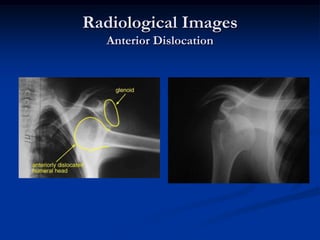
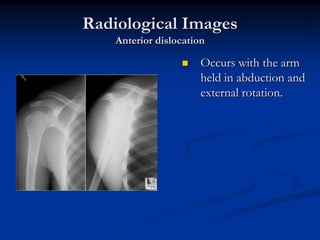
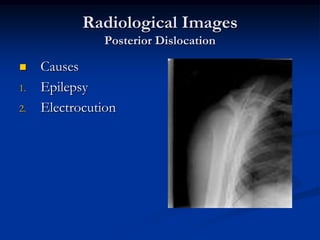
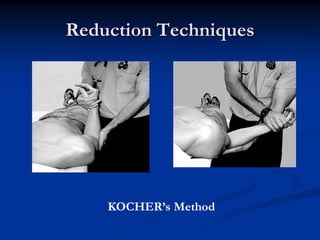
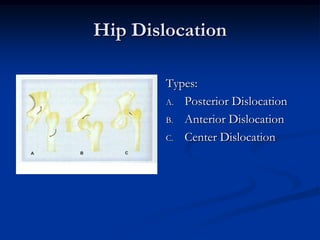
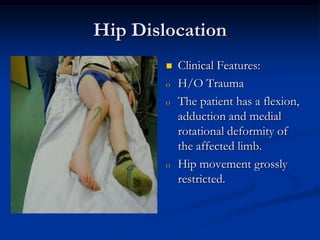
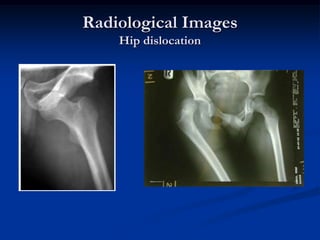
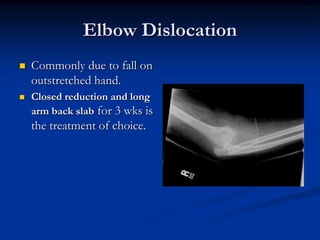
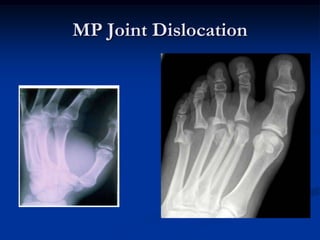
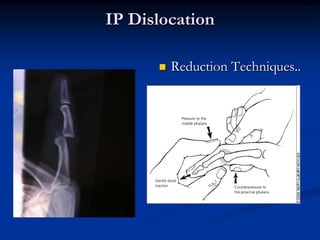
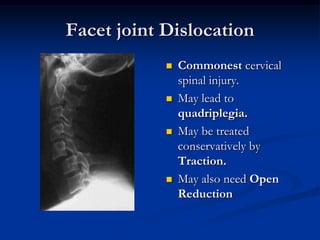
Dislocation occurs when a joint is displaced and the supporting ligaments and joint capsule are disrupted. There are different types including congenital, acquired, traumatic, and pathological dislocations. The most common joints that dislocate are the shoulder, hip, elbow, fingers, and cervical facet joints. Investigations include x-rays from different angles and sometimes CT scans. Management involves reducing acute dislocations promptly through closed reduction under anesthesia if possible to avoid complications like nerve damage, recurrent dislocations, and arthritis. Different techniques are used for reducing specific joints like the shoulder, hip, and fingers. Immobilization after reduction helps prevent recurrence.