Embed presentation
Downloaded 57 times



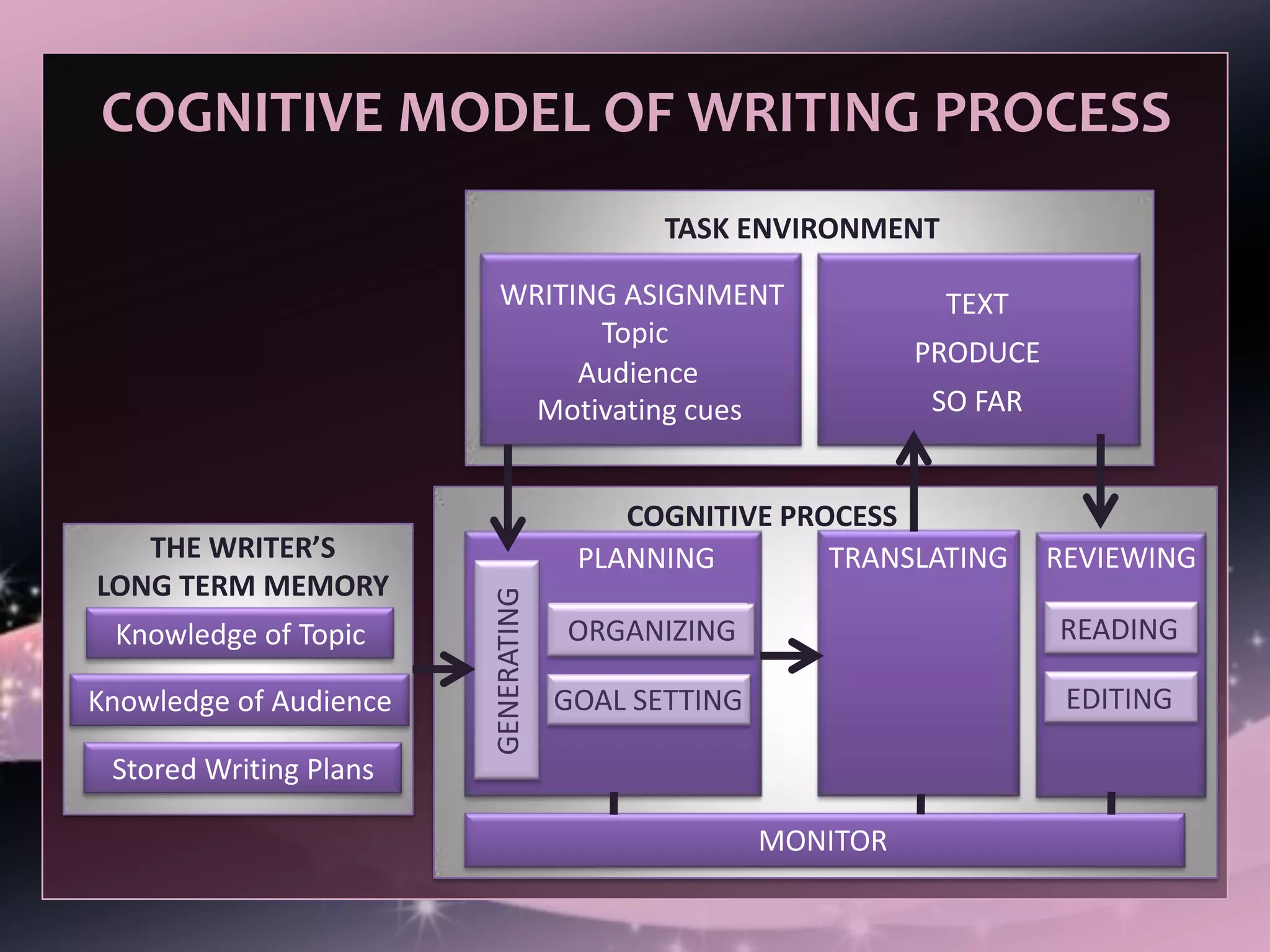



The document outlines Hayes and Flower's cognitive model of the writing process from 1980. The model shows writing as a complex task that involves simultaneous control over language systems and managing audience, purpose, syntax, mechanics, organization, content, and grammar. It depicts the writing process as a series of mental processes where the writer draws from their long-term memory and goes through planning, organizing, goal setting, generating, translating, reviewing, and editing with feedback from an external monitor and task environment.





