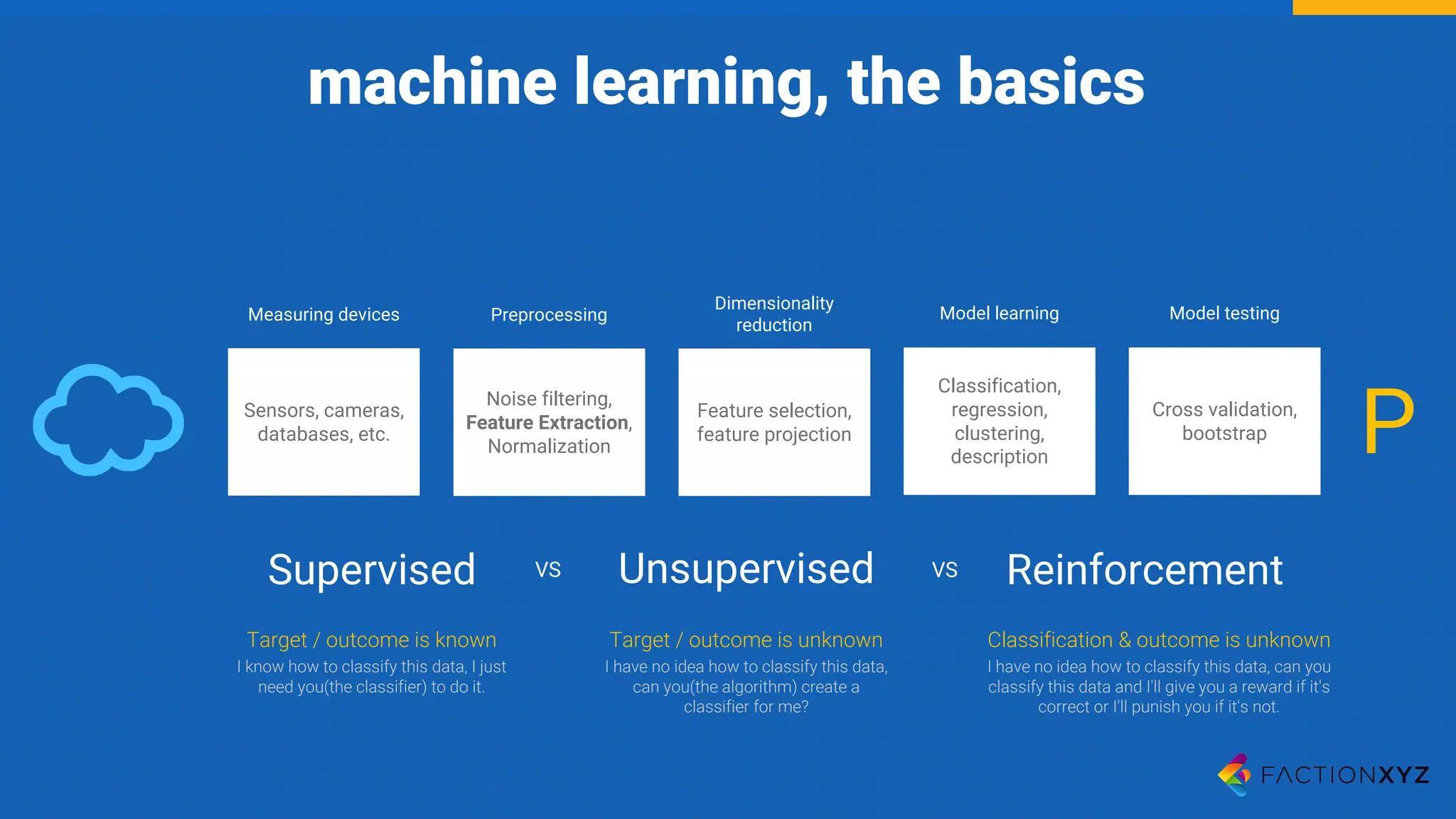
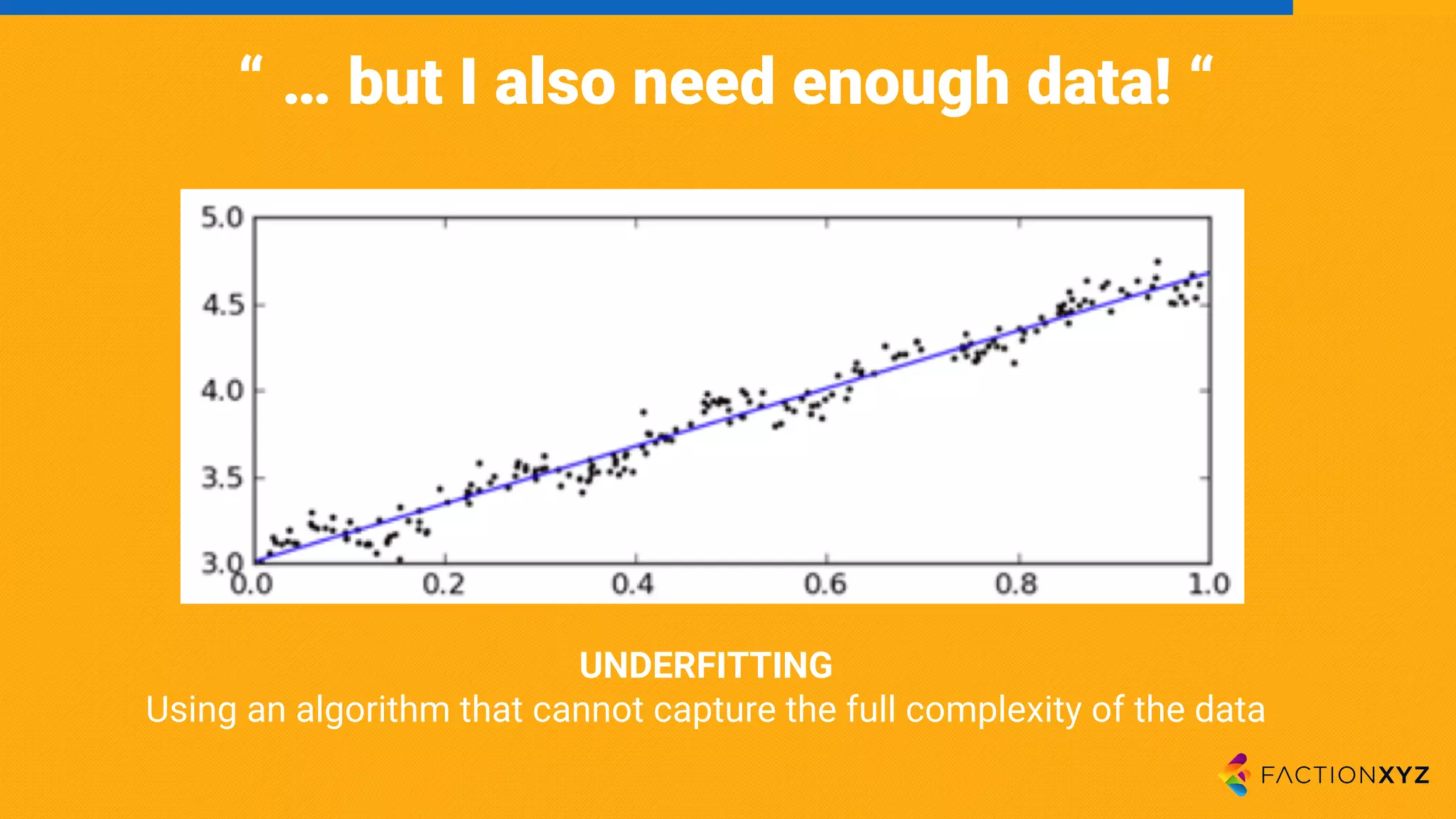
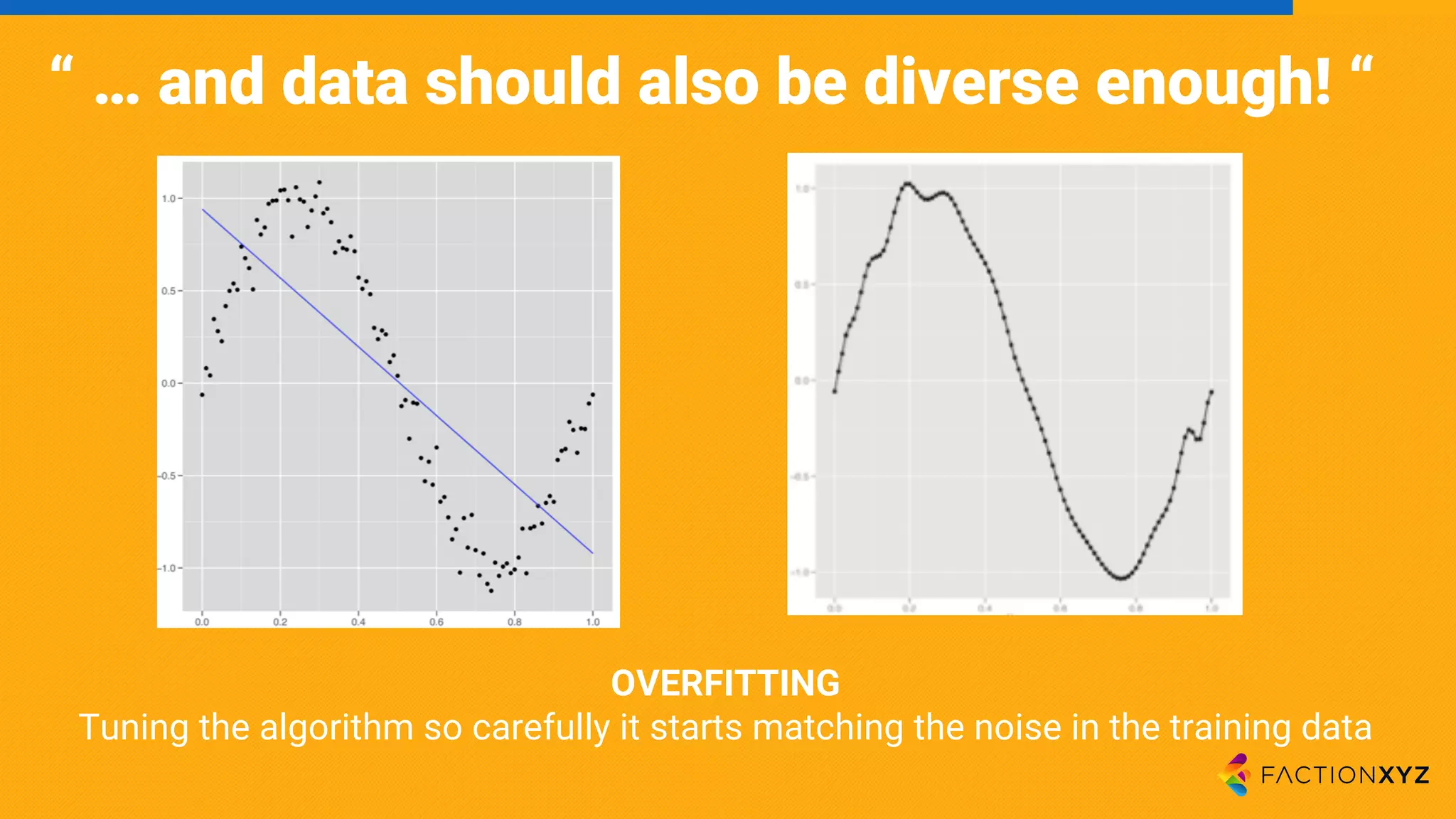
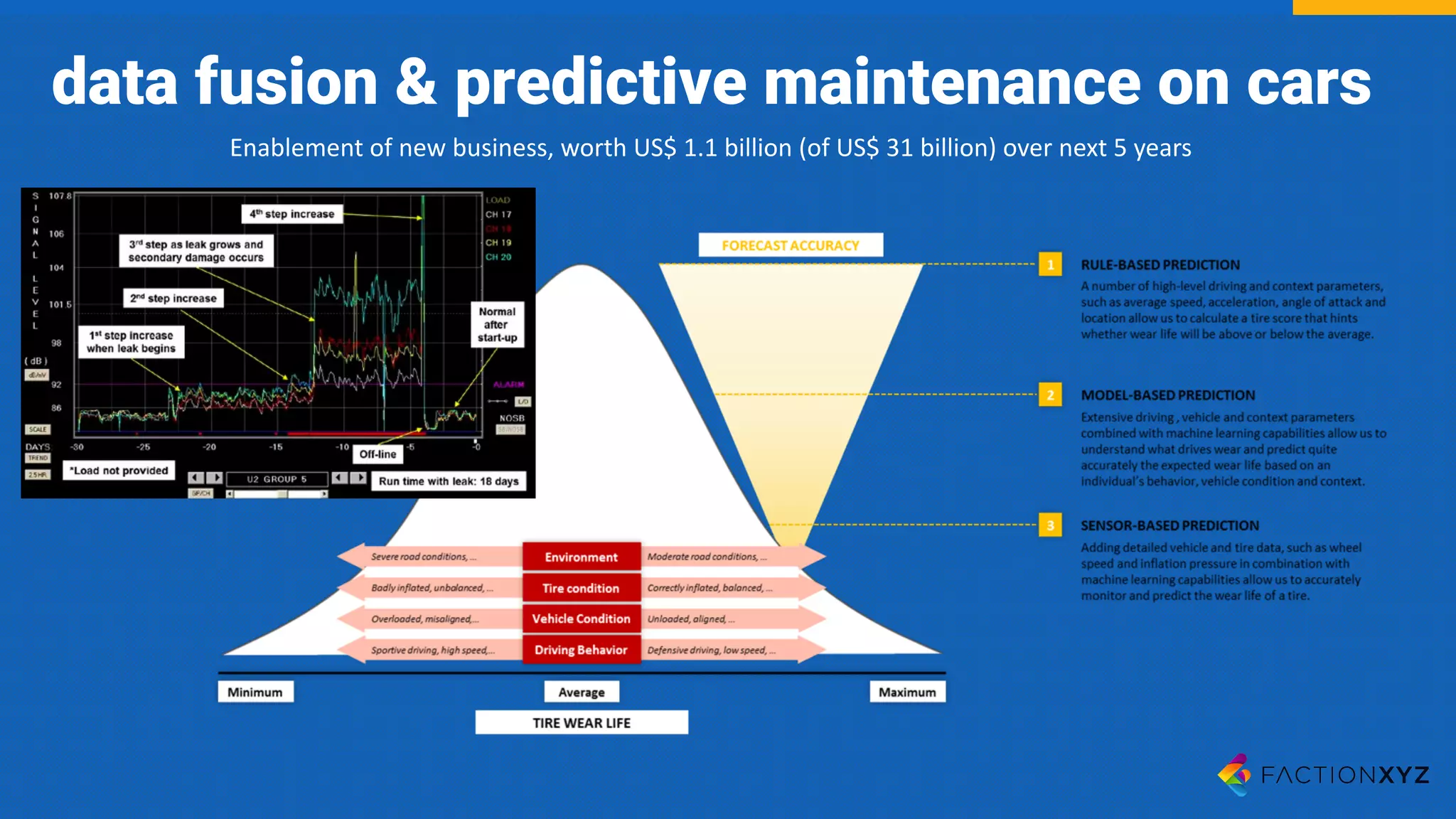
