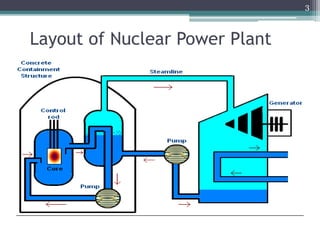
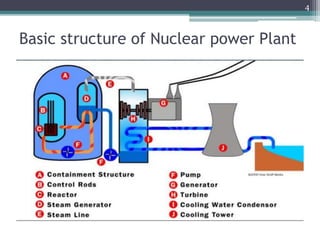
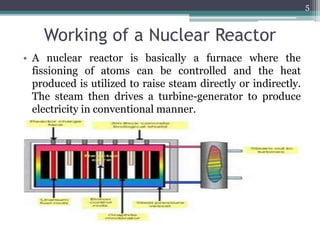
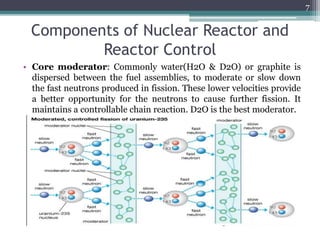
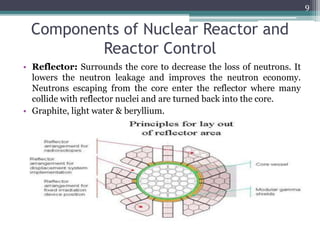
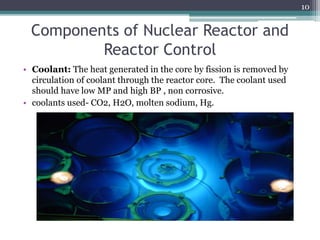
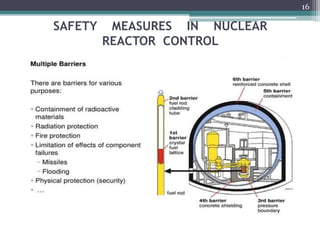
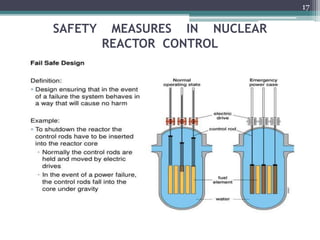
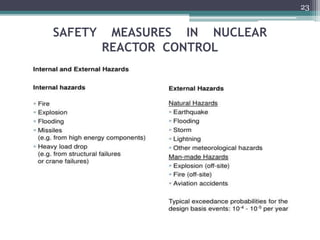
Nuclear power plants generate electricity through nuclear fission in a controlled nuclear reactor. Safety measures are crucial given the risks of radiation. Reactors have multiple redundant safety systems, including control rods to regulate the fission reaction, cooling systems to prevent overheating, shielding to block radiation, and strict limits on radiation exposure. Nuclear waste is also carefully disposed of through segregation, filtration, dilution and burial or storage to isolate it from the environment. Emergency response plans are in place in case of any accidents. With proper precautions, nuclear energy can be harnessed safely for its tremendous power potential without harm.