How enzymes work
•Download as PPT, PDF•
3 likes•4,059 views
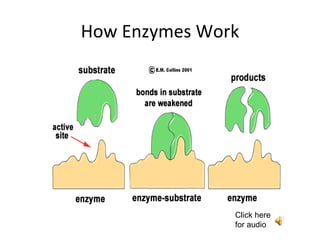
Enzymes work by binding a substrate to their active site, weakening the substrate's chemical bonds, causing the substrate to break down into smaller products which are then released, while the unchanged enzyme remains and is not used up. Enzymes are substrate-specific, fitting a substrate "key" into their active site "lock" like a lock and key, with only the correctly sized substrate fitting into each enzyme's unique active site. The enzyme catalyzes the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen as an example reaction.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
LIPID CHEMISTRY

Lipids are a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, and fat-soluble vitamins. They serve important functions like energy storage, signaling, and as structural components of cell membranes. The main classes of lipids are neutral fats/triglycerides (consisting of glycerol and fatty acids), phospholipids, and sterols. Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids like omega-3 and omega-6 are essential nutrients. Lipids are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents, and are an important energy source in animals and plants.
Biochemistry lecture notes enzymes

Enzymes are protein catalysts that greatly increase the rates of biochemical reactions. They achieve this by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes are highly specific and only catalyze one or a small number of reaction types. The enzyme binds to its substrate at its active site, and uses functional groups to facilitate the reaction, ultimately releasing the product. Many factors can influence an enzyme's activity level, including its concentration, the substrate concentration, temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors.
Enzymes

The document discusses enzymes and their classification. It defines enzymes as biological catalysts that are usually proteins and increase the rate of chemical reactions. It describes the six main classes of enzymes based on their catalytic activity as well as the Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system. The key points are that enzymes have unique active sites that substrates fit into, they are most active at optimal temperatures and pH levels, and their reaction rates depend on enzyme and substrate concentrations.
CHEMISTRY OF ENZYMES

This document provides an overview of enzymes, including their chemistry, nomenclature, classification, mechanisms of action, and factors that affect enzyme activity. It discusses how enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, lowering the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Enzymes are classified according to the type of chemical reactions they catalyze into six main classes: oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. The document also covers enzyme kinetics, regulation, diagnostic and therapeutic uses of enzymes.
Main lecture for lipids

1. The document discusses different types of lipids including fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids.
2. It explains the structures and properties of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Triglycerides are formed from glycerol and three fatty acids and are a major form of fat storage.
3. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes and contain a phosphate group. Cholesterol is an important sterol that is a component of cell membranes and precursor for other substances.
Classification of enzymes and properties of enzymes

Transferases are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of functional groups between molecules. There are five main subclasses of transferases: transaminases, kinases, transmethylases, transpeptidases, and transacylases. Transaminases specifically catalyze the exchange of amino groups between amino acids and keto acids. Phosphotransferases catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups.
Disaccharides

Disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharides joined by an O-glycosidic linkage. The main disaccharides discussed are:
1) Sucrose (table sugar), which hydrolyzes into glucose and fructose. Inversion of sucrose produces invert sugar, which is sweeter.
2) Maltose, formed from two glucose molecules and is a reducing sugar. It is found in germinating seeds.
3) Lactose is the sugar in milk, formed from glucose and galactose. It is hydrolyzed by lactase in the small intestine.
Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics

This document provides an overview of general concepts on enzymes and enzyme kinetics. It discusses the history of enzyme discovery from 1878 onwards. It describes key enzyme properties such as being proteins, heat labile, water-soluble and made of 16% nitrogen. Enzyme units, specificity, coenzymes, metalloenzymes and proteases are defined. The document also examines active sites, factors affecting enzyme activity, inhibition types and specific inhibitor examples. In summary, the document covers the fundamental characteristics and functions of enzymes as well as the historical milestones in the study of enzymology.
Recommended
LIPID CHEMISTRY

