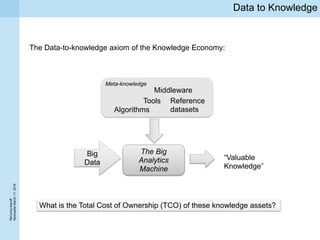
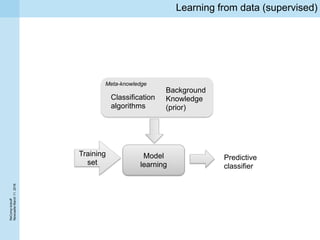
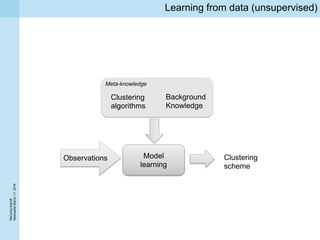
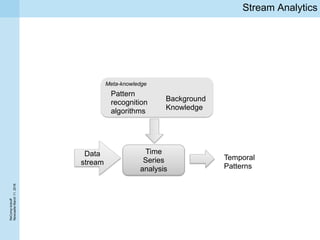
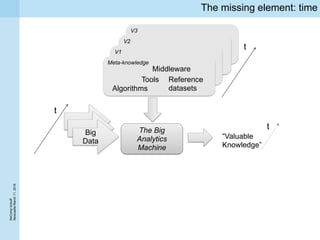
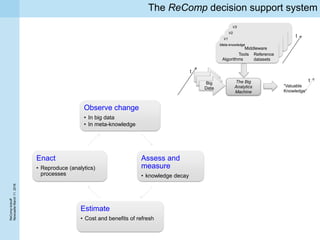
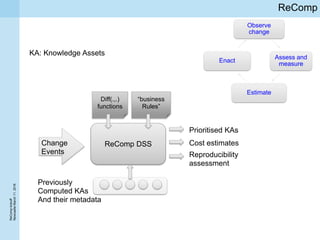
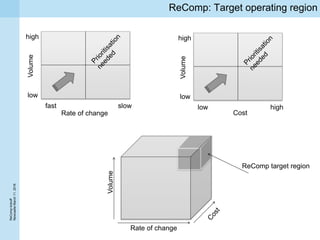
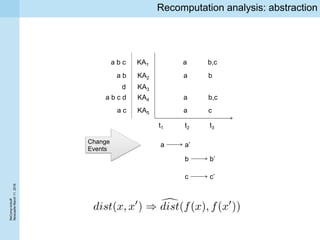
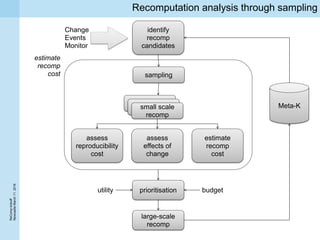
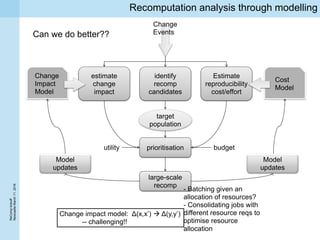
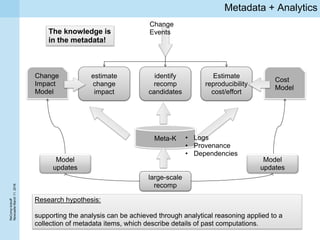
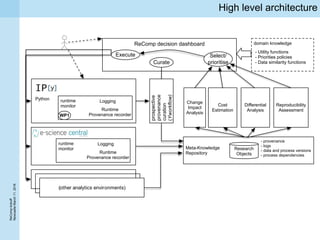
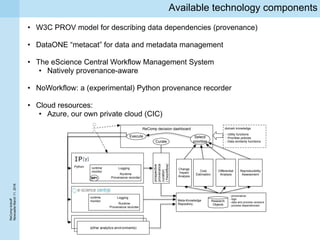
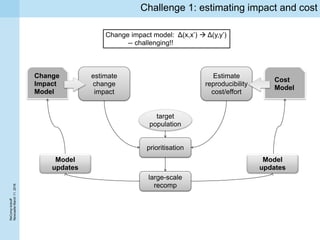
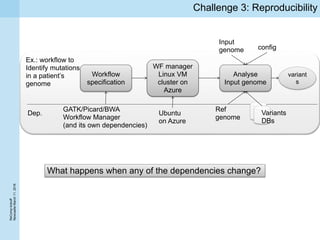
This document summarizes a project kickoff meeting for the ReComp project. The objectives of the ReComp project are to 1) investigate analytics techniques for supporting re-computation decisions, 2) research methods for assessing when re-computing an analytical process is feasible, and 3) create a decision support system to selectively recompute complex analytics processes. The expected outcomes are algorithms and a software framework to help determine when and how to recompute analyses when data or models change over time. The document outlines several challenges for the project, including estimating the impact of changes, managing different types of metadata, assessing reproducibility, and making the solutions reusable across different application cases.