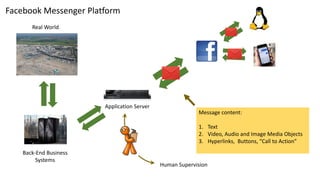
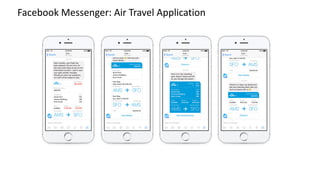
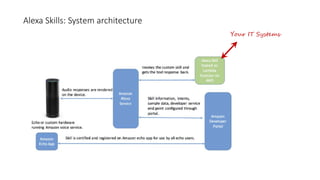
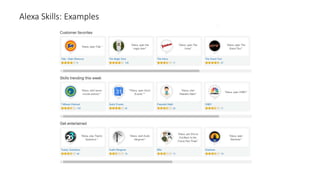
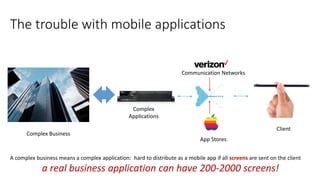
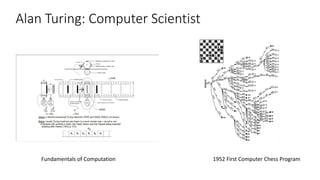
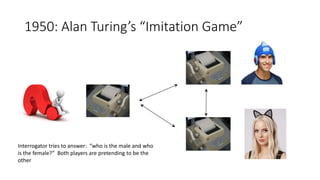
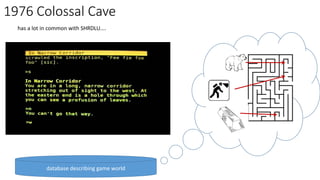
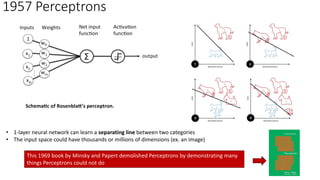
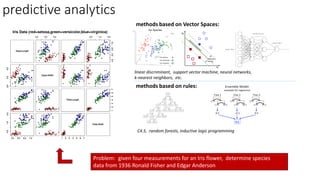
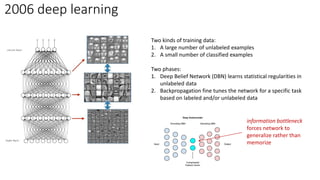
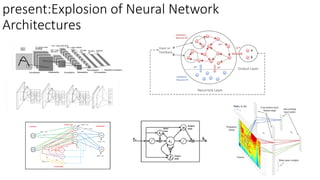
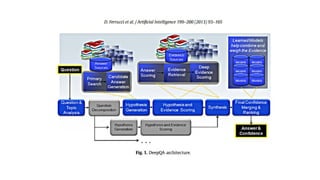
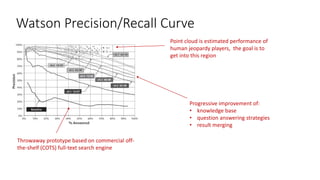
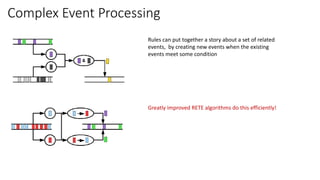
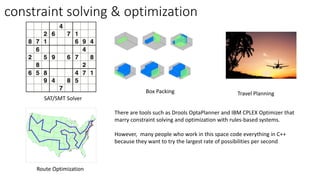
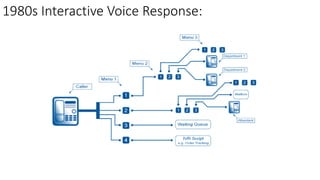
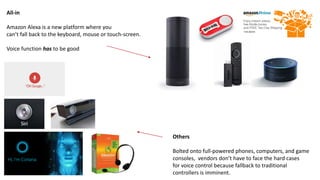
The document discusses the evolution of chatbots, highlighting their current applications like in Facebook Messenger and Alexa, alongside their historical development from early interactions with machines. It covers key technological milestones, significant figures in AI history, and the challenges of building effective conversational interfaces while also forecasting future trends in the chatbot landscape. The importance of data-rich environments and interdisciplinary approaches is emphasized for the advancement of chatbots.