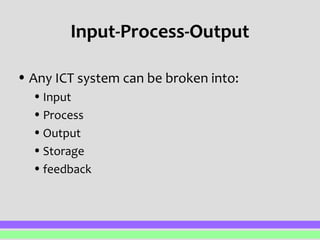
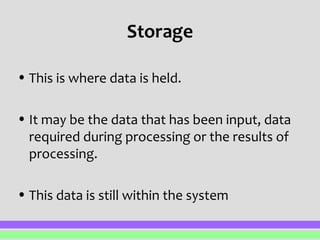
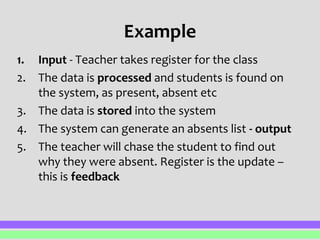
Any information and communication technology system can be broken down into five main components: input, process, output, storage, and feedback. Input involves entering external data, such as through a keyboard, mouse, scanner, or sensor. This data is then processed through operations like sorting, searching, or calculations. The output distributes the results, potentially through printing, displaying on screen, or saving electronically. Storage holds the input data, processing data, and output results within the system. Feedback occurs when the output forms new input in a closed or open loop to influence the system going forward.