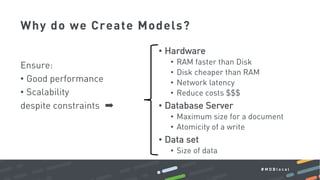
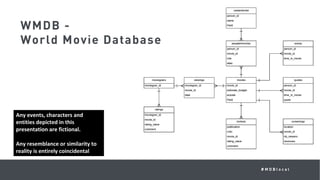
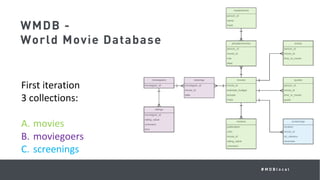
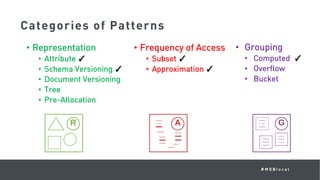
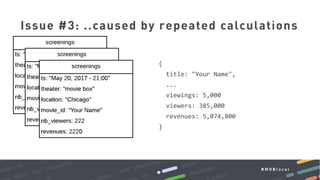
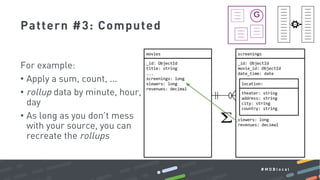
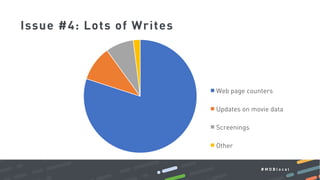
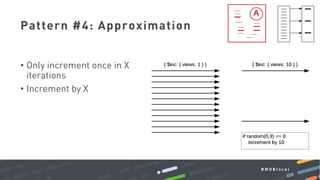
This document summarizes a MongoDB webinar on advanced schema design patterns. It introduces common schema design patterns like attribute, subset, computed, and approximation patterns. It discusses how to use these patterns to address issues like large documents with many fields, working sets that don't fit in RAM, high CPU usage from repeated calculations, and changing schemas over time. The webinar provides examples of each pattern and encourages learning a common vocabulary for designing MongoDB schemas by applying these reusable patterns.

![# M D B l o c a l
{ "name": "Daniel Coupal",
"jobs_at_MongoDB": [
{ "job": "Senior Curriculum Engineer",
"from": new Date("2016-11") },
{ "job": "Senior Technical Service Engineer",
"from": new Date("2013-11") }
],
"previous_jobs": [
"Consultant",
"Developer",
"Manager Quality & Tools Team",
"Manager Software Team",
"Tools Developer"
],
"likes": [ "food", "beers", "movies", "MongoDB" ]
}
Who Am I?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webinar-2017-10-18-advanced-sc-a8130291-e8c3-4b15-91b0-7548aa7243f7-1055906262-171018205601/85/Advanced-Schema-Design-Patterns-2-320.jpg)