The document discusses key considerations for developing a micro-credential strategy at an institution. It addresses three main questions:
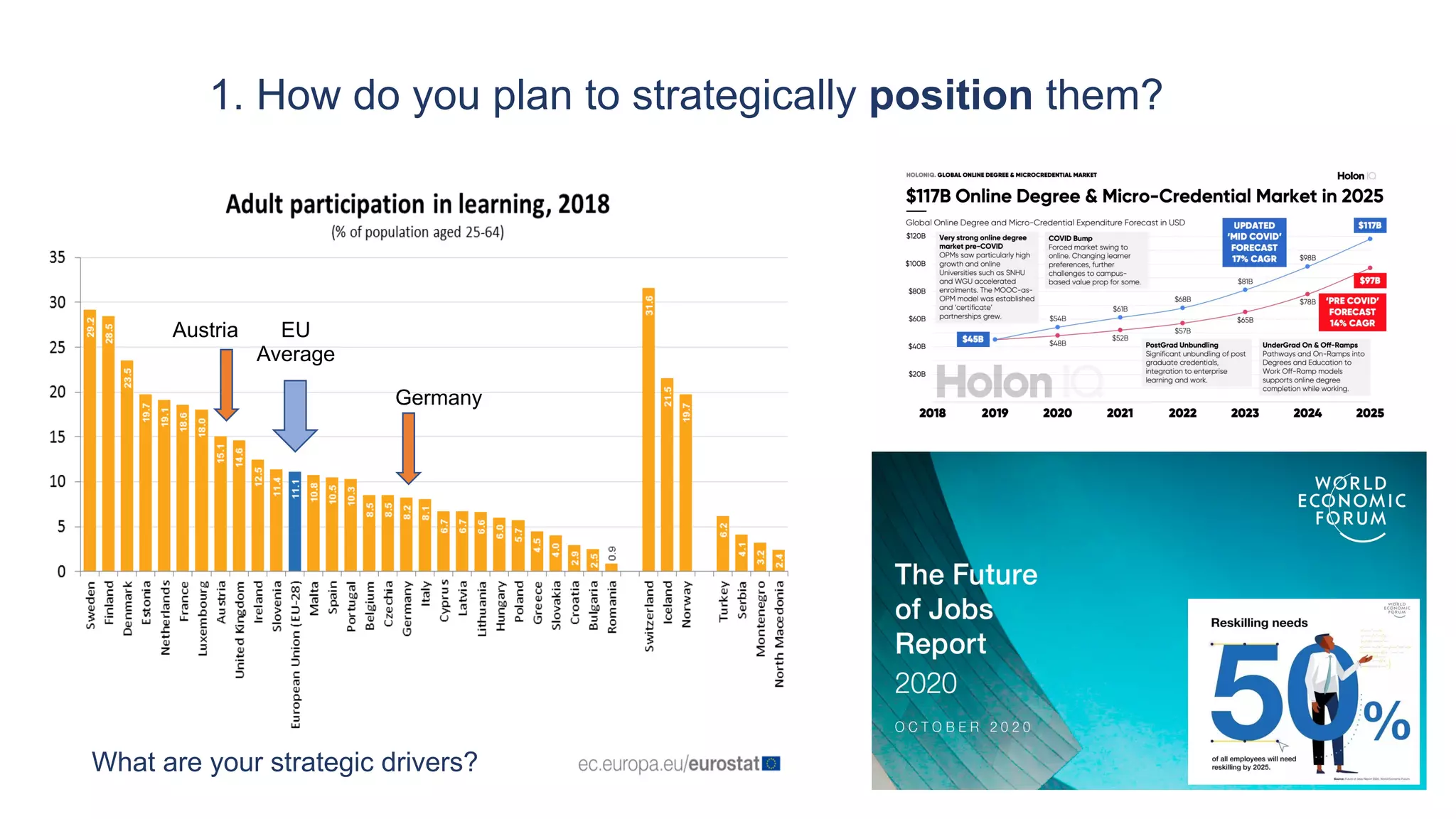
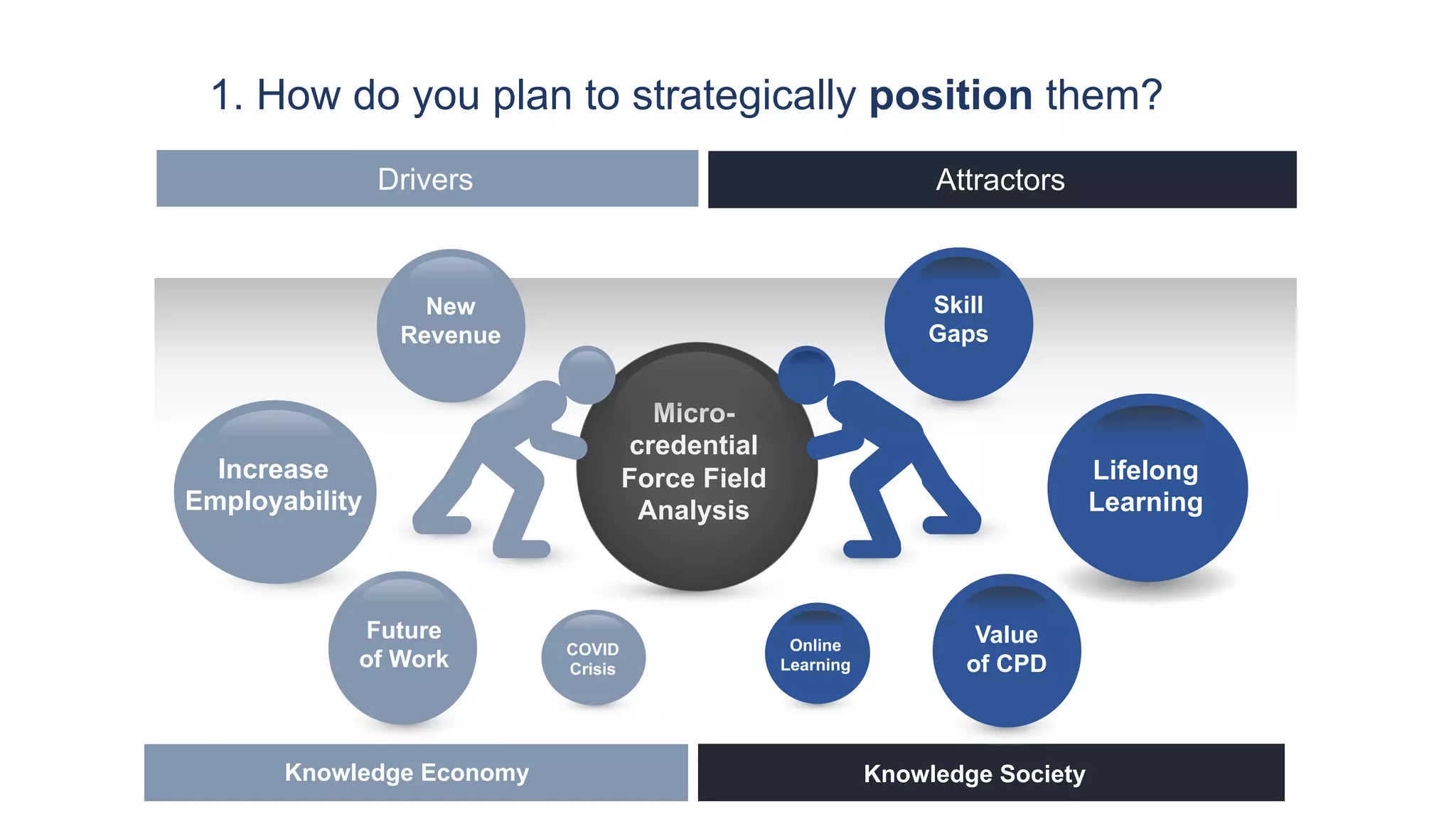
1. How to strategically position micro-credentials, including