 units Component B = 300 units – (50 units x 3 weeks) = 150 units (iii) Maximum Level = Reorder level – Reorder Quantity – (Minimum consumption per day/per week, etc. X Minimum Time Required to get supplies) Component A = 450 units + 400 units – (25 units x 4 weeks) = 850 units – 100 units = 750 units Component B = 300 units + 600 units – (25 units x 2 weeks) = 900 units – 50 units = 850 units Average Stock Level = Minimum Level + 1/2 (Reorder Quantity) Component A = 200 units + (1 / 2 X 400 units) = 400 units Component B = 150 units + (1/2 X 600 units) = 450 units Problem 3 Calculation Of Material Turnover Ratio Following figures were taken from the records of John and Co. for the year 31st March 2019. The valuation of inventory is $1 per kg: Material ‘X’ Material ‘Y’ $ $ Opening Stock 1,700 Purchases 51,000 Closing Stock 1,200 Required: Calculate the material turnover ratio and express in number of days the average inventory is held. Solution Working notes: 1. Material consumed Also Check: Pricing Methods of Material Issued
- 5. Material ‘X’ (kgs.) Material ‘Y’ (kgs.) Opening stock Add: Purchases 1,700 51,000 52,700 Less: Closing Stock 1,200 51,500 2. Average Inventory Average inventory = (Opening Stock + Closing Stock) / 2 Material X = (1,700 + 1,200) / 2 = 1,450 kgs. Material Y = (1,200 + 1,000) / 2 = 1,100 kgs. 3. Material Turnover Ratio = Material consumed during the period / Average Inventory Material X = 51,500 / 1,450 = 35.5 times (approx.) Material Y = 32,200 / 1,100 = 29.3 times (approx.) 4. Number of days Average Inventory is held = Total No. of days in the period / Material Turnover Material X = 365 / 35.5 = 10.3 days (approx.) Material Y = 365 / 29.3 = 12.5 days (approx.) Problem 4 Calculation Of Economic Order Quantity (1). Do as directed: Annual consumption: 40,00,000 kgs. Cost of placing one order: $100 Cost of carrying one kg. of raw material for one year: $0.5 Required: Calculate the Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) Solution:
- 6. (2). The annual demand for a product is 6,400 units. The unit cost is $6 and inventory carrying cost is 25% per annum. If the cost of one procurement is $75 determine: (i) Economic order quantity (ii) No. of orders per year (iii) Time between two consecutive orders. Solution (i) Economic Order Quantity (ii) No. of orders per year = Annual consumption / Size of one order = 6,400 units / 800 units = 8 orders (iii) Time gap between two consecutive orders = 12 months / No. of orders = 12 months / 8 orders = 1.5 months
