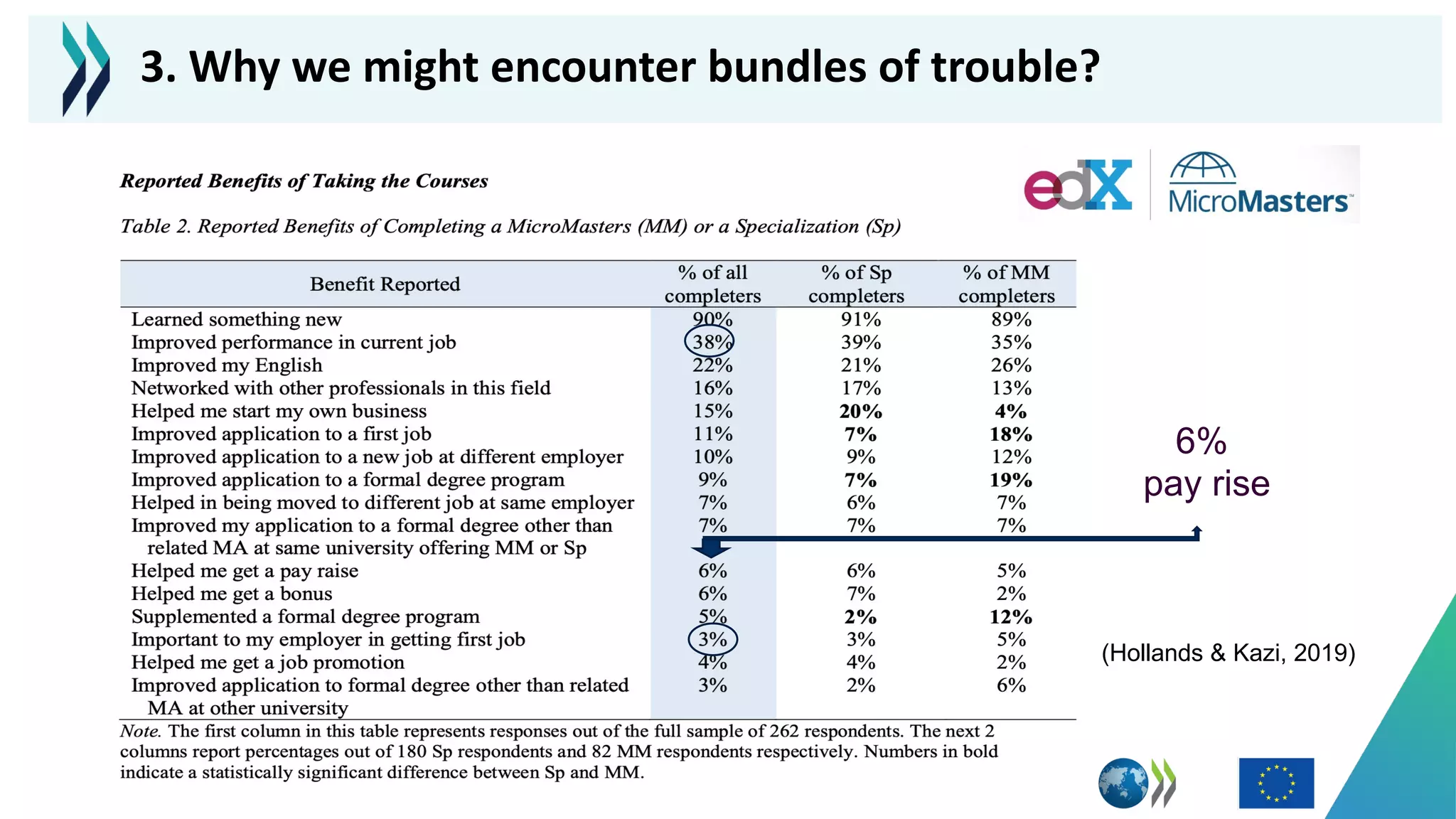
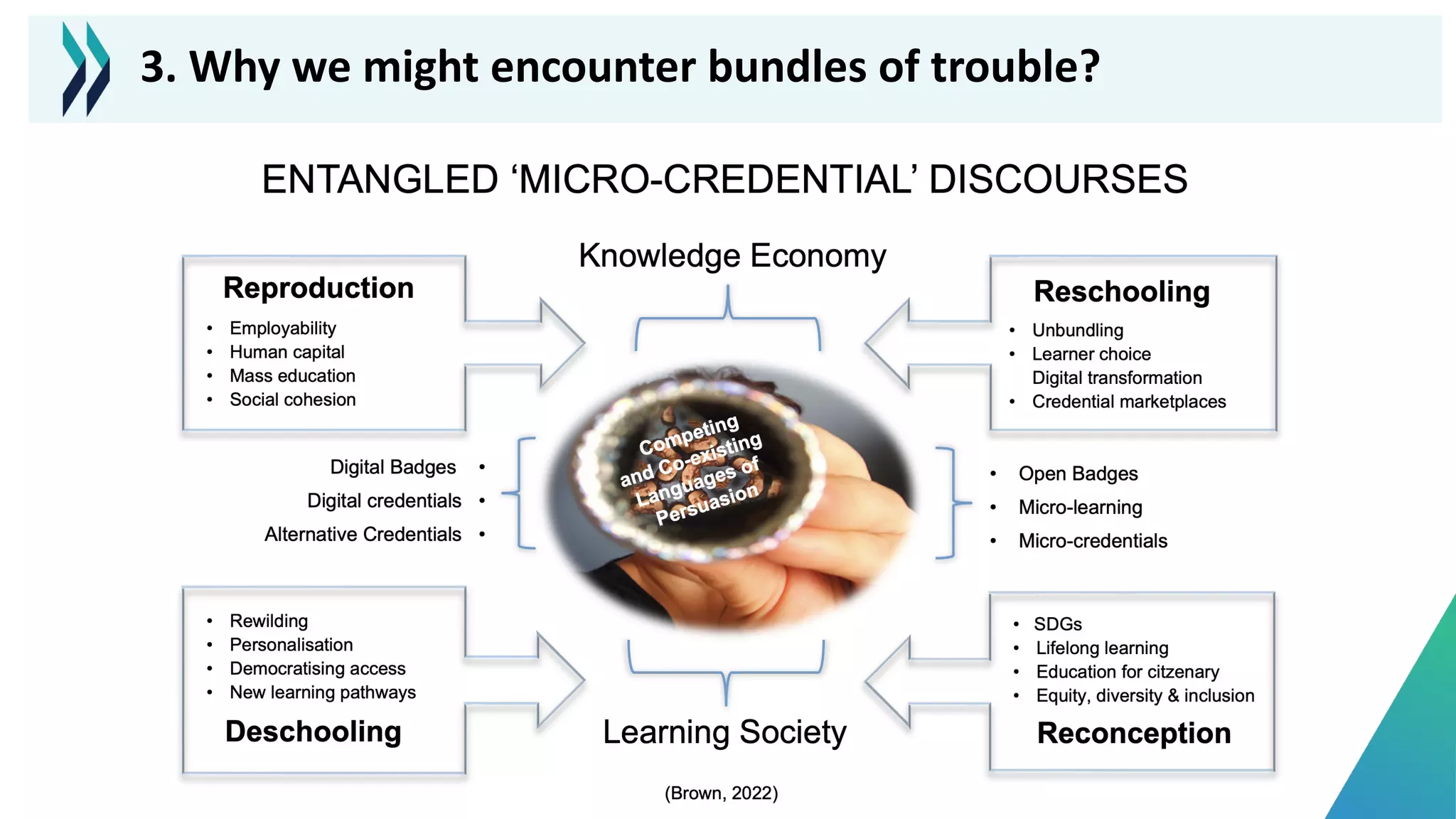
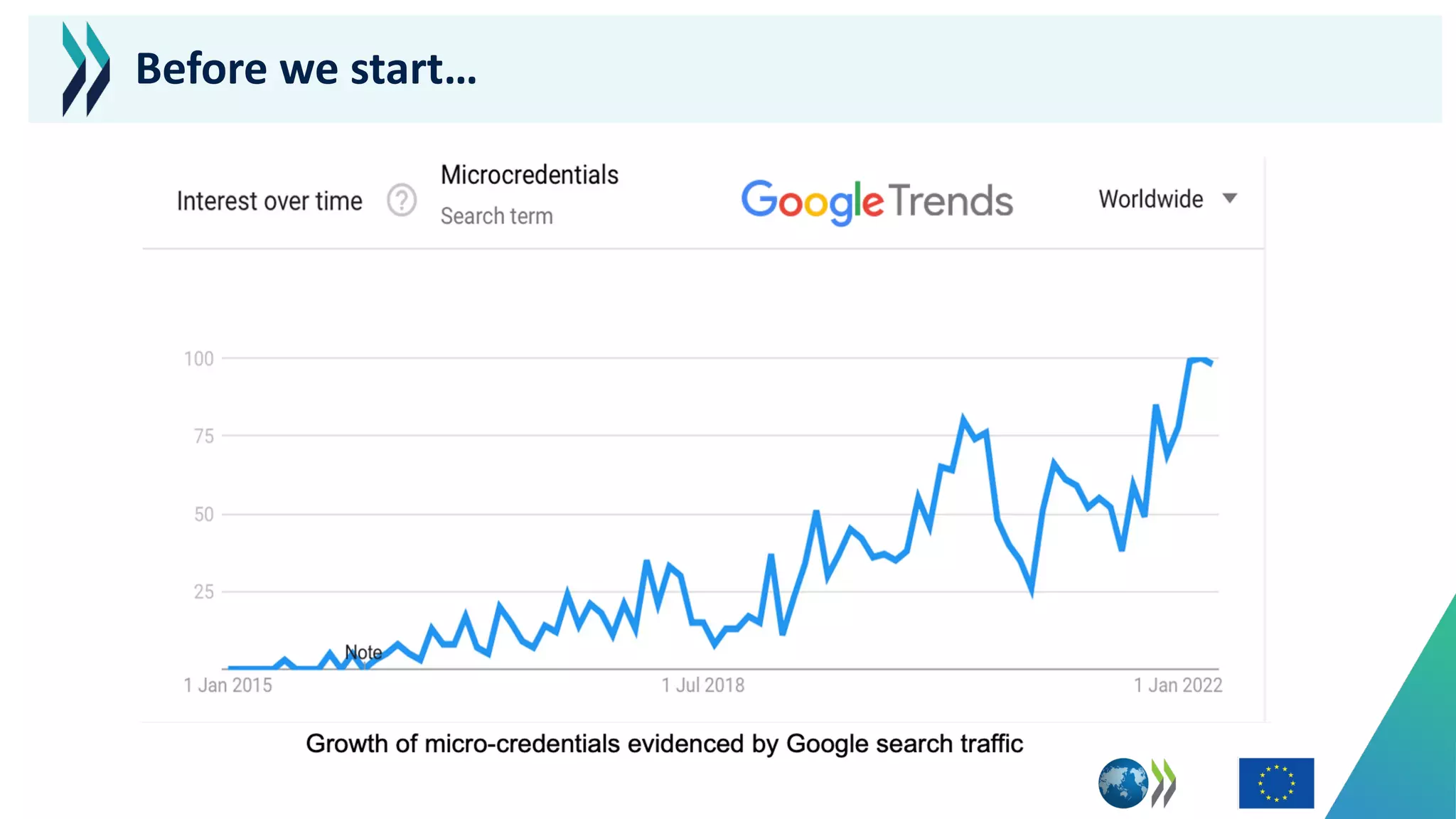
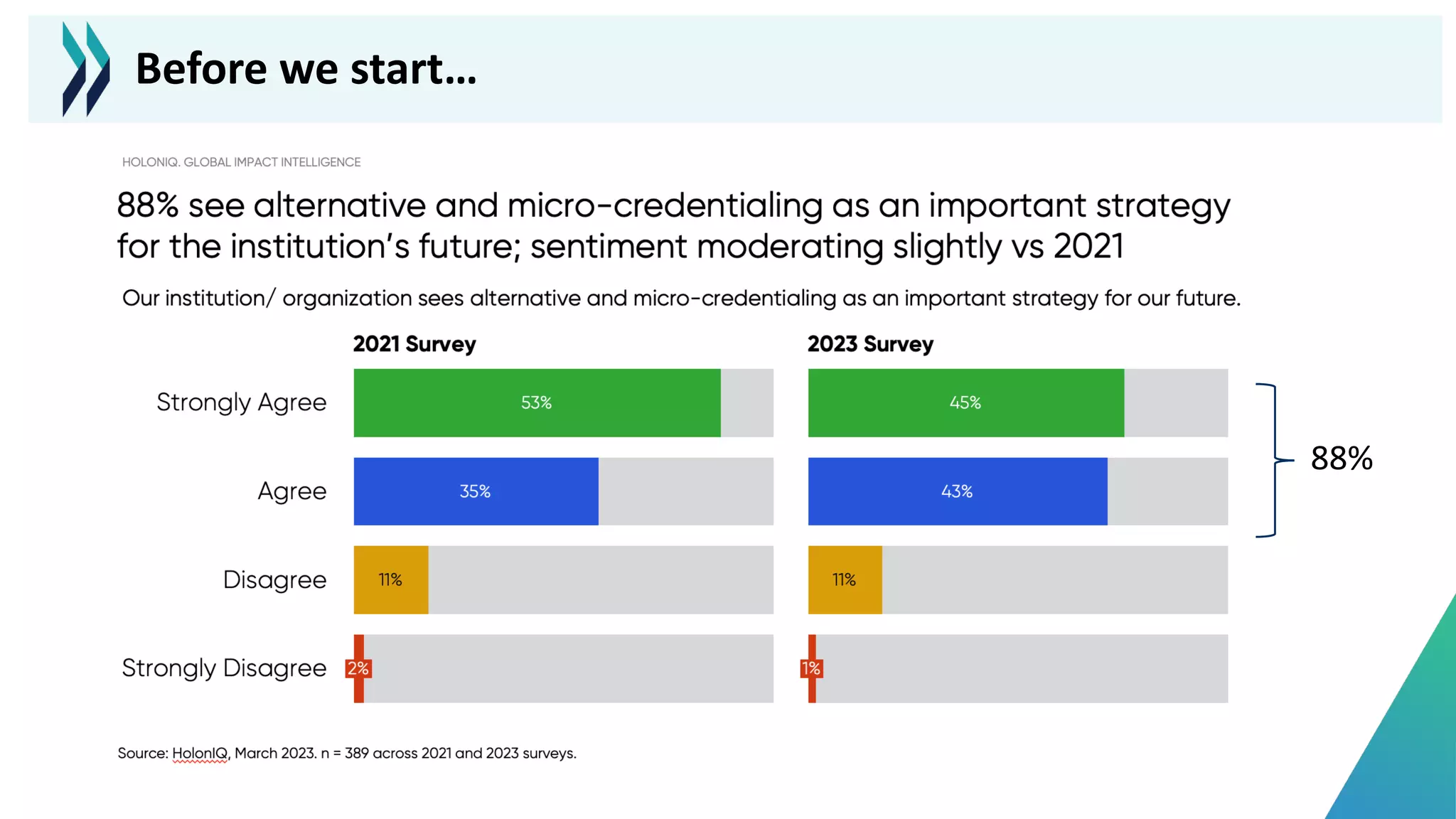
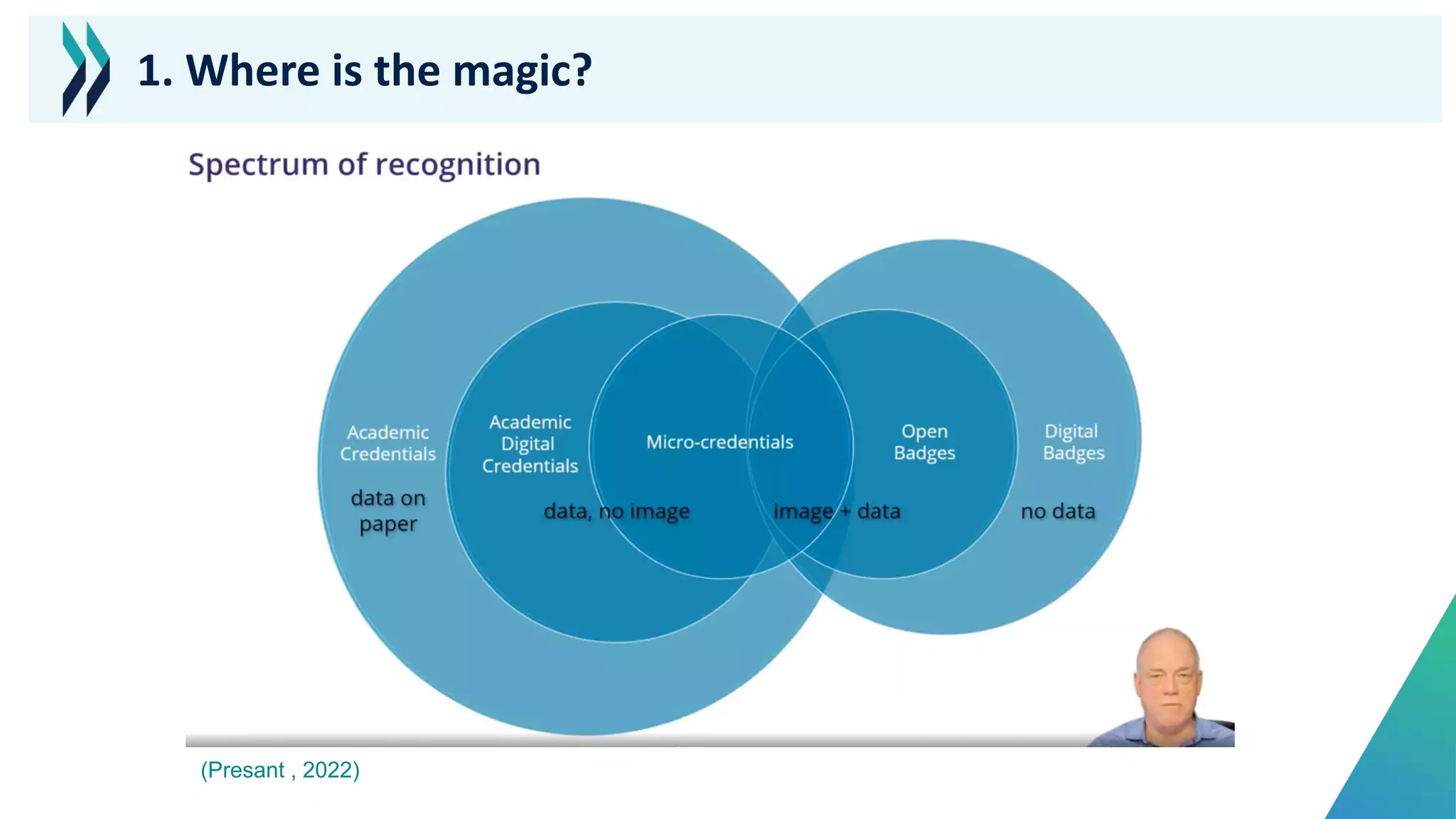
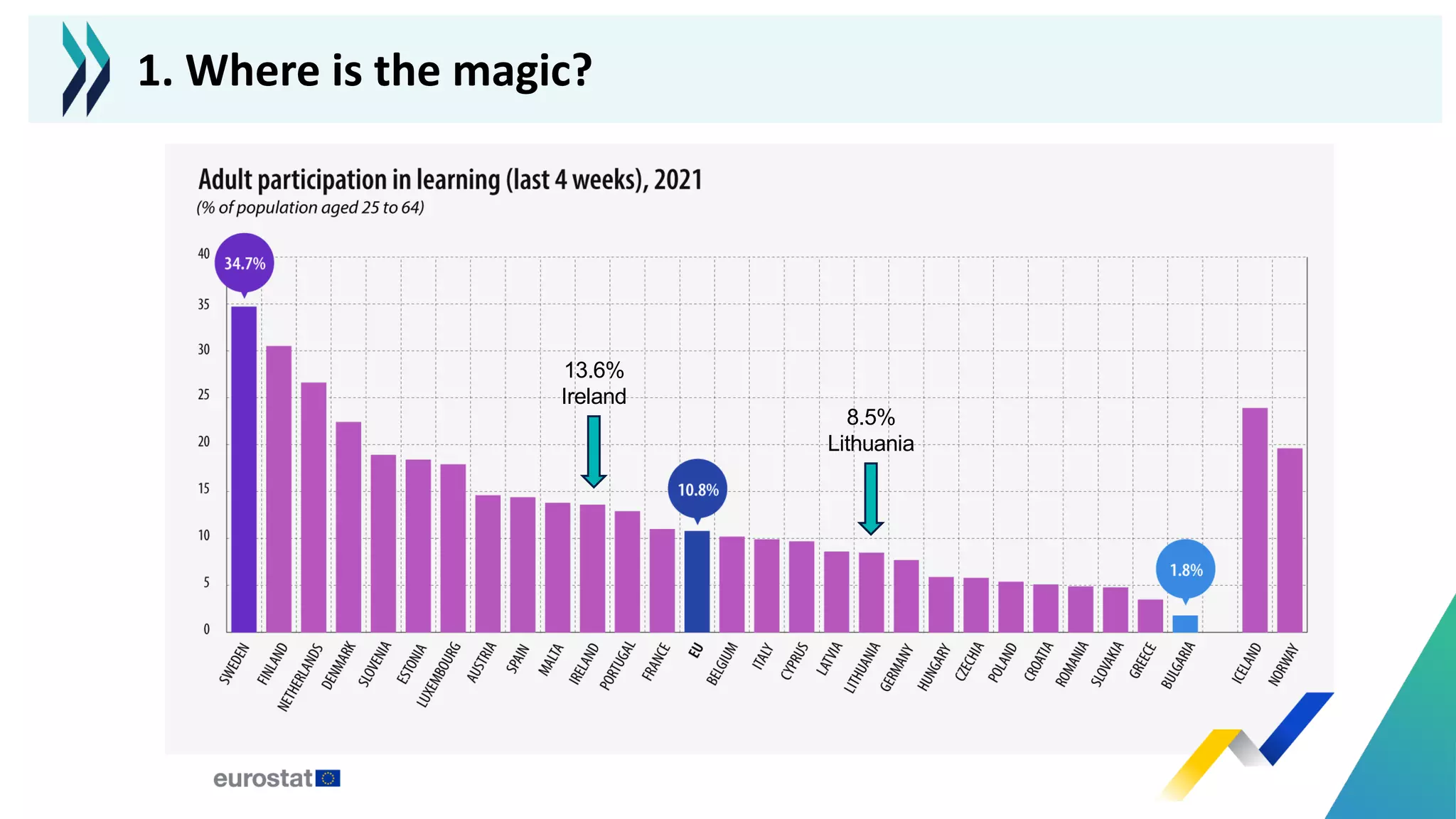
This document discusses micro-credentials and some of the challenges associated with them. It begins by defining micro-credentials and outlining some of their potential benefits. It then examines different strategies for implementing micro-credentials and some of the structural options institutions face. Finally, it looks at potential issues regarding costs, quality assurance, and a lack of data around micro-credentials that could cause problems if not addressed properly. The overall message is that micro-credentials are promising but institutions need to carefully consider challenges around execution and quality.



























![Specific QA issues for online [MCs]
Includes
M
icro-credentials
Organisational context
• Business continuity
• Access to IT infrastructure
• Learners outside of country
Programme context
• Online teaching experience
• Training and professional development
• Synchronous vs asynchronous delivery
Learner context
• Learner readiness
• Access to online resources
• Equivalency of learning support
3. Why we might encounter bundles of trouble?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-230523074621-dc207dea/75/The-Magic-of-Micro-credentials-Digital-Transformation-or-Bundles-of-Trouble-45-2048.jpg)