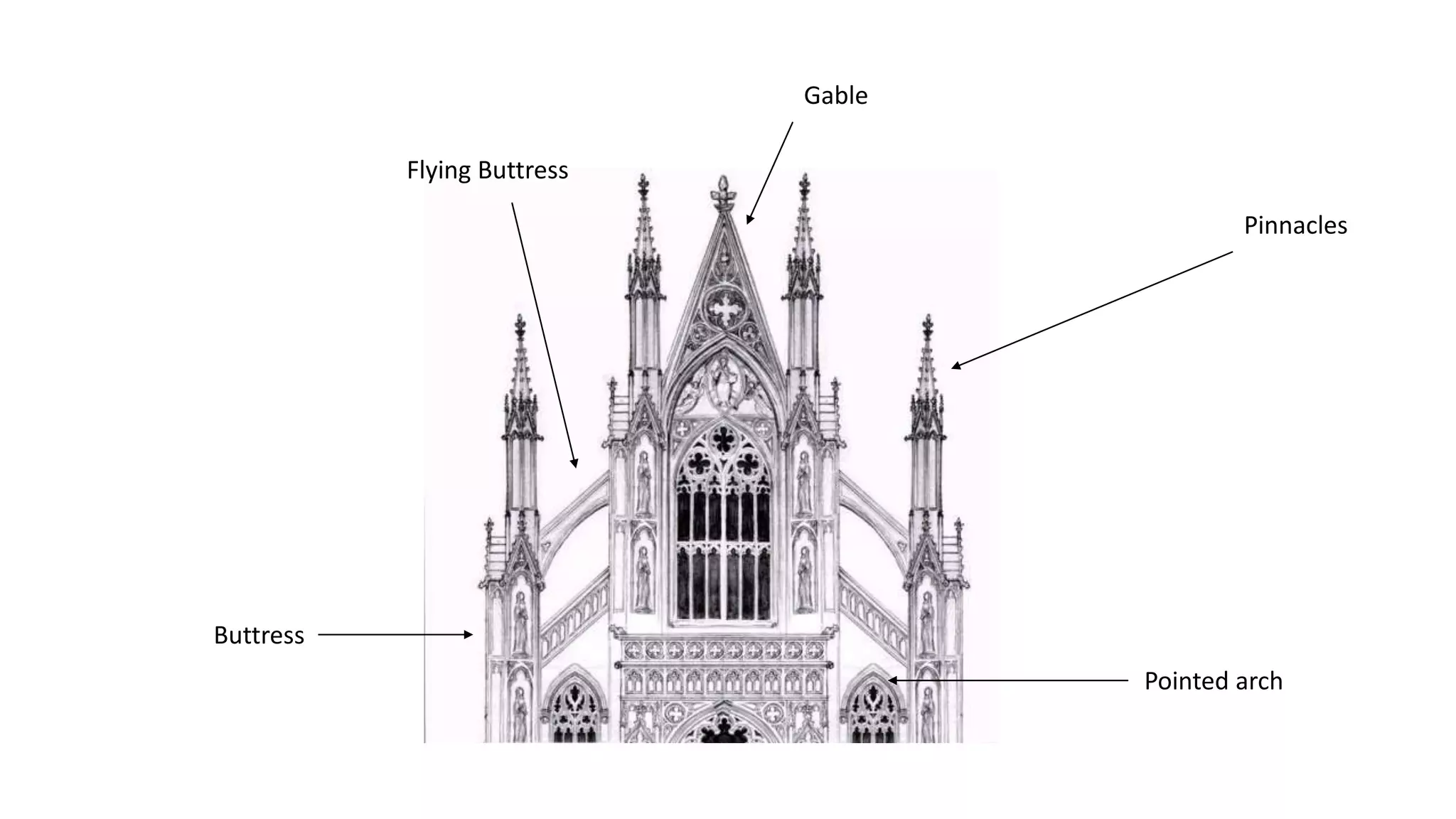
Gothic art, emerging in 12th century France, led to high, bright, and complex buildings in Western Europe until the 15th century, characterized by features like pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and large stained glass windows. Decorative sculptures, often with religious themes, were integrated into architectural elements, showcasing realism and expression. Painting evolved with large windows in churches, resulting in more panel paintings and altarpieces, focusing on naturalistic representations and emotional expression.