Lipids are a group of naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes, sterols, and fat-soluble vitamins. They serve important functions like energy storage, signaling, and as structural components of cell membranes. The main classes of lipids are neutral fats/triglycerides (consisting of glycerol and fatty acids), phospholipids, and sterols. Fatty acids can be saturated or unsaturated, and polyunsaturated fatty acids like omega-3 and omega-6 are essential nutrients. Lipids are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents, and are an important energy source in animals and plants.
Biochemistry lecture notes enzymes

Enzymes are protein catalysts that greatly increase the rates of biochemical reactions. They achieve this by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes are highly specific and only catalyze one or a small number of reaction types. The enzyme binds to its substrate at its active site, and uses functional groups to facilitate the reaction, ultimately releasing the product. Many factors can influence an enzyme's activity level, including its concentration, the substrate concentration, temperature, pH, and the presence of inhibitors.
Enzymes

The document discusses enzymes and their classification. It defines enzymes as biological catalysts that are usually proteins and increase the rate of chemical reactions. It describes the six main classes of enzymes based on their catalytic activity as well as the Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system. The key points are that enzymes have unique active sites that substrates fit into, they are most active at optimal temperatures and pH levels, and their reaction rates depend on enzyme and substrate concentrations.
CHEMISTRY OF ENZYMES

This document provides an overview of enzymes, including their chemistry, nomenclature, classification, mechanisms of action, and factors that affect enzyme activity. It discusses how enzymes are proteins that act as biological catalysts, lowering the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Enzymes are classified according to the type of chemical reactions they catalyze into six main classes: oxidoreductases, transferases, hydrolases, lyases, isomerases, and ligases. The document also covers enzyme kinetics, regulation, diagnostic and therapeutic uses of enzymes.
Main lecture for lipids

1. The document discusses different types of lipids including fatty acids, triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids.
2. It explains the structures and properties of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Triglycerides are formed from glycerol and three fatty acids and are a major form of fat storage.
3. Phospholipids are a major component of cell membranes and contain a phosphate group. Cholesterol is an important sterol that is a component of cell membranes and precursor for other substances.
Classification of enzymes and properties of enzymes

Transferases are enzymes that catalyze the transfer of functional groups between molecules. There are five main subclasses of transferases: transaminases, kinases, transmethylases, transpeptidases, and transacylases. Transaminases specifically catalyze the exchange of amino groups between amino acids and keto acids. Phosphotransferases catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups.
Disaccharides

Disaccharides are composed of two monosaccharides joined by an O-glycosidic linkage. The main disaccharides discussed are:
1) Sucrose (table sugar), which hydrolyzes into glucose and fructose. Inversion of sucrose produces invert sugar, which is sweeter.
2) Maltose, formed from two glucose molecules and is a reducing sugar. It is found in germinating seeds.
3) Lactose is the sugar in milk, formed from glucose and galactose. It is hydrolyzed by lactase in the small intestine.
Enzymes and Enzyme Kinetics

This document provides an overview of general concepts on enzymes and enzyme kinetics. It discusses the history of enzyme discovery from 1878 onwards. It describes key enzyme properties such as being proteins, heat labile, water-soluble and made of 16% nitrogen. Enzyme units, specificity, coenzymes, metalloenzymes and proteases are defined. The document also examines active sites, factors affecting enzyme activity, inhibition types and specific inhibitor examples. In summary, the document covers the fundamental characteristics and functions of enzymes as well as the historical milestones in the study of enzymology.
BIOLOGICAL OXIDATION/ ETC/ OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION

This document discusses biological oxidation and the thermodynamic principles involved. It describes the key variables of enthalpy, entropy and free energy. Biological oxidation involves the transfer of electrons through redox couples and redox potential is a quantitative measure of electron transfer tendency. ATP is an important energy currency produced through substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation, where electrons are transferred through the electron transport chain and energy is trapped as ATP.
Enzymes Biochemistry

This document provides an overview of enzymes. It discusses that enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being used up. The active site of the enzyme is responsible for its catalytic action. Enzymes are highly specific and their activity is closely regulated. Enzyme activity depends on factors like temperature, pH, substrate and inhibitor concentrations. Measurement of plasma enzyme levels can help diagnose conditions like heart attacks and liver disease. Isozymes are variants of the same enzyme that serve diagnostic purposes.
Enzymes