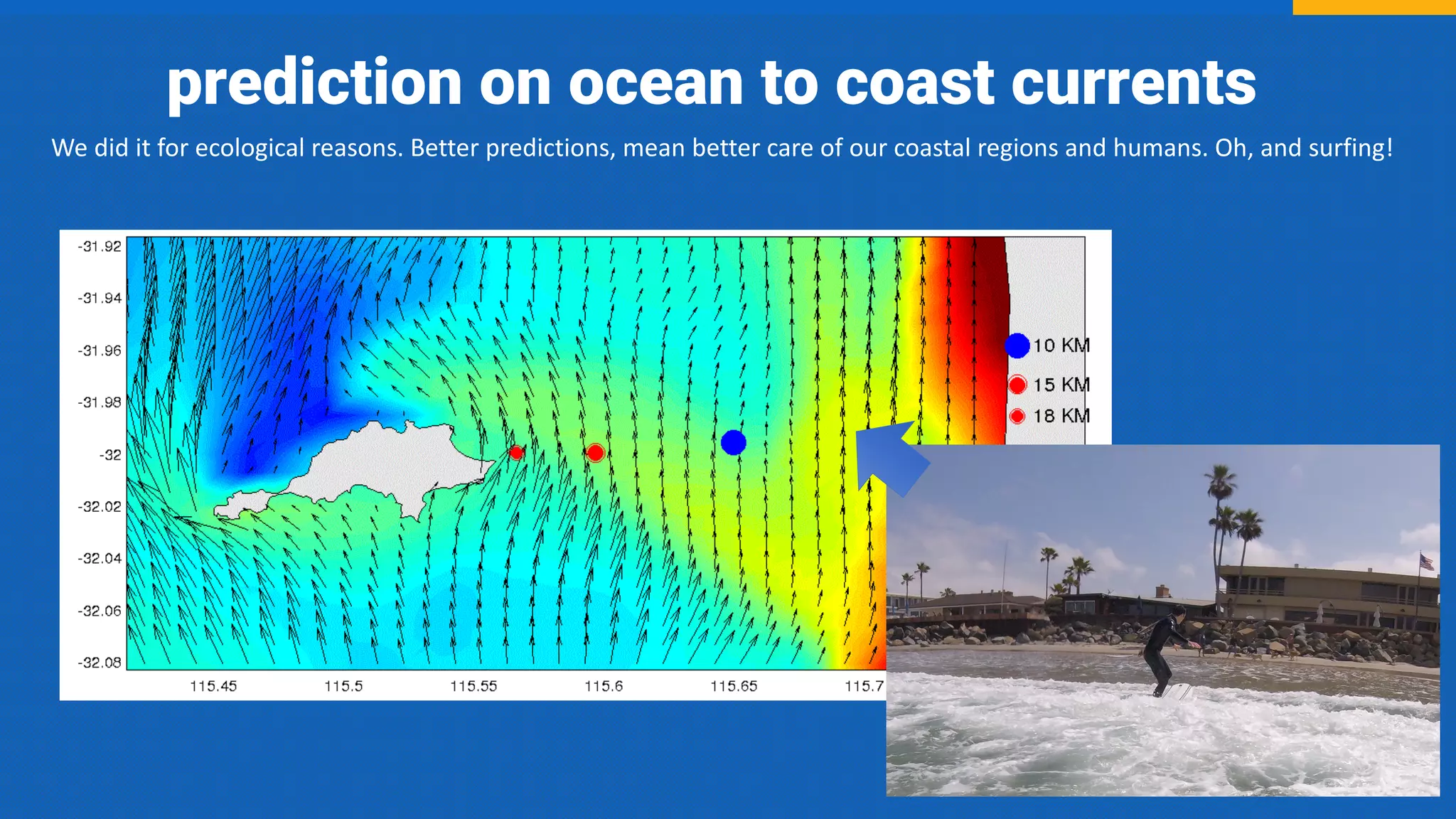
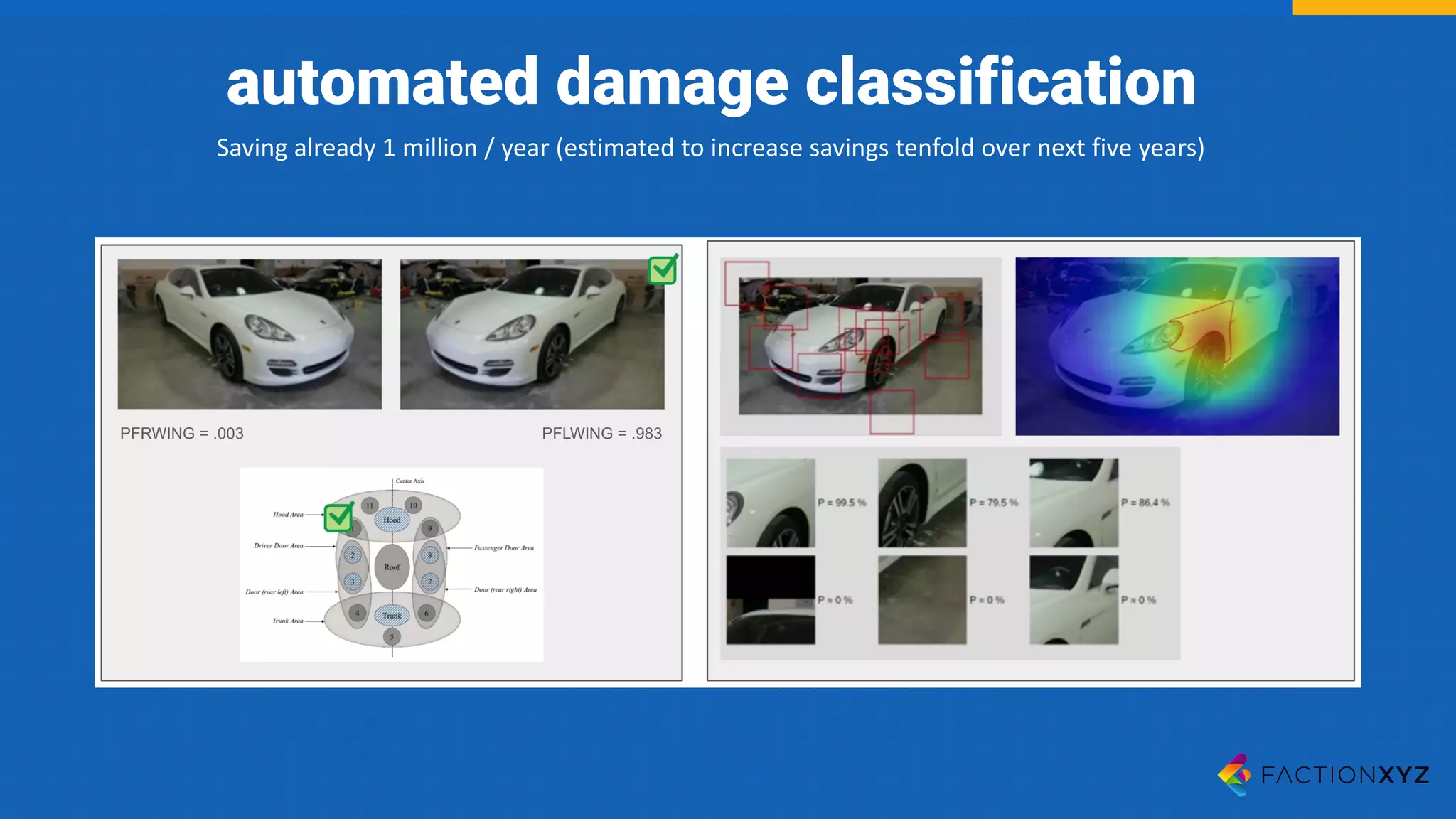
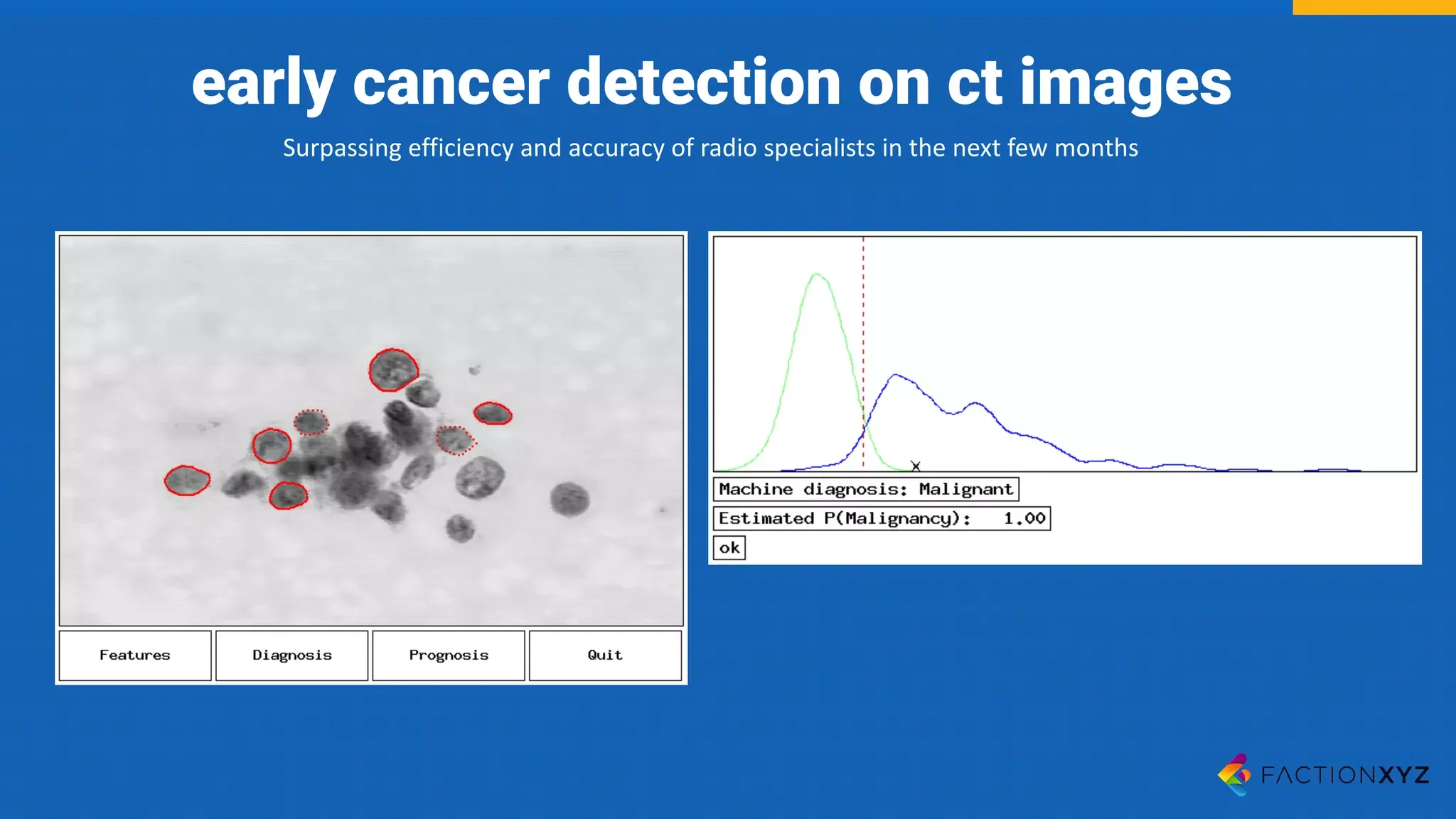
