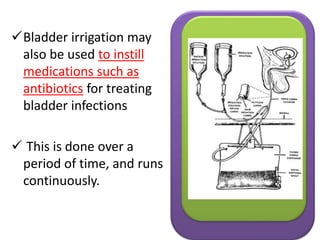
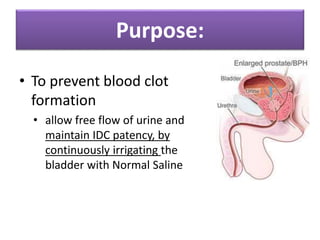
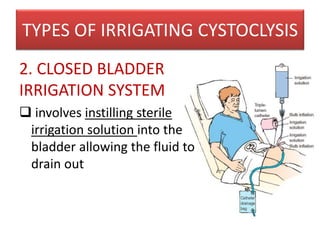
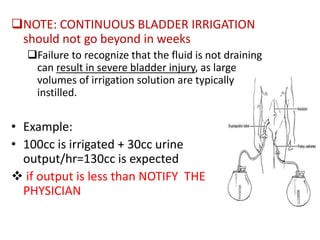
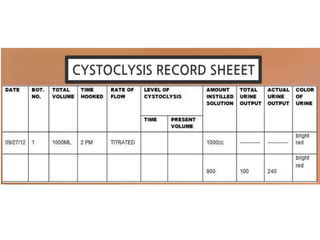
This document discusses cystoclysis, or bladder irrigation, which involves flushing the bladder with normal saline to prevent or treat clot formation. It can also be used to instill medications like antibiotics. There are two types of irrigation systems - open and closed. Nursing responsibilities include monitoring urine output and color, ensuring patient comfort, and documenting care provided to minimize risks like infection.