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed. They work by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes have specific active sites that bind substrates and induce a conformational change through induced fit. This allows the enzyme to accelerate the reaction and produce products. The rate of enzyme reactions can be affected by environmental factors like temperature, pH, and concentrations of enzymes and substrates.
Oxidation of fatty acids

All types of oxidation of fatty acids are covered in this presentation which includes alpha, beta, omega and peroxisomal oxidation
Lipids.pptx

LIPIDS
Introduction
Bloor's classification
Simple Lipids
Fats and oils (Triglycerides)
Hydrolysis
Fatty acids
Structure of fatty acid
Fatty acid classification
Saturated straight chain fatty acids
Branched saturated fatty acids
Unsaturated fatty acids
Properties
Functions or biological role of lipids
Simple Triglycerides
Mixed triglycerides
Waxes
Phospholipids
Compound lipids
Phospholipids
Phosphoglyceride - Lecithin
Cephalin
Plasmologens
Phosphoinositols - phosphotidyl inositols
Phosphosphingosides - Sphingomyelins
BIOCHEMISTRY
Biomolecules
Enzymes 2019

enzymes for medical students made by Ayman Mohammed Hany
lecturer of biochemistry and molecular biology
Monosaccharides

This document discusses carbohydrates and monosaccharides. It defines carbohydrates as compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and include trioses, tetroses, pentoses, and hexoses. The document discusses various properties of monosaccharides including isomerism, anomerism, mutarotation, and common chemical reactions like oxidation, reduction, and reactions with acids and bases. It also summarizes important derivatives of monosaccharides such as amino sugars, deoxy sugars, sugar acids, sugar alcohols, esters, and glycosides.
Biochemistry Bioenergetics

This document discusses bioenergetics and how cells obtain and use energy. It explains that life requires energy to perform functions like muscle movement and cell growth. Energy exists in kinetic or potential forms. Cells capture energy from exergonic reactions through ATP synthesis, then use that stored energy from ATP hydrolysis to drive endergonic reactions. The main energy pathways involve breaking down carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins to form acetyl-CoA, which feeds into the Krebs cycle to generate ATP. This allows cells to couple energy inputs from food molecules to the outputs required for cellular work.
Atp And Metabolism

ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy currency of cells that is constantly recycled. ATP consists of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups. All living cells continuously make ATP, which is used almost immediately and lasts less than a minute before being broken down. When cells need energy, ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP and inorganic phosphate, releasing energy. Like money, ATP is constantly recycled as cells use and replenish their supply.
Enzymes-Biochemistry

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed. They have binding sites called active sites that substrates fit into, forming enzyme-substrate complexes. All known enzymes are proteins except for some RNA enzymes. Enzymes require cofactors like coenzymes, prosthetic groups, or metal ions to function and exhibit varying degrees of specificity. They are named based on their substrates or reactions and have standardized EC numbers denoting their class and function. The first isolated and characterized enzyme was urease in 1926, proving enzymes are proteins.
Triacylglycerols ((Chemistry of Lipids (Part - III)

Chemistry of Lipids (Part - III)
Triacylglycerols chemistry.
Chemistry, Structure, Properties of Triacylglycerols.
Glycogenolysis

Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate. It occurs in three steps:
1) Phosphorolysis by glycogen phosphorylase cleaves α-1,4 glycosidic linkages, producing glucose-1-phosphate until four glucose residues remain.
2) A debranching enzyme removes these four residue branches through two activities, producing linear chains of glucose residues.
3) Phosphoglucomutase converts glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate, which can then enter glycolysis to produce energy or be released as free glucose from the liver. Glycogenolysis is regulated by allosteric effectors, hormones like glucagon and
DONNAN EQUILIBRIUM-1.pptx

Donnan equilibrium occurs when a permeable membrane separates a saline solution from distilled water. When equilibrium is reached, the concentrations of diffusible ions (e.g. Na and Cl) will be equal on both sides of the membrane. However, if a non-diffusible ion is present on one side, the concentrations of diffusible ions will not be equal. Specifically, the product of concentrations of a diffusible ion pair (e.g. Na and Cl) will be equal on both sides, but their individual concentrations will differ. This phenomenon is important physiologically as it can generate electric potentials and influence acidity across membranes in the body.
Lipids by Dr Ripudaman,Assistant Professor ,Anjuman Islam School of Pharmacy ...