where they fit within credit structures and programs.
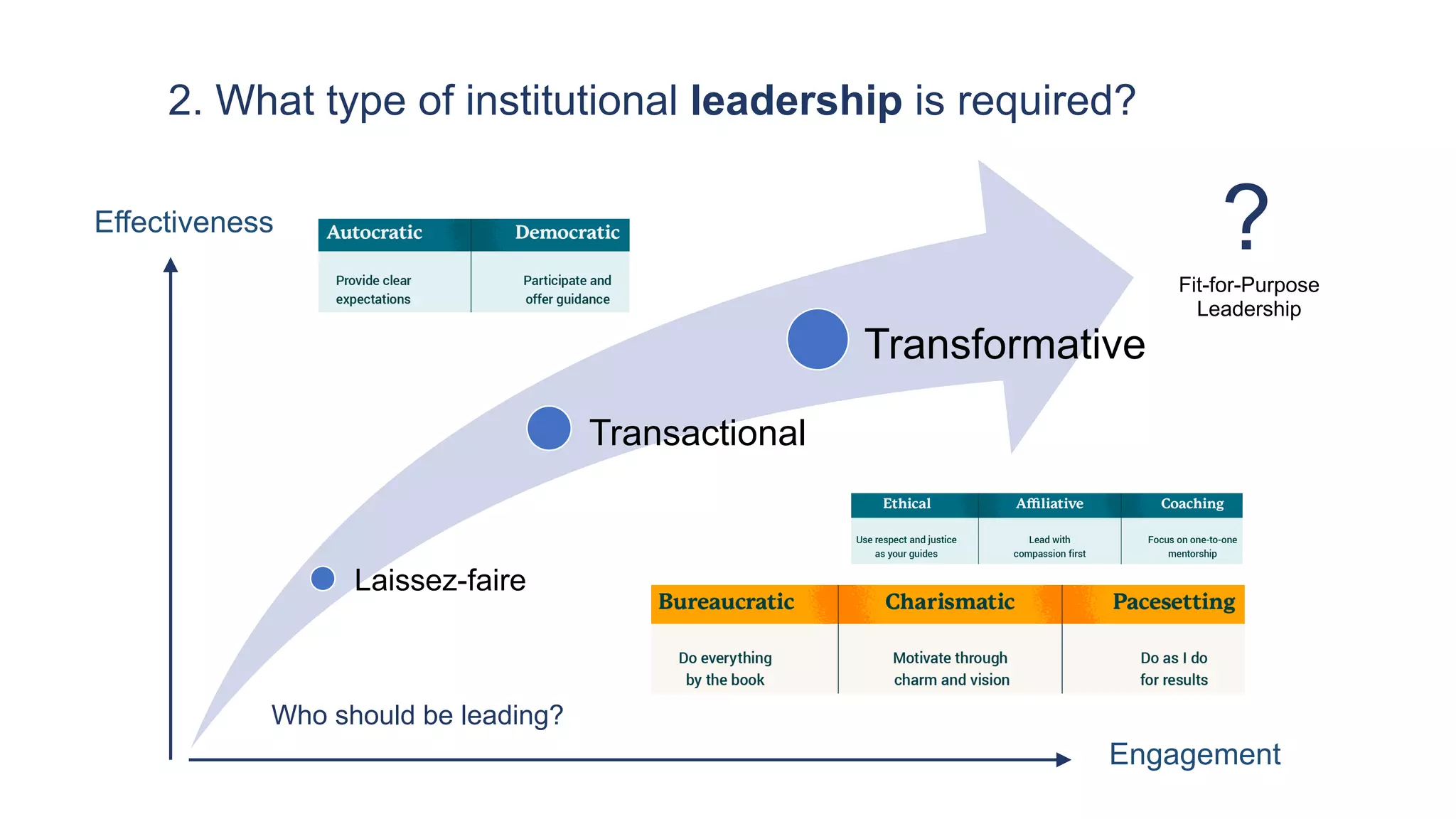
2. What type of institutional