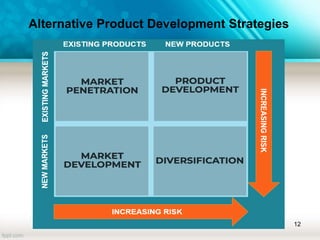
Product planning is the ongoing process of identifying market requirements and defining a product's feature set. There are 7 phases to new product planning: idea generation, screening ideas, concept testing, business analysis, product development, test marketing, and commercialization. There are 4 alternative product development strategies: market penetration, market development, product development, and diversification. Cannibalization refers to a reduction in sales as a result of introducing a new product.