Lipids by Dr Ripudaman,Assistant Professor ,Anjuman Islam School of Pharmacy ...Ripudaman Manjitsingh
This document defines lipids and classifies them by structure and function. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, sphingolipids and others. They serve important roles like energy storage, cell membrane structure, and as precursors to hormones. Fatty acids are classified as saturated or unsaturated. Unsaturated fatty acids exhibit positional and geometric isomerism. Linoleic and alpha-linolenic acids are essential fatty acids that must be obtained through diet. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oils confer various health benefits. Nomenclature systems describe fatty acid structure and double bond positions.Carbohydrate structure

The document discusses carbohydrate structure and properties. It covers the biological and medical importance of carbohydrates, including their functions as energy stores and structural components. It also describes the chemical nature of carbohydrates as polyhydroxy alcohols with an aldehyde or keto group. Carbohydrate structure is examined using Fisher, Haworth and chair conformations. Carbohydrates are classified as monosaccharides, oligosaccharides like disaccharides, and polysaccharides including homo- and heteropolysaccharides. Important monosaccharides, derivatives, disaccharides and polysaccharides are identified. Properties of monosaccharides such as isomerism, optical activity, epimerism, hemiacetal/ketal formation,
13 Biochemistry _ Glycolysis

Glycolysis is a catabolic pathway that breaks down glucose to extract energy. It occurs in 10 steps and involves 2 phases. In the first phase, energy is invested to phosphorylate and cleave glucose. In the second phase, the products are further broken down with a net generation of ATP. Glycolysis converts one glucose into two pyruvate molecules, produces 2 NADH, uses 2 ATP and generates a net of 2 ATP per glucose. This pathway is regulated by controlling the activity of three key enzymes: hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase.
Chapter-6 enzymes - Biochemistry 

Enzymes are biological catalysts that greatly accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are typically proteins that precisely bind substrates in their active sites, properly orienting them and bringing reactive groups close together. This organization lowers the activation energy barrier for reactions. Enzymes achieve catalysis by stabilizing transition state interactions even more than ground state interactions, through complementary shapes and interactions optimized for the transition state geometry. As a result, enzymes can tremendously increase reaction rates without disrupting chemical equilibrium.
Lipids Biomolecules 

This document provides information about lipids. It defines lipids as long chains of carbon and hydrogen molecules that are insoluble in water. Lipids serve as an important energy source and provide structure to cell membranes. They are classified based on their components, with simple lipids like fats and oils consisting of fatty acids and glycerol, and complex lipids also containing additional groups like phosphates or carbohydrates. Lipids play key roles in the body such as energy storage, insulation, and as precursors to hormones and vitamins. The document discusses the structure and examples of different lipid types as well as their biological functions.
Enzymes

Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being used up. They are proteins folded into complex shapes with active sites that substrates fit into like locks and keys. Enzymes are usually named for their substrates with the ending "-ase", such as lipase and proteases. Enzymes have five key characteristics: they are always proteins, are specific to reactions, can be reused, are denatured at 50°C, and have optimal pH levels. They are made inside cells and can work inside or outside of cells to speed chemical reactions. Enzymes are widely used in industry due to their ability to work at low temperatures and only be needed in small amounts.
enzymes

Enzymes are proteins that catalyse chemical reactions of other substances without itself being destroyed or altered upon completion of the reactions.
Frog Dissection Lab Manual