leadership is required, such as transformational leaders who engage staff across the organization.
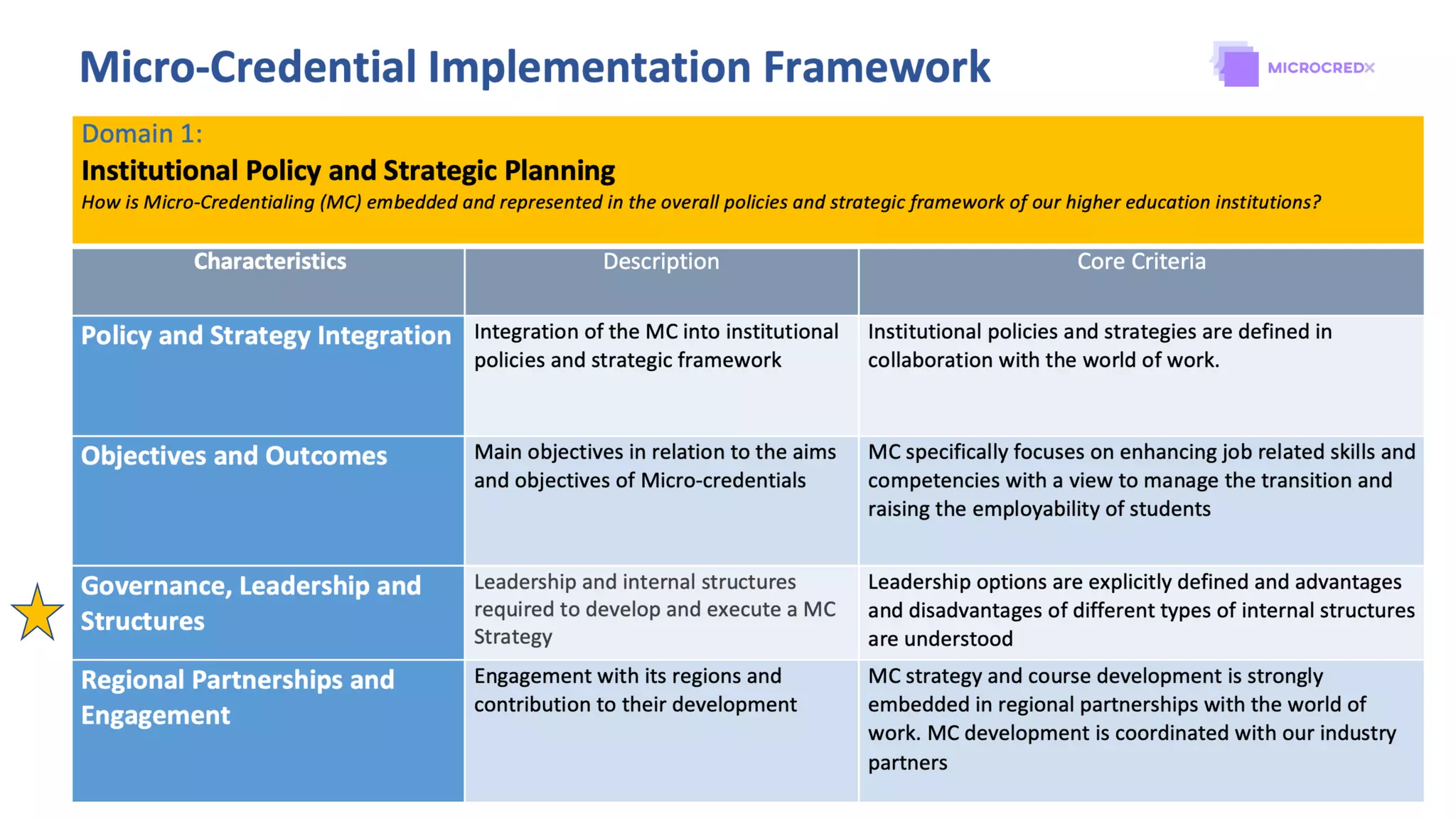