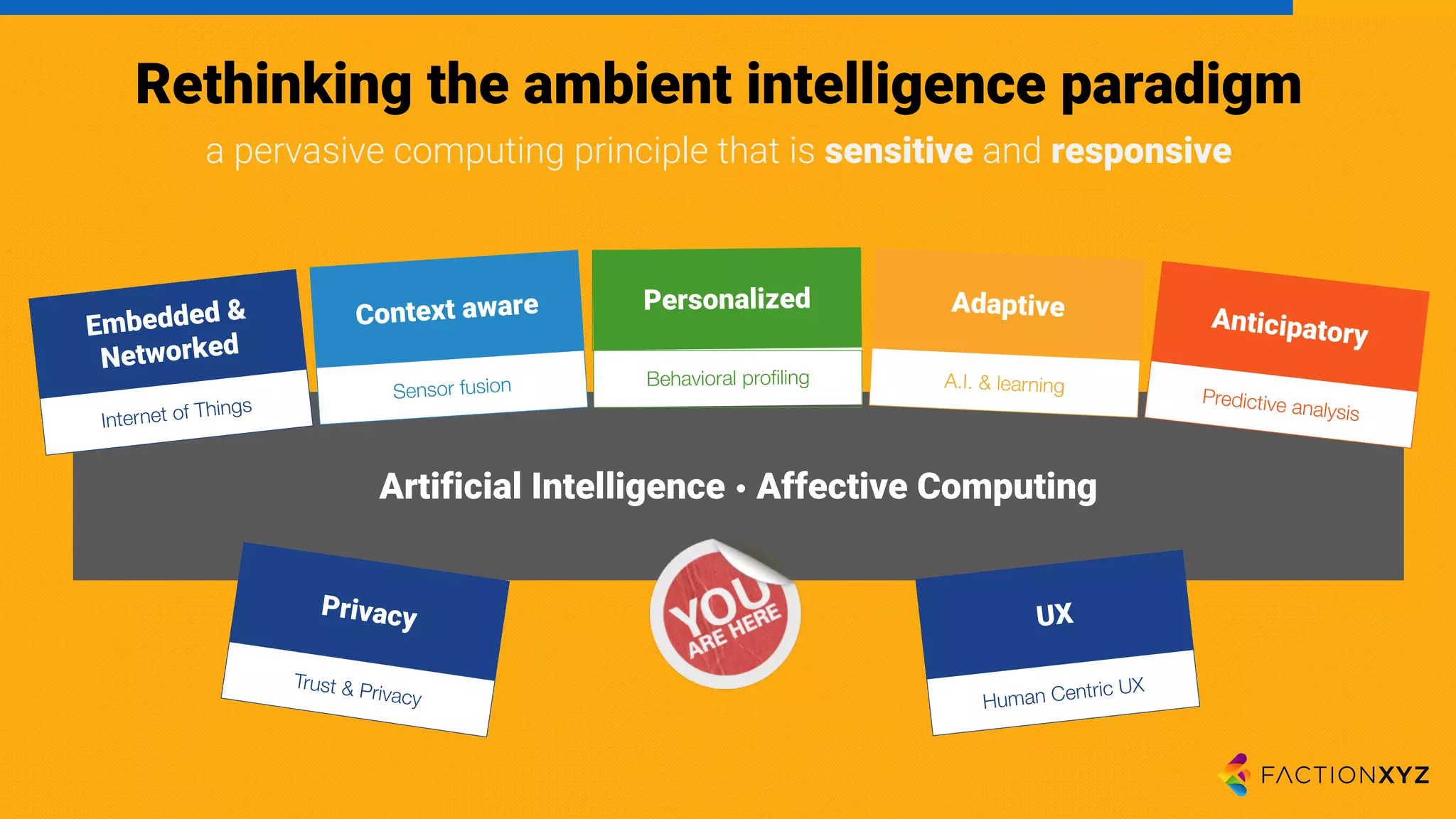
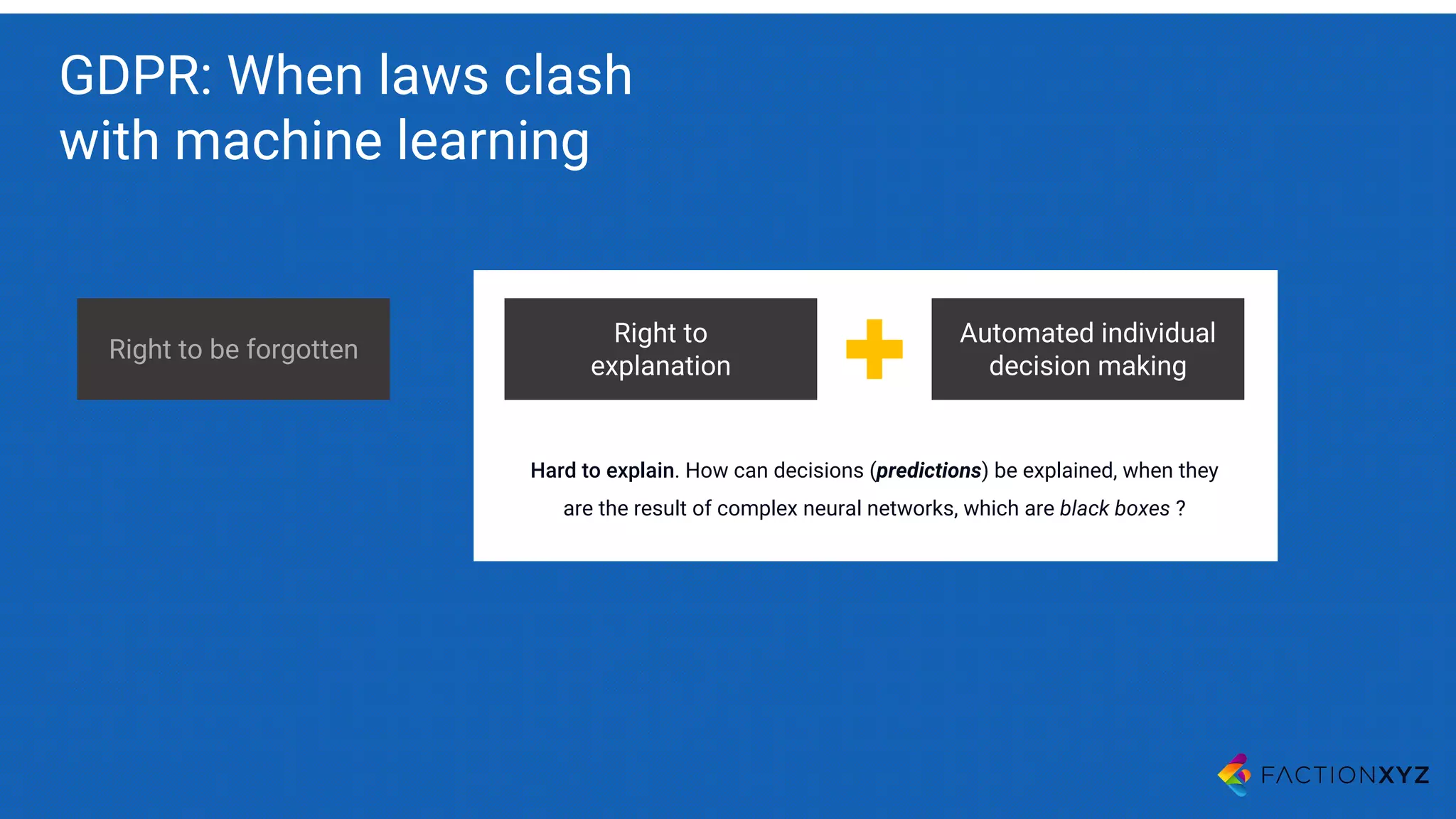
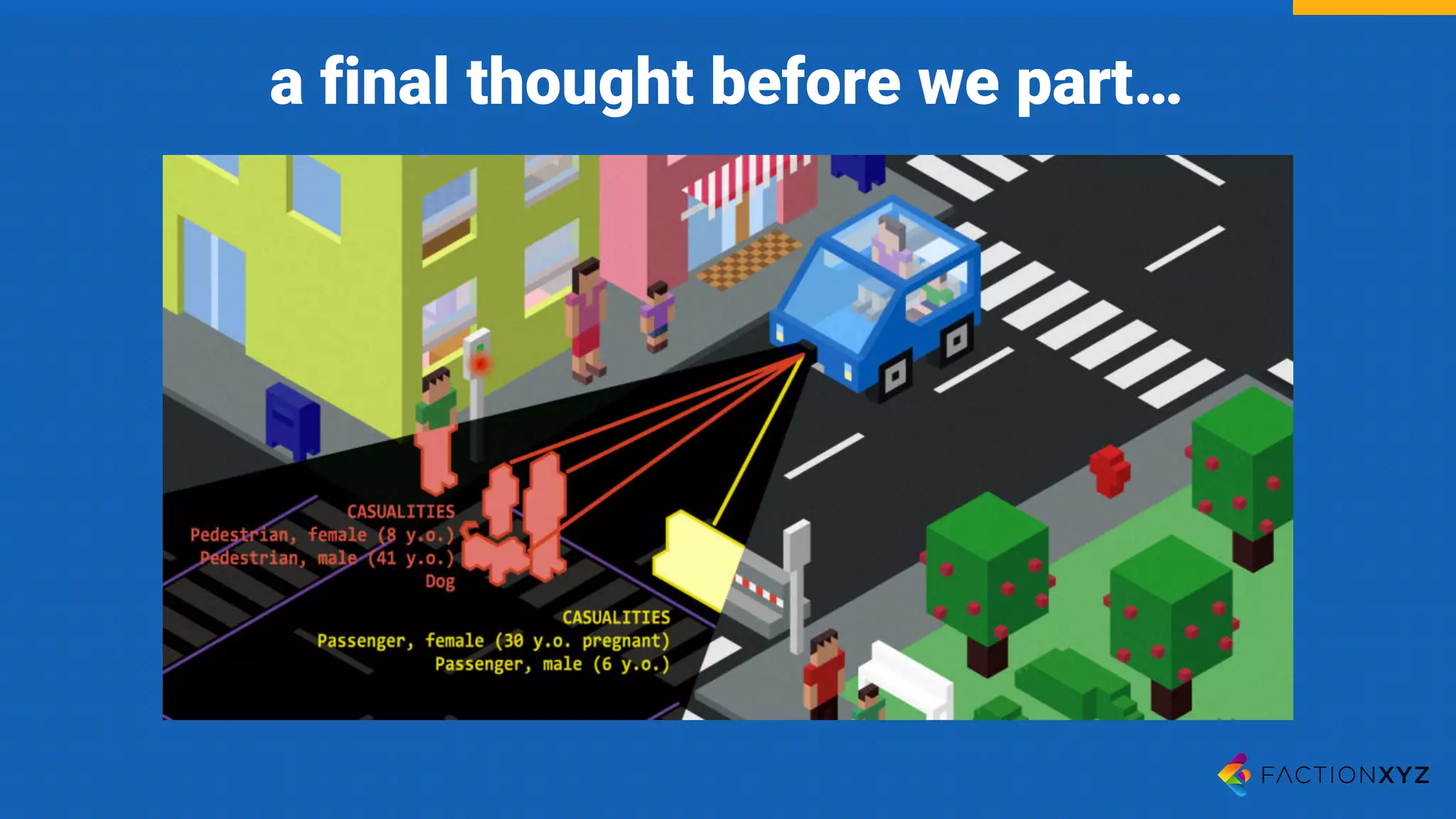
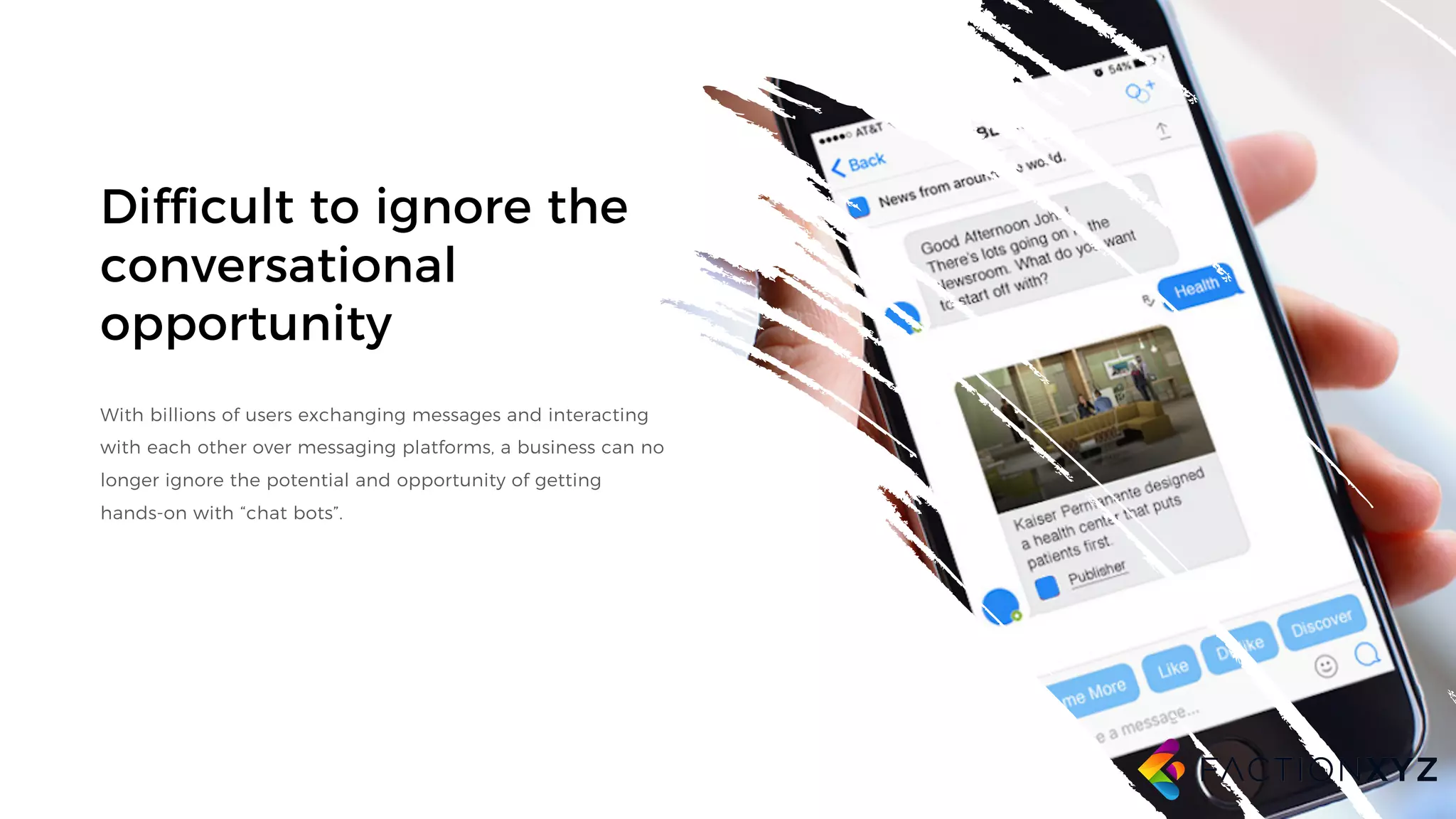