The document summarizes the steps of a frog dissection lab, where students examine the external and internal anatomy of a frog. Students observe the frog's dorsal and ventral sides, measure various parts, and locate structures like the eyes, tympanic membranes, and mouthparts. Upon cutting open the frog, they identify internal organs like the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, intestines, kidneys and reproductive structures. The purpose is to learn frog anatomy through hands-on examination and labelling of both external and internal features.
Earthworm dissection lab report

1) The document provides directions for a lab to dissect and examine the external and internal anatomy of an earthworm. Students are to identify external structures like the clitellum, setae, and internal structures including the crop, gizzard, and intestines.
2) Data on the earthworm's length, number of segments, and locations of reproductive structures are to be recorded. The contents of the digestive system are also observed.
3) Questions analyze the functions of setae and parts of the anatomy, and summarize what was learned from the dissection.
More Related Content
What's hot
BIOLOGICAL OXIDATION/ ETC/ OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION

This document discusses biological oxidation and the thermodynamic principles involved. It describes the key variables of enthalpy, entropy and free energy. Biological oxidation involves the transfer of electrons through redox couples and redox potential is a quantitative measure of electron transfer tendency. ATP is an important energy currency produced through substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation, where electrons are transferred through the electron transport chain and energy is trapped as ATP.
Enzymes Biochemistry

This document provides an overview of enzymes. It discusses that enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions without being used up. The active site of the enzyme is responsible for its catalytic action. Enzymes are highly specific and their activity is closely regulated. Enzyme activity depends on factors like temperature, pH, substrate and inhibitor concentrations. Measurement of plasma enzyme levels can help diagnose conditions like heart attacks and liver disease. Isozymes are variants of the same enzyme that serve diagnostic purposes.
Enzymes

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed. They work by lowering the activation energy of reactions. Enzymes have specific active sites that bind substrates and induce a conformational change through induced fit. This allows the enzyme to accelerate the reaction and produce products. The rate of enzyme reactions can be affected by environmental factors like temperature, pH, and concentrations of enzymes and substrates.
Oxidation of fatty acids

All types of oxidation of fatty acids are covered in this presentation which includes alpha, beta, omega and peroxisomal oxidation
Lipids.pptx

LIPIDS
Introduction
Bloor's classification
Simple Lipids
Fats and oils (Triglycerides)
Hydrolysis
Fatty acids
Structure of fatty acid
Fatty acid classification
Saturated straight chain fatty acids
Branched saturated fatty acids
Unsaturated fatty acids
Properties
Functions or biological role of lipids
Simple Triglycerides
Mixed triglycerides
Waxes
Phospholipids
Compound lipids
Phospholipids
Phosphoglyceride - Lecithin
Cephalin
Plasmologens
Phosphoinositols - phosphotidyl inositols
Phosphosphingosides - Sphingomyelins
BIOCHEMISTRY
Biomolecules
Enzymes 2019

enzymes for medical students made by Ayman Mohammed Hany
lecturer of biochemistry and molecular biology
Monosaccharides

This document discusses carbohydrates and monosaccharides. It defines carbohydrates as compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Monosaccharides are the simplest form of carbohydrates and include trioses, tetroses, pentoses, and hexoses. The document discusses various properties of monosaccharides including isomerism, anomerism, mutarotation, and common chemical reactions like oxidation, reduction, and reactions with acids and bases. It also summarizes important derivatives of monosaccharides such as amino sugars, deoxy sugars, sugar acids, sugar alcohols, esters, and glycosides.
Biochemistry Bioenergetics

This document discusses bioenergetics and how cells obtain and use energy. It explains that life requires energy to perform functions like muscle movement and cell growth. Energy exists in kinetic or potential forms. Cells capture energy from exergonic reactions through ATP synthesis, then use that stored energy from ATP hydrolysis to drive endergonic reactions. The main energy pathways involve breaking down carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins to form acetyl-CoA, which feeds into the Krebs cycle to generate ATP. This allows cells to couple energy inputs from food molecules to the outputs required for cellular work.
Atp And Metabolism

ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the energy currency of cells that is constantly recycled. ATP consists of adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups. All living cells continuously make ATP, which is used almost immediately and lasts less than a minute before being broken down. When cells need energy, ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP and inorganic phosphate, releasing energy. Like money, ATP is constantly recycled as cells use and replenish their supply.
Enzymes-Biochemistry

Enzymes are protein catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions without being consumed. They have binding sites called active sites that substrates fit into, forming enzyme-substrate complexes. All known enzymes are proteins except for some RNA enzymes. Enzymes require cofactors like coenzymes, prosthetic groups, or metal ions to function and exhibit varying degrees of specificity. They are named based on their substrates or reactions and have standardized EC numbers denoting their class and function. The first isolated and characterized enzyme was urease in 1926, proving enzymes are proteins.
Triacylglycerols ((Chemistry of Lipids (Part - III)

Chemistry of Lipids (Part - III)
Triacylglycerols chemistry.
Chemistry, Structure, Properties of Triacylglycerols.
Glycogenolysis

Glycogenolysis is the breakdown of glycogen into glucose-1-phosphate. It occurs in three steps:
1) Phosphorolysis by glycogen phosphorylase cleaves α-1,4 glycosidic linkages, producing glucose-1-phosphate until four glucose residues remain.
2) A debranching enzyme removes these four residue branches through two activities, producing linear chains of glucose residues.
3) Phosphoglucomutase converts glucose-1-phosphate to glucose-6-phosphate, which can then enter glycolysis to produce energy or be released as free glucose from the liver. Glycogenolysis is regulated by allosteric effectors, hormones like glucagon and
DONNAN EQUILIBRIUM-1.pptx

Donnan equilibrium occurs when a permeable membrane separates a saline solution from distilled water. When equilibrium is reached, the concentrations of diffusible ions (e.g. Na and Cl) will be equal on both sides of the membrane. However, if a non-diffusible ion is present on one side, the concentrations of diffusible ions will not be equal. Specifically, the product of concentrations of a diffusible ion pair (e.g. Na and Cl) will be equal on both sides, but their individual concentrations will differ. This phenomenon is important physiologically as it can generate electric potentials and influence acidity across membranes in the body.
Lipids by Dr Ripudaman,Assistant Professor ,Anjuman Islam School of Pharmacy ...

Lipids by Dr Ripudaman,Assistant Professor ,Anjuman Islam School of Pharmacy ...Ripudaman Manjitsingh
This document defines lipids and classifies them by structure and function. Lipids include fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, sphingolipids and others. They serve important roles like energy storage, cell membrane structure, and as precursors to hormones. Fatty acids are classified as saturated or unsaturated. Unsaturated fatty acids exhibit positional and geometric isomerism. Linoleic and alpha-linolenic acids are essential fatty acids that must be obtained through diet. Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oils confer various health benefits. Nomenclature systems describe fatty acid structure and double bond positions.Carbohydrate structure

The document discusses carbohydrate structure and properties. It covers the biological and medical importance of carbohydrates, including their functions as energy stores and structural components. It also describes the chemical nature of carbohydrates as polyhydroxy alcohols with an aldehyde or keto group. Carbohydrate structure is examined using Fisher, Haworth and chair conformations. Carbohydrates are classified as monosaccharides, oligosaccharides like disaccharides, and polysaccharides including homo- and heteropolysaccharides. Important monosaccharides, derivatives, disaccharides and polysaccharides are identified. Properties of monosaccharides such as isomerism, optical activity, epimerism, hemiacetal/ketal formation,
13 Biochemistry _ Glycolysis

Glycolysis is a catabolic pathway that breaks down glucose to extract energy. It occurs in 10 steps and involves 2 phases. In the first phase, energy is invested to phosphorylate and cleave glucose. In the second phase, the products are further broken down with a net generation of ATP. Glycolysis converts one glucose into two pyruvate molecules, produces 2 NADH, uses 2 ATP and generates a net of 2 ATP per glucose. This pathway is regulated by controlling the activity of three key enzymes: hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase.
Chapter-6 enzymes - Biochemistry 

