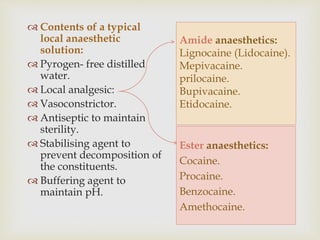
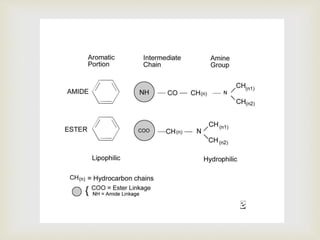
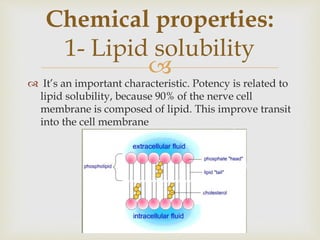
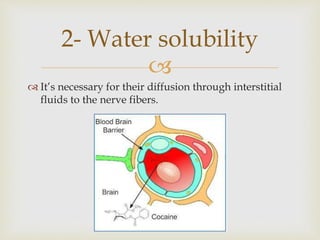
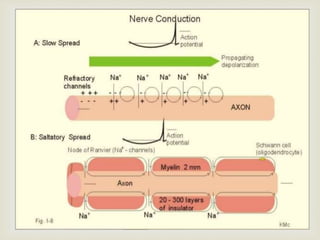
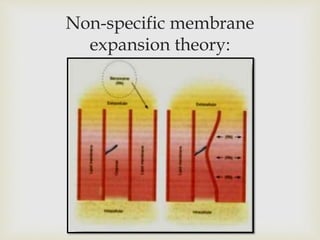
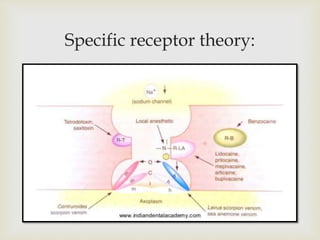
Local anesthesia is defined as a transient reversible loss of sensation caused by blocking nerve conduction in a localized area. There are two types of local anesthetics: amides and esters. Amides such as lidocaine are preferred due to their longer duration of action and lower risk of allergic reactions. Local anesthetic solutions also contain vasoconstrictors to prolong the effects and buffering agents. The document discusses the mechanisms, uses, contraindications and toxicity of local anesthesia in detail. It provides classifications based on duration and vasoconstrictor types used. Potential adverse effects on the central nervous system, cardiovascular system and risks of methemoglobinemia are outlined.