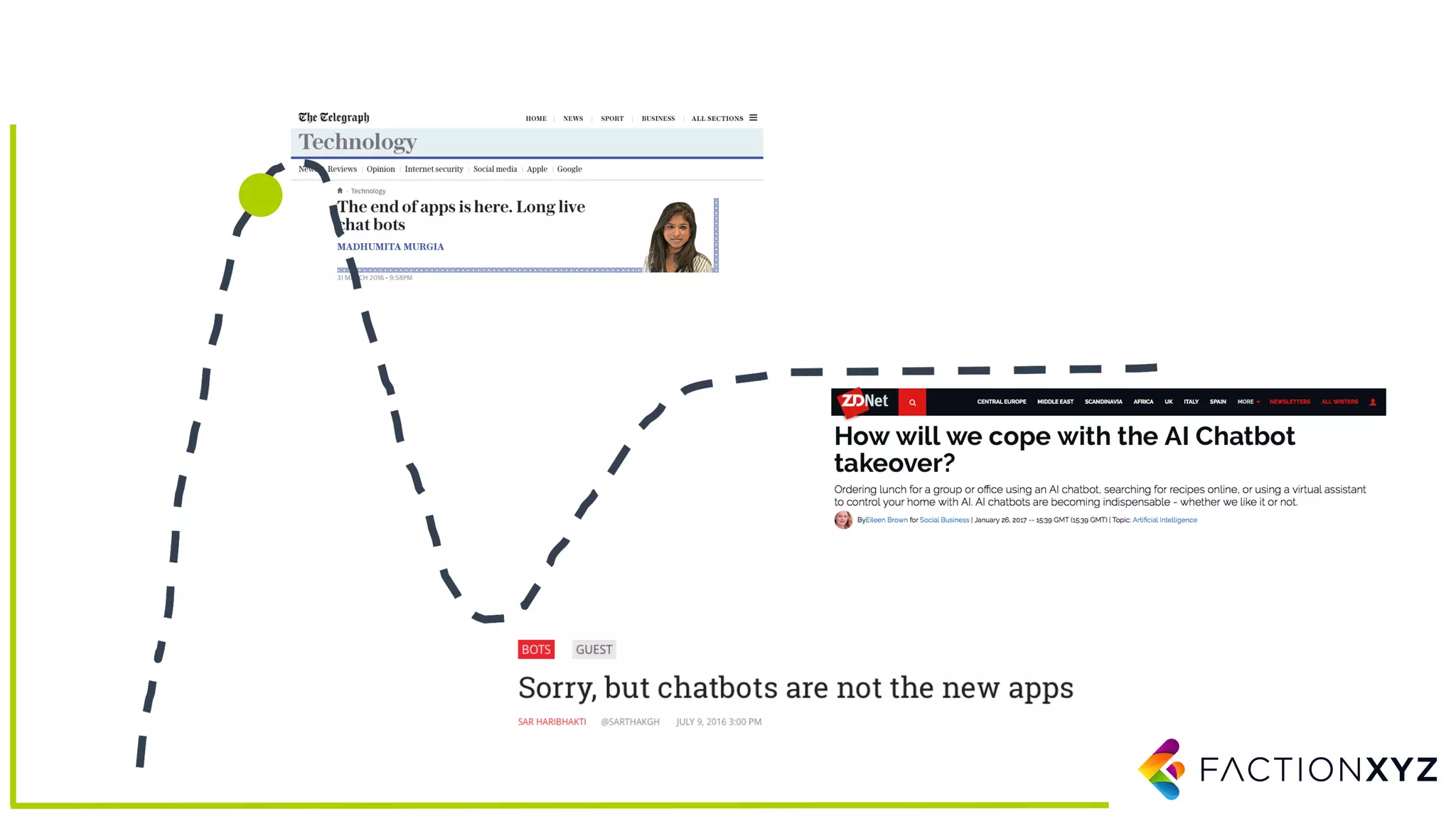
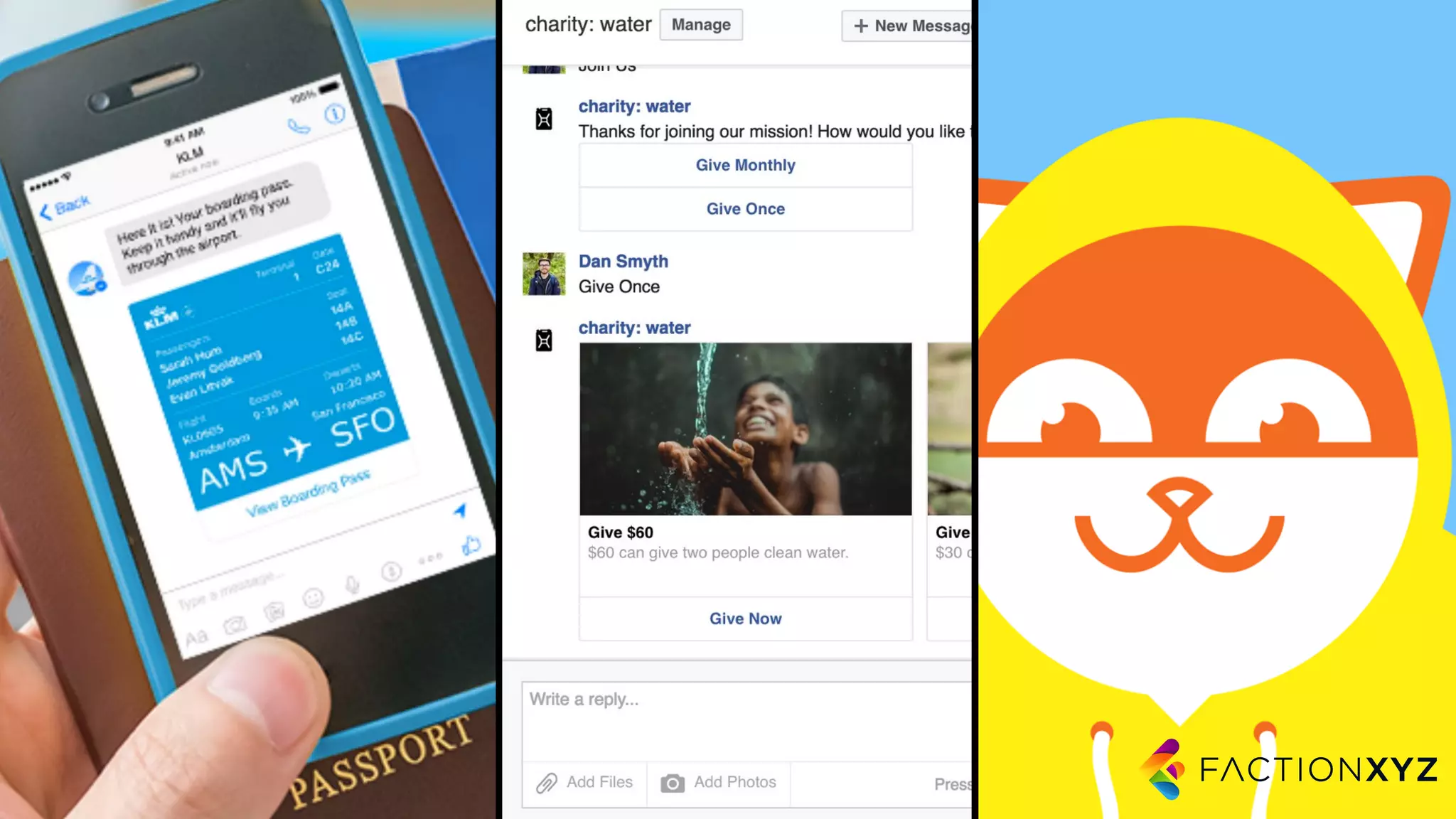
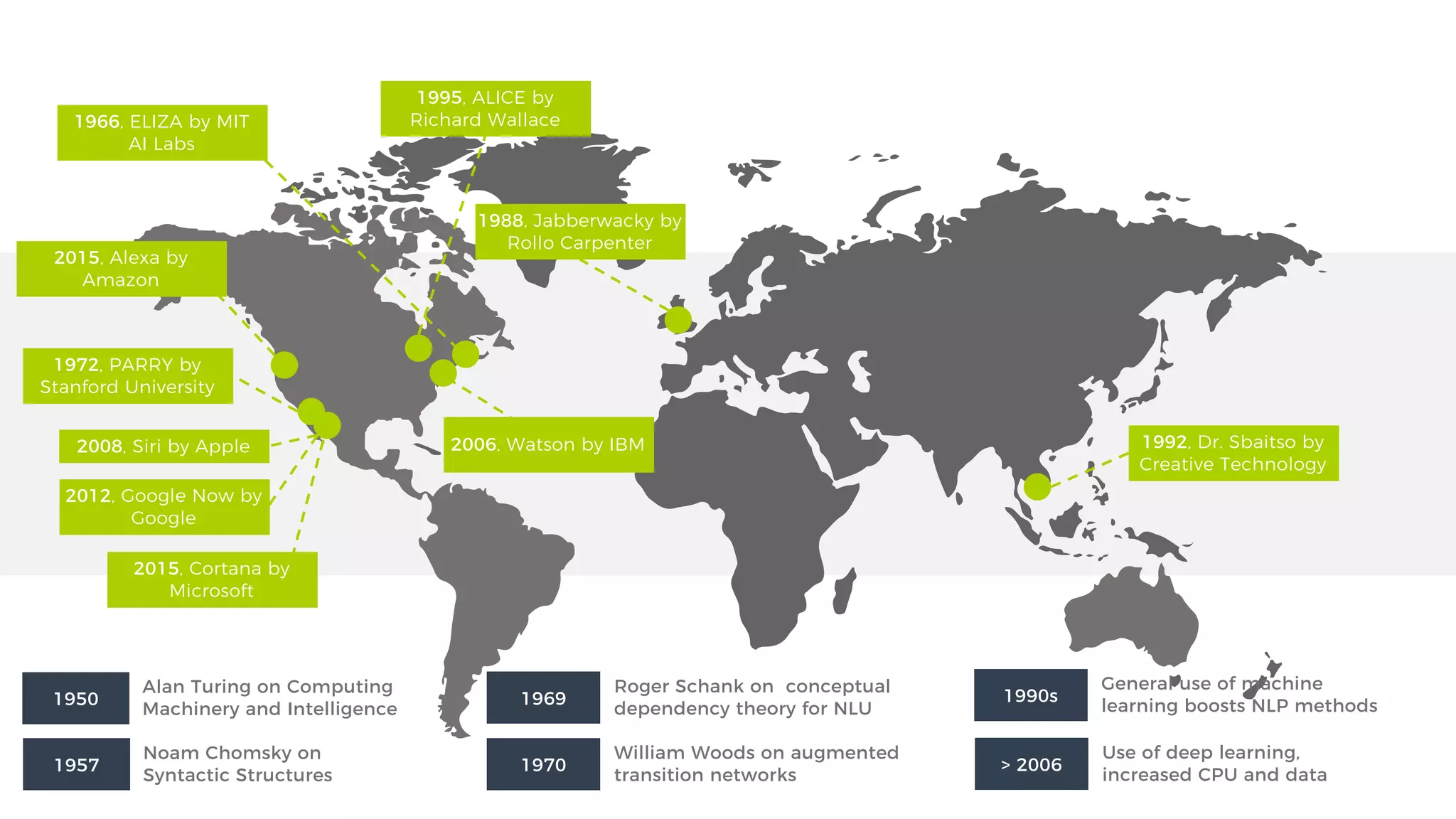