Enzymes are biological catalysts that greatly accelerate chemical reactions in living organisms. They are typically proteins that precisely bind substrates in their active sites, properly orienting them and bringing reactive groups close together. This organization lowers the activation energy barrier for reactions. Enzymes achieve catalysis by stabilizing transition state interactions even more than ground state interactions, through complementary shapes and interactions optimized for the transition state geometry. As a result, enzymes can tremendously increase reaction rates without disrupting chemical equilibrium.
Lipids Biomolecules 

This document provides information about lipids. It defines lipids as long chains of carbon and hydrogen molecules that are insoluble in water. Lipids serve as an important energy source and provide structure to cell membranes. They are classified based on their components, with simple lipids like fats and oils consisting of fatty acids and glycerol, and complex lipids also containing additional groups like phosphates or carbohydrates. Lipids play key roles in the body such as energy storage, insulation, and as precursors to hormones and vitamins. The document discusses the structure and examples of different lipid types as well as their biological functions.
Enzymes

Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being used up. They are proteins folded into complex shapes with active sites that substrates fit into like locks and keys. Enzymes are usually named for their substrates with the ending "-ase", such as lipase and proteases. Enzymes have five key characteristics: they are always proteins, are specific to reactions, can be reused, are denatured at 50°C, and have optimal pH levels. They are made inside cells and can work inside or outside of cells to speed chemical reactions. Enzymes are widely used in industry due to their ability to work at low temperatures and only be needed in small amounts.
enzymes

Enzymes are proteins that catalyse chemical reactions of other substances without itself being destroyed or altered upon completion of the reactions.
What's hot (20)
BIOLOGICAL OXIDATION/ ETC/ OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION

BIOLOGICAL OXIDATION/ ETC/ OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION
Triacylglycerols ((Chemistry of Lipids (Part - III)

Triacylglycerols ((Chemistry of Lipids (Part - III)
Lipids by Dr Ripudaman,Assistant Professor ,Anjuman Islam School of Pharmacy ...

Lipids by Dr Ripudaman,Assistant Professor ,Anjuman Islam School of Pharmacy ...
More from D Sanders
Frog Dissection Lab Manual

The document summarizes the steps of a frog dissection lab, where students examine the external and internal anatomy of a frog. Students observe the frog's dorsal and ventral sides, measure various parts, and locate structures like the eyes, tympanic membranes, and mouthparts. Upon cutting open the frog, they identify internal organs like the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, intestines, kidneys and reproductive structures. The purpose is to learn frog anatomy through hands-on examination and labelling of both external and internal features.
Earthworm dissection lab report

1) The document provides directions for a lab to dissect and examine the external and internal anatomy of an earthworm. Students are to identify external structures like the clitellum, setae, and internal structures including the crop, gizzard, and intestines.
2) Data on the earthworm's length, number of segments, and locations of reproductive structures are to be recorded. The contents of the digestive system are also observed.
3) Questions analyze the functions of setae and parts of the anatomy, and summarize what was learned from the dissection.
Cell model rubric

This rubric provides criteria for evaluating 3D cell models. Students must create a model no larger than 21 cm depicting a plant or animal cell that includes and labels all organelles. Models will be scored on a scale of 1 to 4 in the categories of title, labeling, design, with subtotals multiplied by 1.5 for a total possible score of 24.
Cell transport worksheet

The document provides a list of Greek and Latin roots, prefixes, and suffixes related to cell transport and their definitions. It asks students to use the definitions to infer the literal meanings of several combined terms, and then look up the actual definitions in their textbook. Terms include endo-cyto-sis, exo-cyto-sis, phago-cyto-sis, pino-cyto-sis, hyper-tonic, hypo-tonic, and iso-tonic.
Onion and cheek cell lab

This lab document outlines procedures for observing plant and animal cells under a microscope. Students will examine onion and cheek cells stained with iodine. For the onion cell lab, students will slice an onion, apply iodine stain, and observe the cells under low, medium, and high powers of a microscope, drawing and labeling their observations. For the cheek cell lab, students will rub the inside of their cheek with a toothpick, stir the toothpick in iodine stain, observe the stained cheek cells under the microscope, and draw and label their observations. Students will then analyze their results and write a conclusion describing what was done in the lab and what was discovered about plant and animal cells.
Onion and cheek cell, DNA extraction lab

