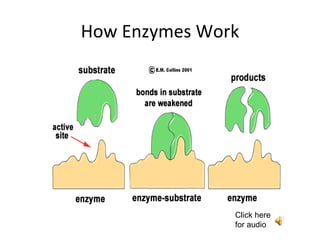
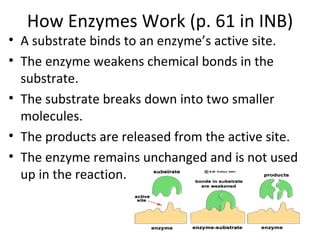
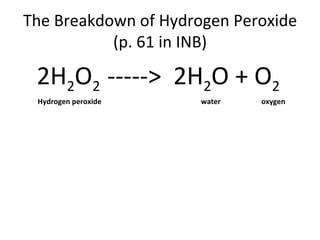
Enzymes work by binding a substrate to their active site, weakening the substrate's chemical bonds, causing the substrate to break down into smaller products which are then released, while the unchanged enzyme remains and is not used up. Enzymes are substrate-specific, fitting a substrate "key" into their active site "lock" like a lock and key, with only the correctly sized substrate fitting into each enzyme's unique active site. The enzyme catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen as an example reaction.