Interaction design is a complex, multidisciplinary field that draws from areas like psychology, anthropology, information architecture, and human-computer interaction. The goal of interaction designers is to create meaningful relationships between people and the products/services they use.
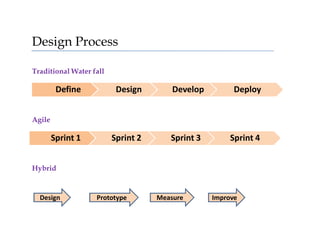
The interaction design process can follow traditional waterfall or agile models. It involves defining problems through observation and research, then ideating, prototyping, and designing solutions. Core principles of interaction design are consistency, perceivability, learnability, predictability, and feedback.
When building interfaces, designers should understand the context, audience, and users' behaviors and goals. The interface should be simple, consistent, and designed in a way that doesn't require extra thought