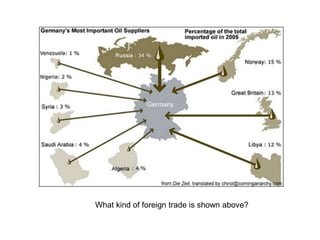
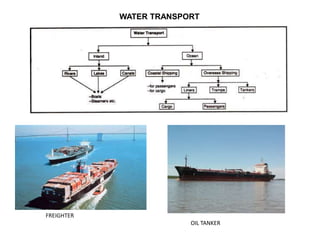
The document discusses several key aspects of the tertiary sector of the economy and trade. It begins by explaining that the tertiary sector includes service-based activities like trade, transportation, tourism, banking, and more. It notes that developed countries have over 70% of their population working in this sector. It then covers different types of trade, including wholesale and retail trade, as well as imports and exports between countries. The document discusses factors like transportation revolutions, free trade agreements, and impacts of globalization on developing countries. It also outlines tourism as an economic activity and its positive and negative impacts on local economies.