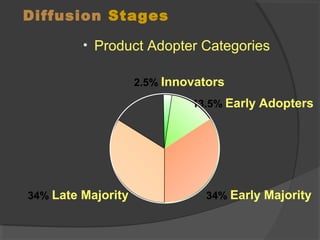
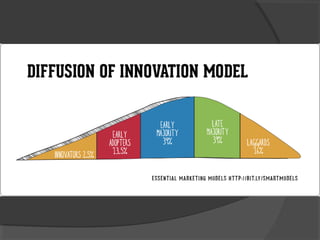
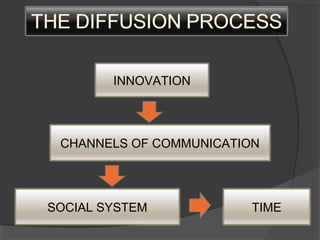
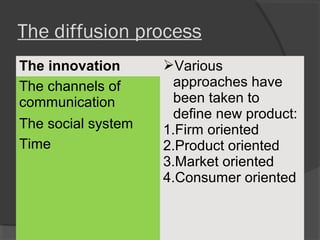
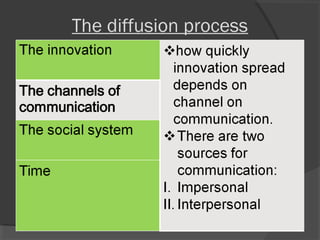
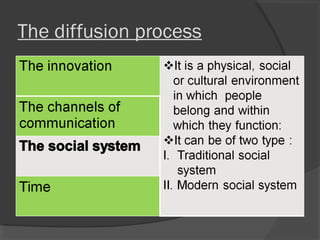
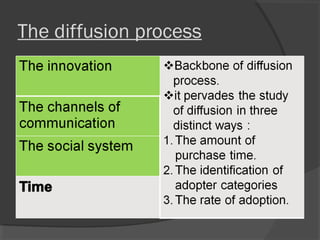
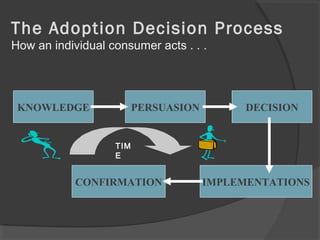
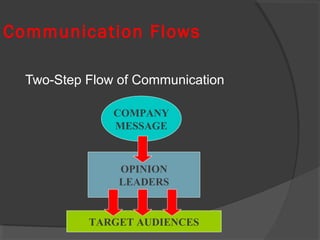
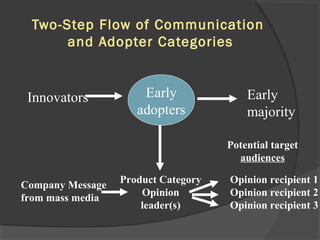
The document discusses diffusion of innovations theory, which seeks to explain how new ideas and practices are adopted over time. It involves two processes: diffusion, which is the spread of an innovation from its source to consumers, and adoption, which refers to a consumer's decision to accept or reject an innovation. Key aspects of diffusion include the innovation itself, communication channels, the social system, and the passage of time. Adoption depends on factors like an innovation's relative advantage, compatibility, trialability, observability, and complexity. The document also examines characteristics of innovators, early adopters, and other categories of adopters.