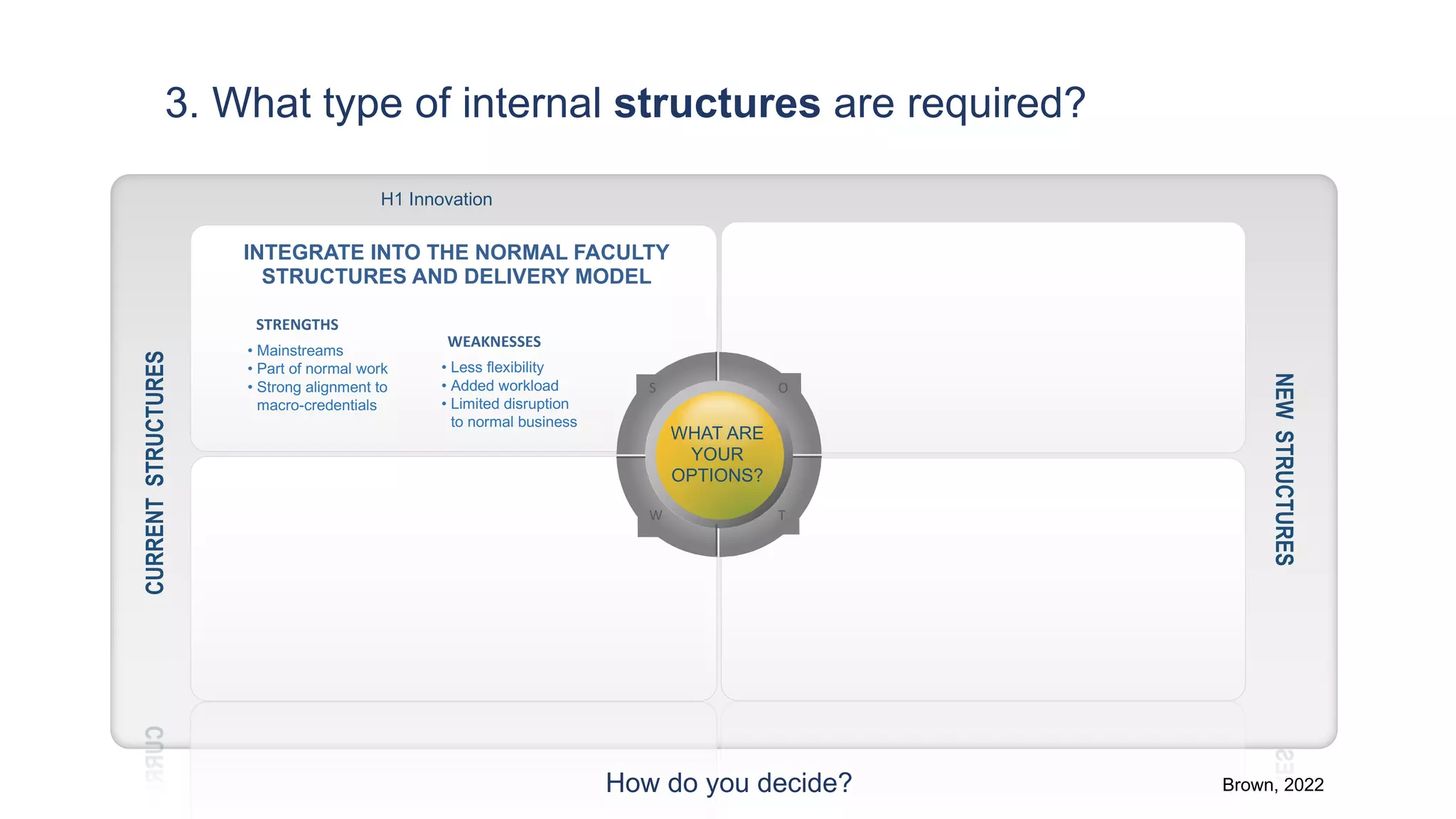
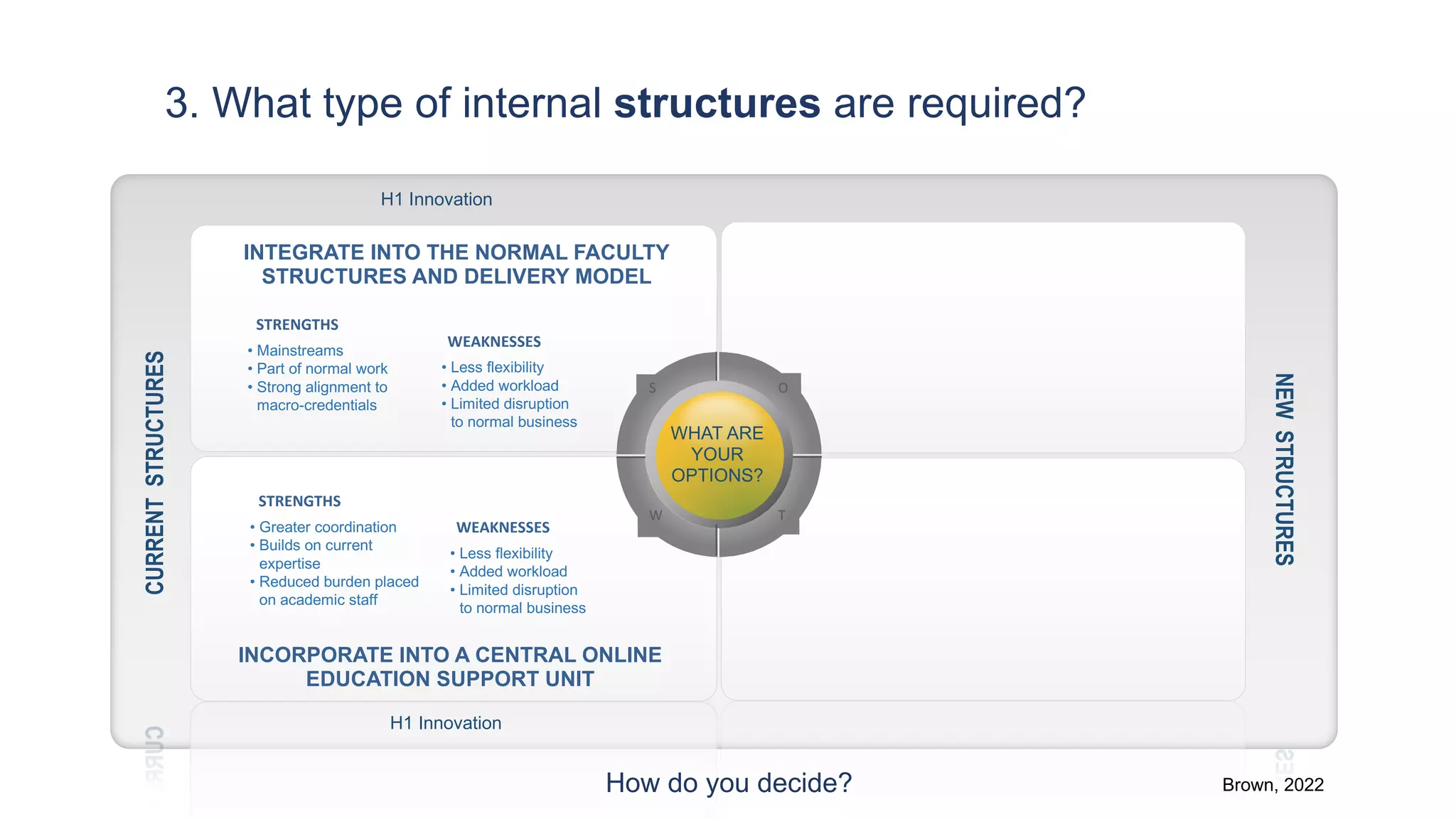
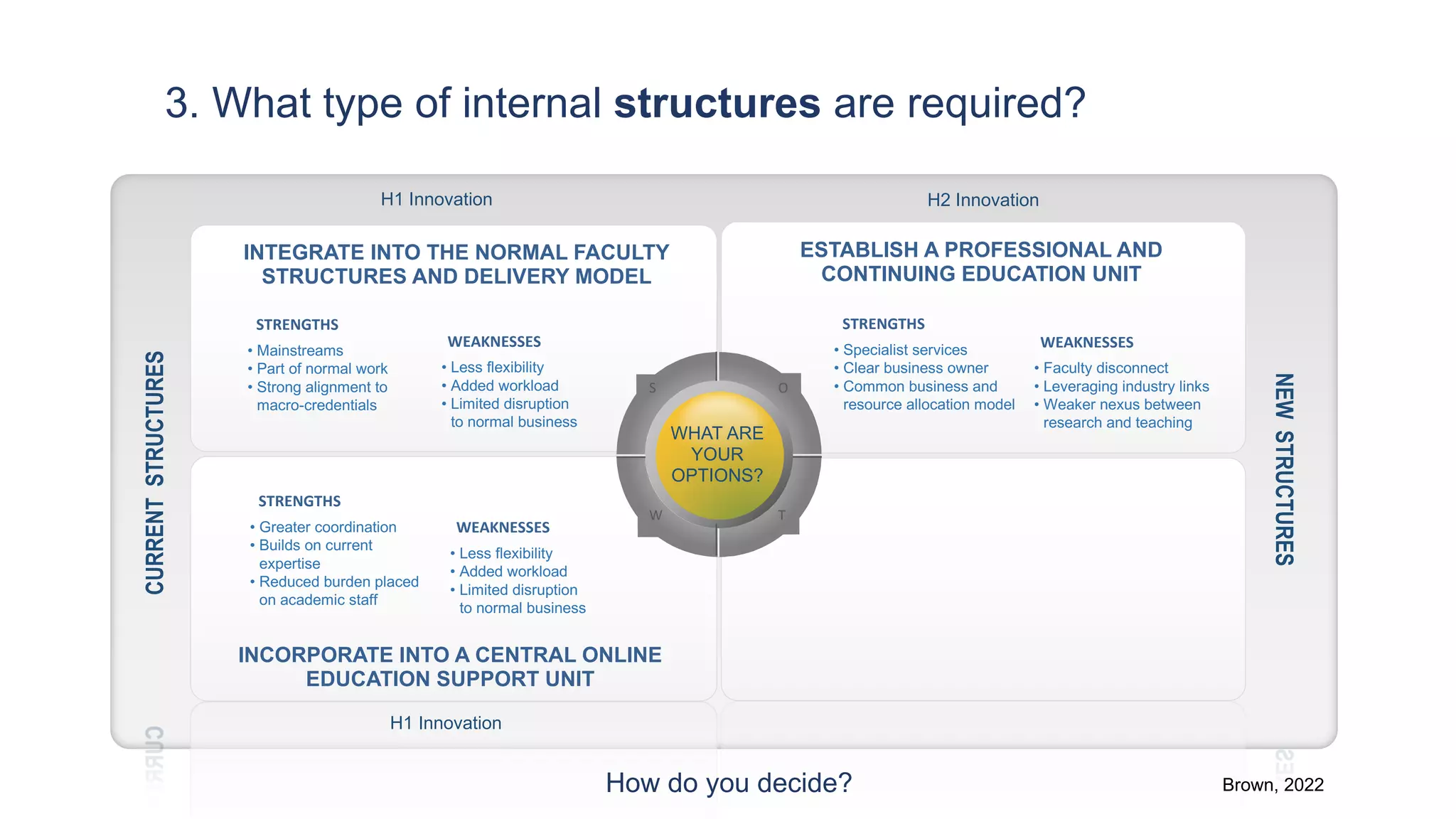