This document provides instructions for a lab report on observing plant and animal cells. The lab involves three parts: Part A examines onion cells under a microscope after staining with iodine. Part B examines cheek cells from inside the mouth under a microscope after staining. Part C involves completing a virtual DNA extraction lab and extracting DNA from split peas to observe under a microscope. Students are directed to write an introduction explaining the purpose of the lab, document the materials and procedures for each part, and create data tables to record observations.
Comparing plant and animal cells

The document is a worksheet about cell organelles. It contains tables to match cell structures and functions with organelle names. It also includes diagrams of plant and animal cells to label. The worksheet teaches about key differences in plant and animal cells like the presence of a cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells.
Word splash

This document provides instructions for two vocabulary activities - a word splash and foldable. For the word splash, students are directed to write 3 sentences predicting how 3 chosen vocabulary words relate to a center word, then check their predictions against a text. For the foldable, students create a 9-flap fold with a vocabulary word, picture, and definition on each flap, due on Wednesday.
Cell theory/prokaryotic and eukaryotic

Cells are the basic unit of life that arise from other cells. They contain organelles that carry out cellular processes. There are similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Both have DNA, plasma membranes, and cytoplasm but prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler while eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, having a nucleus containing membrane-bound DNA.
Enzyme lab (yeast) assessment

The document describes an experiment with hydrogen peroxide, a cork, and yeast. Hydrogen peroxide was observed for odor, color, thickness, and flammability. When a cork was added to hydrogen peroxide in a test tube, bubbling occurred due to the production of oxygen gas, as evidenced by the gas produced. After the reaction, water was likely remaining in the test tube, with different properties than the original hydrogen peroxide. Yeast played a role in the chemical reaction by catalyzing the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas.
Enzymes pre lab

The document discusses hydrogen peroxide and how it can be broken down by the enzyme catalase. It provides instructions for a lab experiment to test if yeast contains catalase that can break down hydrogen peroxide. Students are asked to write a hypothesis that if yeast is added to hydrogen peroxide, then the peroxide will break down due to catalase in the yeast. The experiment observes the reaction between yeast and peroxide over time.
More from D Sanders (12)
How enzymes work
- 1. How Enzymes Work Click here for audio
- 3. Lock and Key Analogy Click here for audio
Editor's Notes
- A substrate binds to an enzyme’s active site. An example of a substrate could be a disaccharide, which means two sugars stuck together. This forms an enzyme-substrate complex. While attached to the substrate, the enzyme causes a weakening of certain chemical bonds in the substrate molecule, resulting in a breakdown (hydrolysis) of the substrate into two smaller product molecules (such as monosaccharides). The enzyme is unaltered during the reaction and is free to catalyze the breakdown of another substrate molecule.
- A substrate binds to an enzyme’s active site. An example of a substrate could be a polysaccharide. This forms an enzyme-substrate complex. While attached to the substrate, the enzyme causes a weakening of certain chemical bonds in the substrate molecule, resulting in a breakdown (hydrolysis) of the substrate into smaller product molecules (such as monosaccharides). The enzyme is unaltered during the reaction and is free to catalyze the breakdown of another substrate molecule.
- The active site has a unique geometric shape that is complementary to the geometric shape of a substrate molecule, similar to the fit of puzzle pieces. This means that enzymes specifically react with only one or a very few similar compounds. In this analogy, the lock is the enzyme and the key is the substrate. Only the correctly sized key (substrate) fits into the key hole (active site) of the lock (enzyme) . (incorrectly shaped or sized substrate molecules) do not fit into the lock (enzyme) and a chemical reaction will not occur.
- The active site has a unique geometric shape that is complementary to the geometric shape of a substrate molecule, similar to the fit of puzzle pieces. This means that enzymes specifically react with only one or a very few similar compounds.