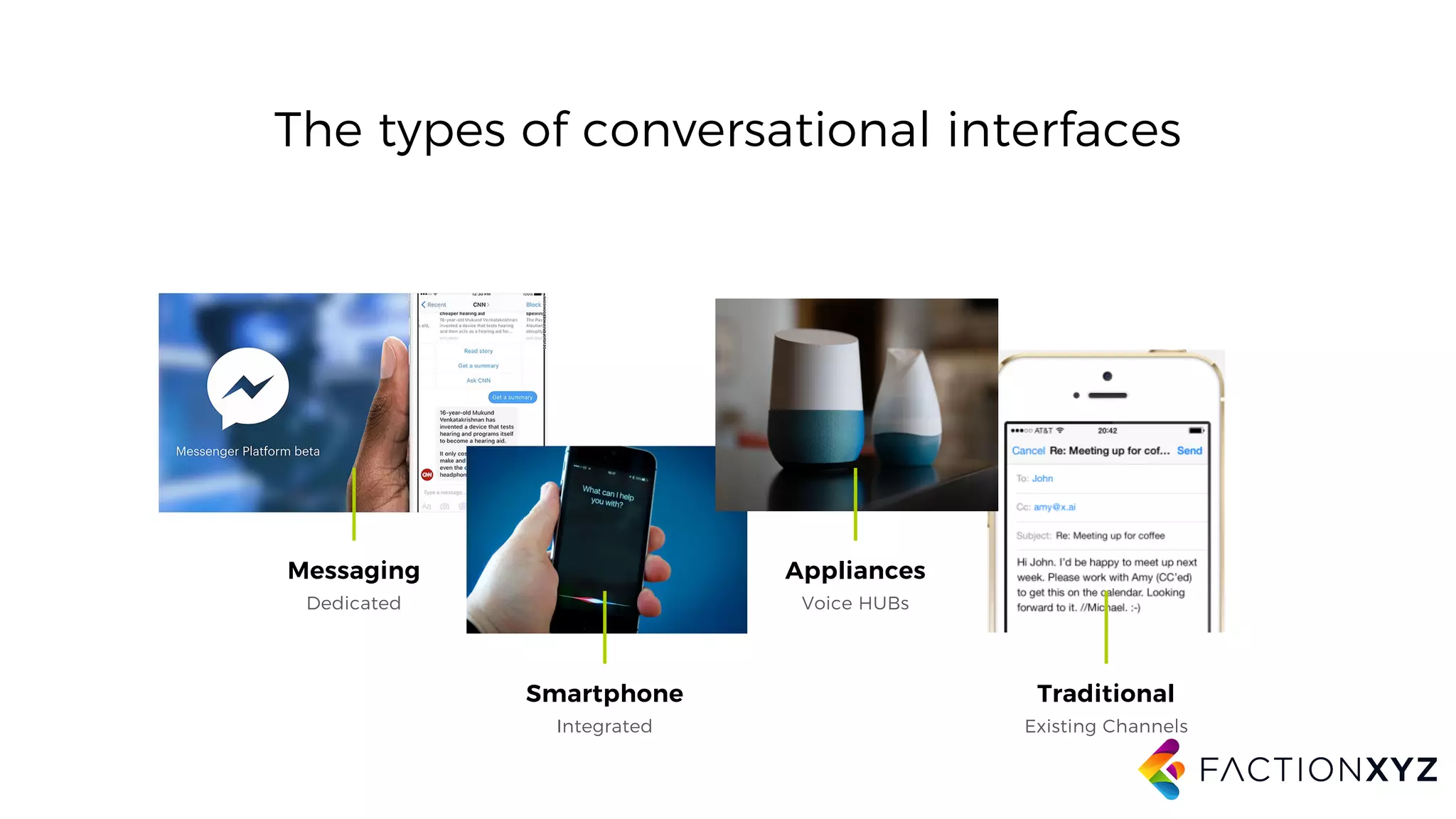
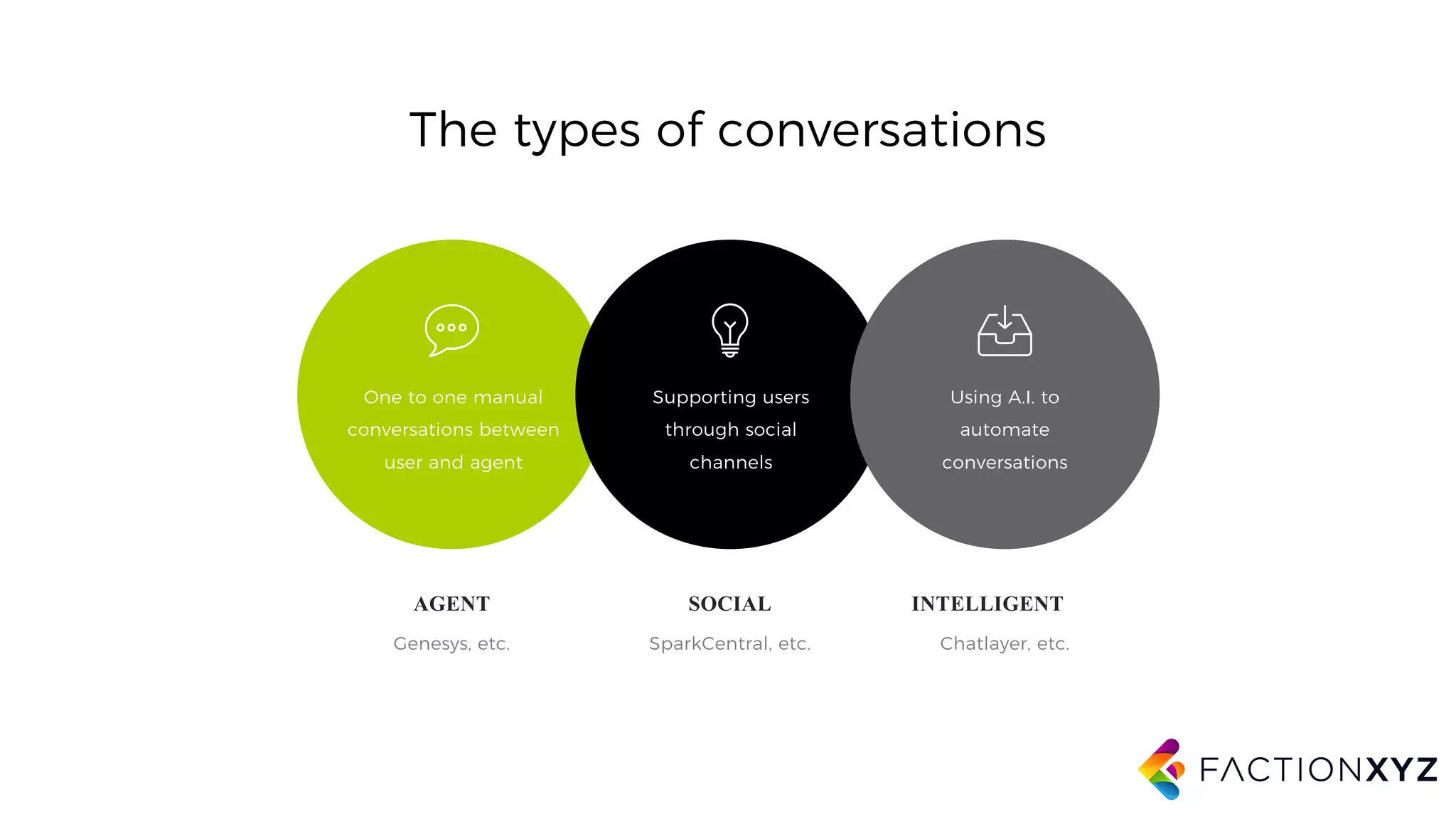
The document discusses the integration of AI, machine learning, and chatbots in modern technology, highlighting the evolution and potential of conversational agents. It emphasizes the importance of good-quality data, the challenges surrounding data processing, and the application of AI in various fields including customer support and healthcare. The seminar covers the transformation of user experiences through conversational interfaces, aiming for seamless interactions between humans and machines.