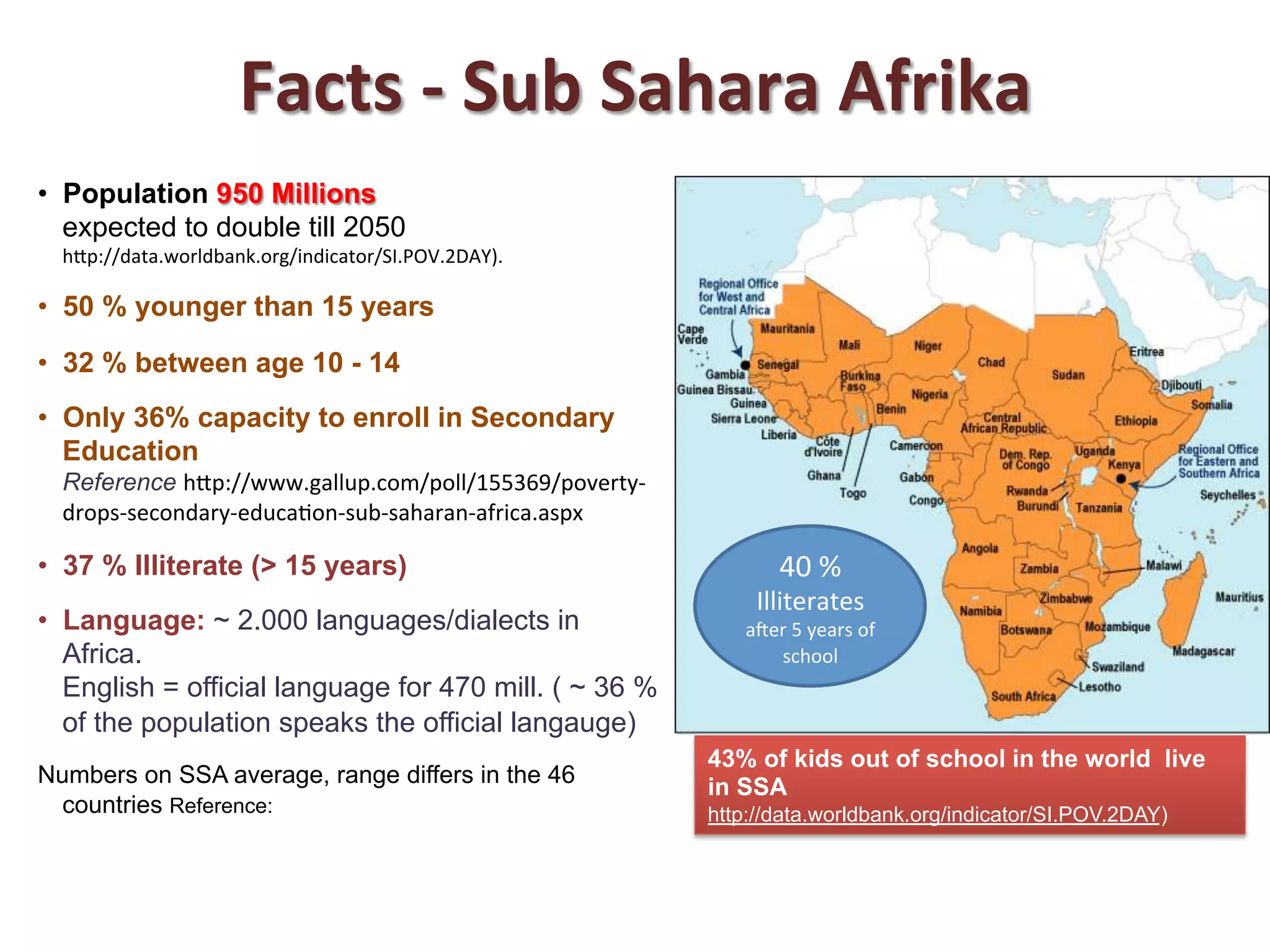
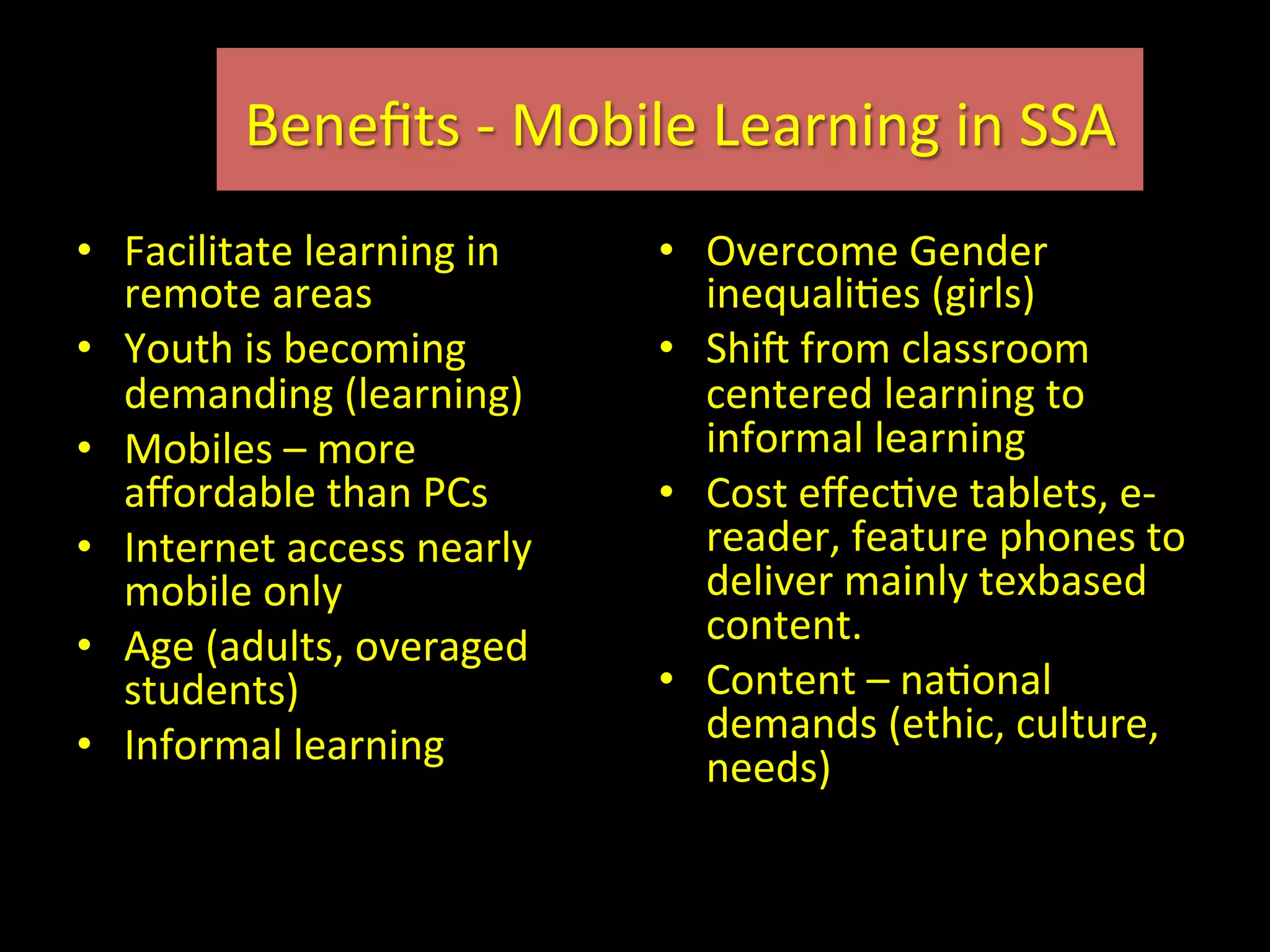
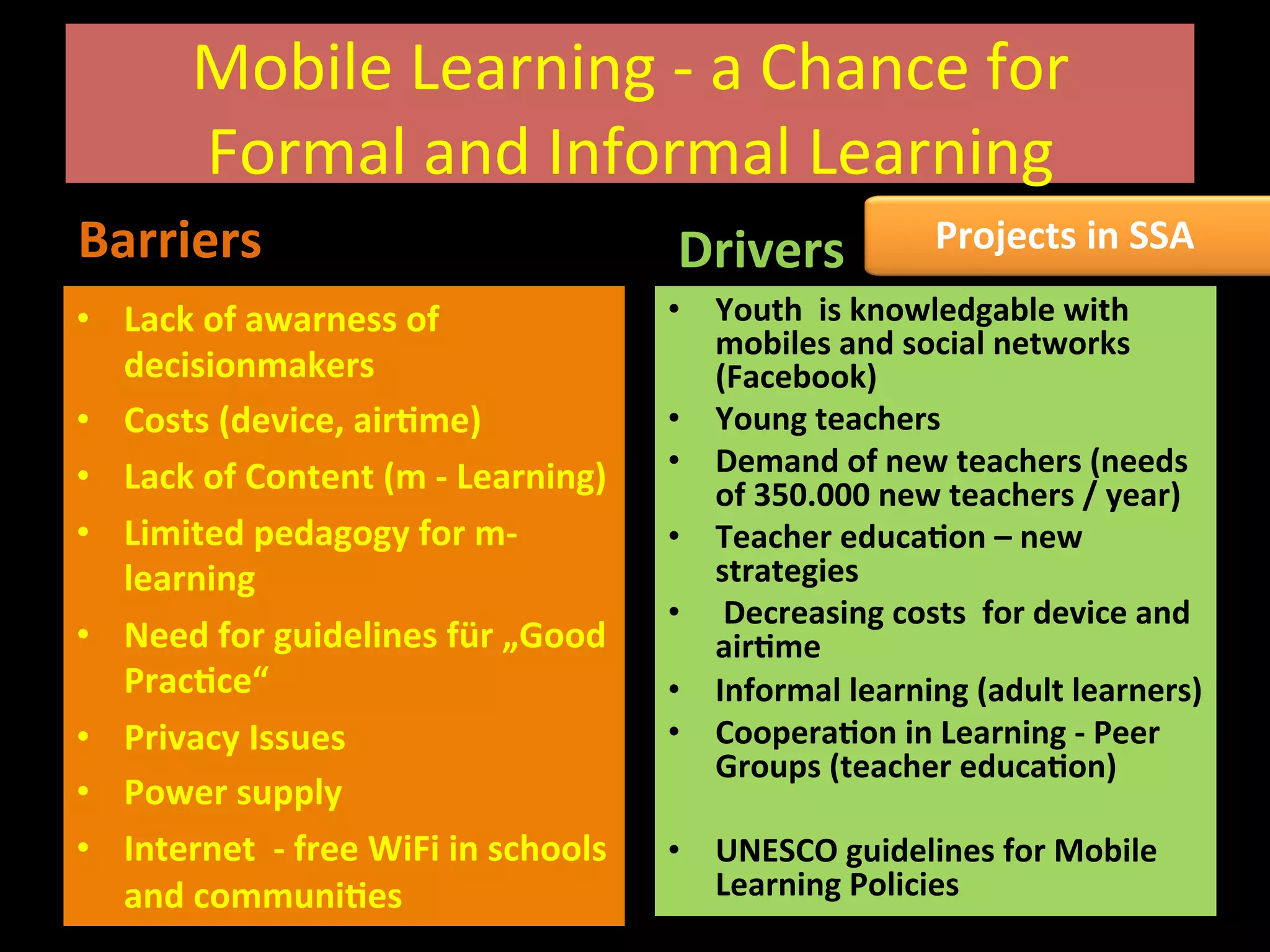
This document discusses the potential for mobile learning in Sub-Saharan Africa. It notes that while education faces many challenges in SSA, including lack of resources and trained teachers, mobile phones provide an opportunity as they are widespread. Mobile learning could help improve education quality by facilitating learning outside the classroom and helping to overcome barriers like distance. However, realizing this potential will require addressing issues such as lack of awareness, costs, limited educational content and apps, and need for pedagogical guidance on mobile learning. Examples of existing mobile learning projects in SSA countries are provided.