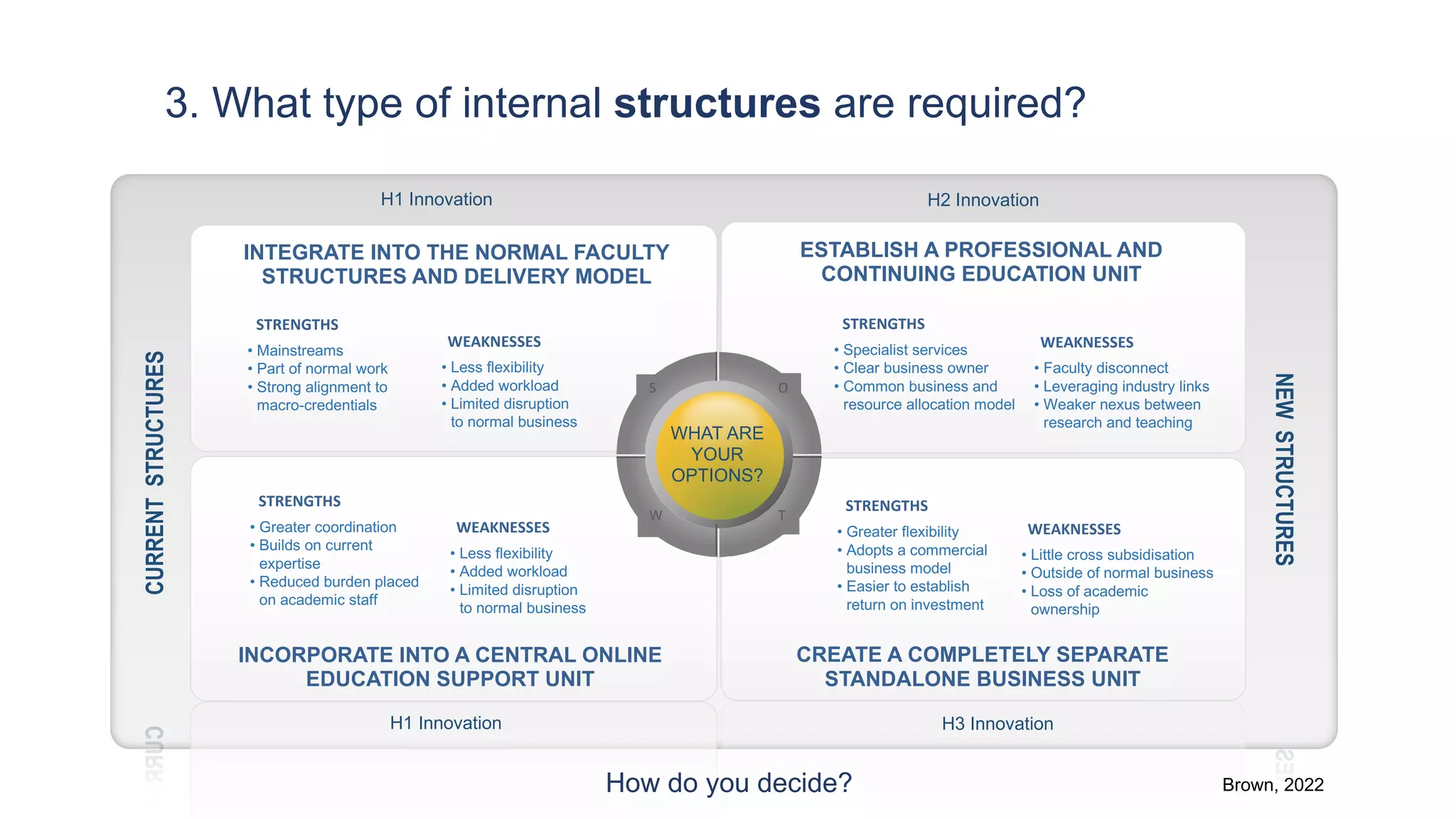
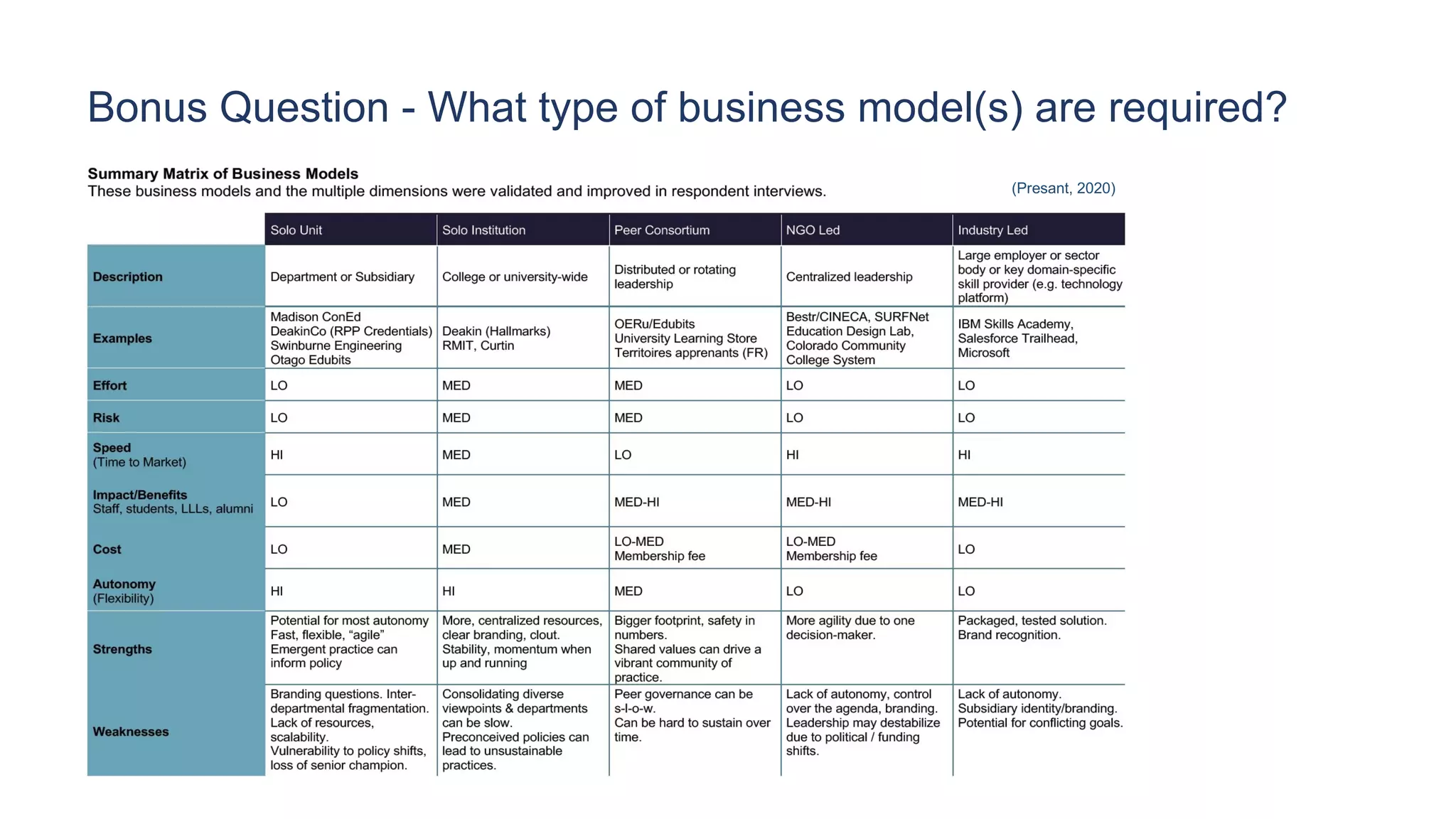
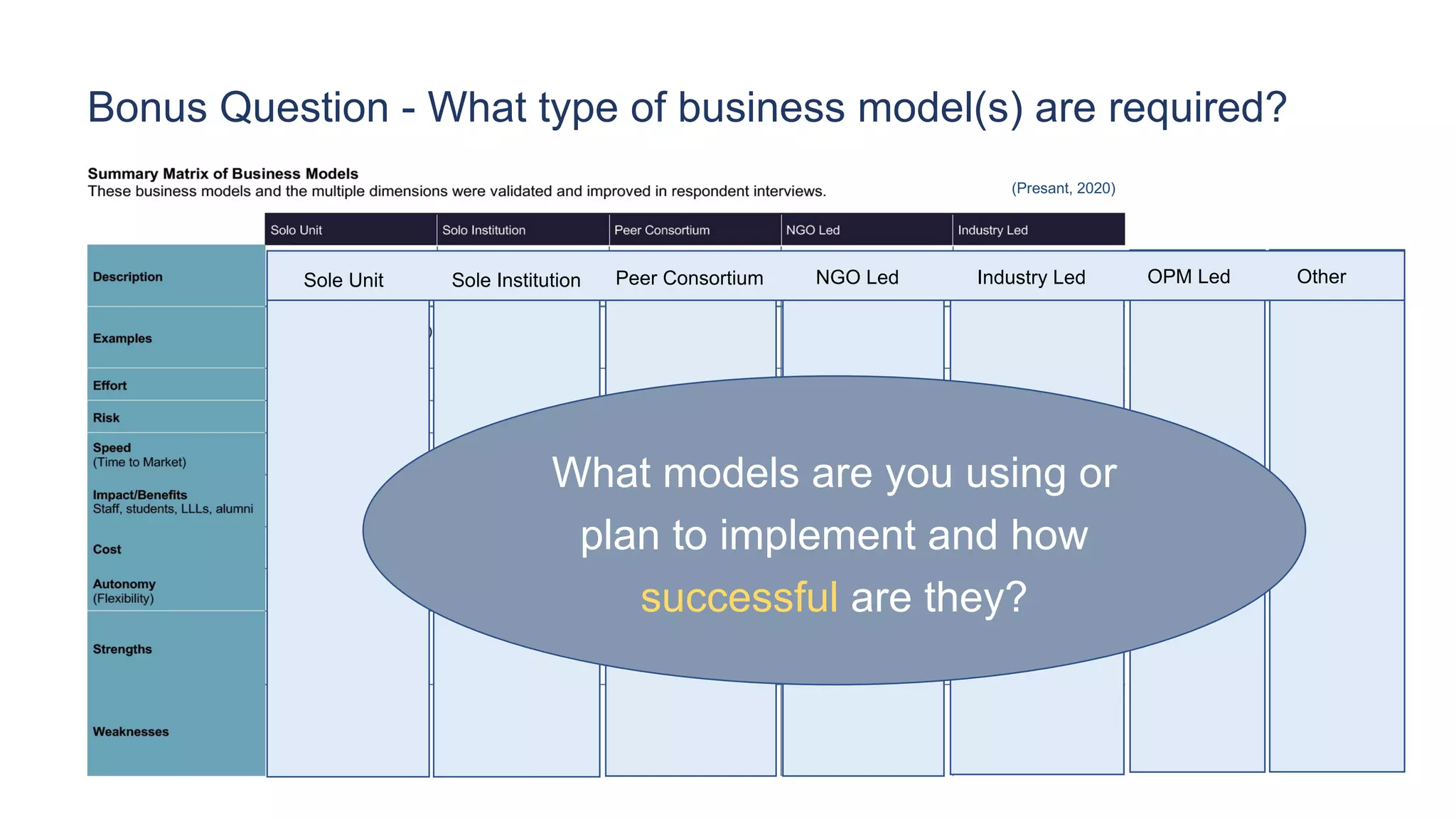
3. What type of internal structures are needed, such as integrating micro-credentials into existing faculty structures or creating a new professional education unit.
The document provides analysis and examples to help institutions determine the best approaches for their context and strategic drivers.