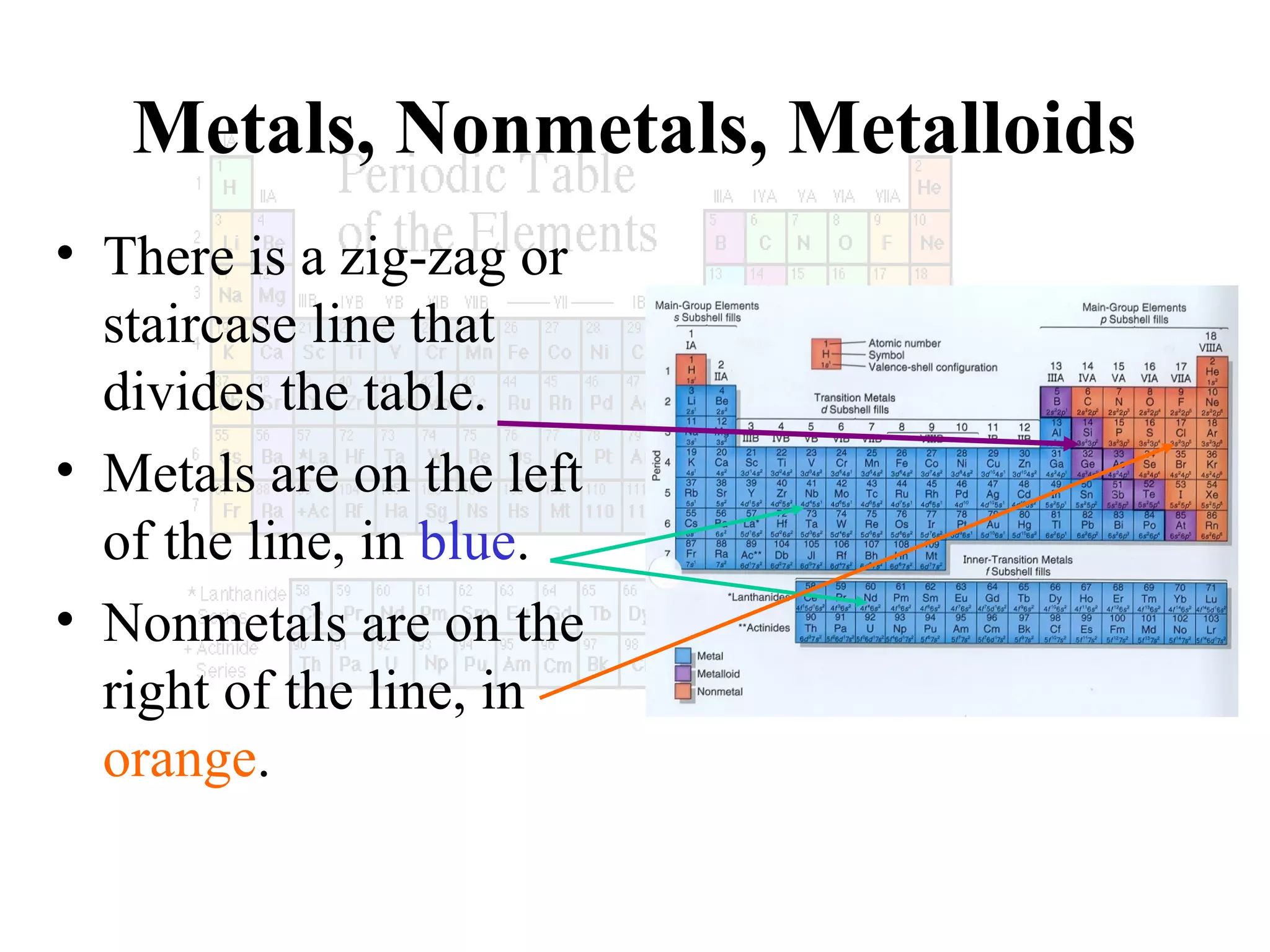
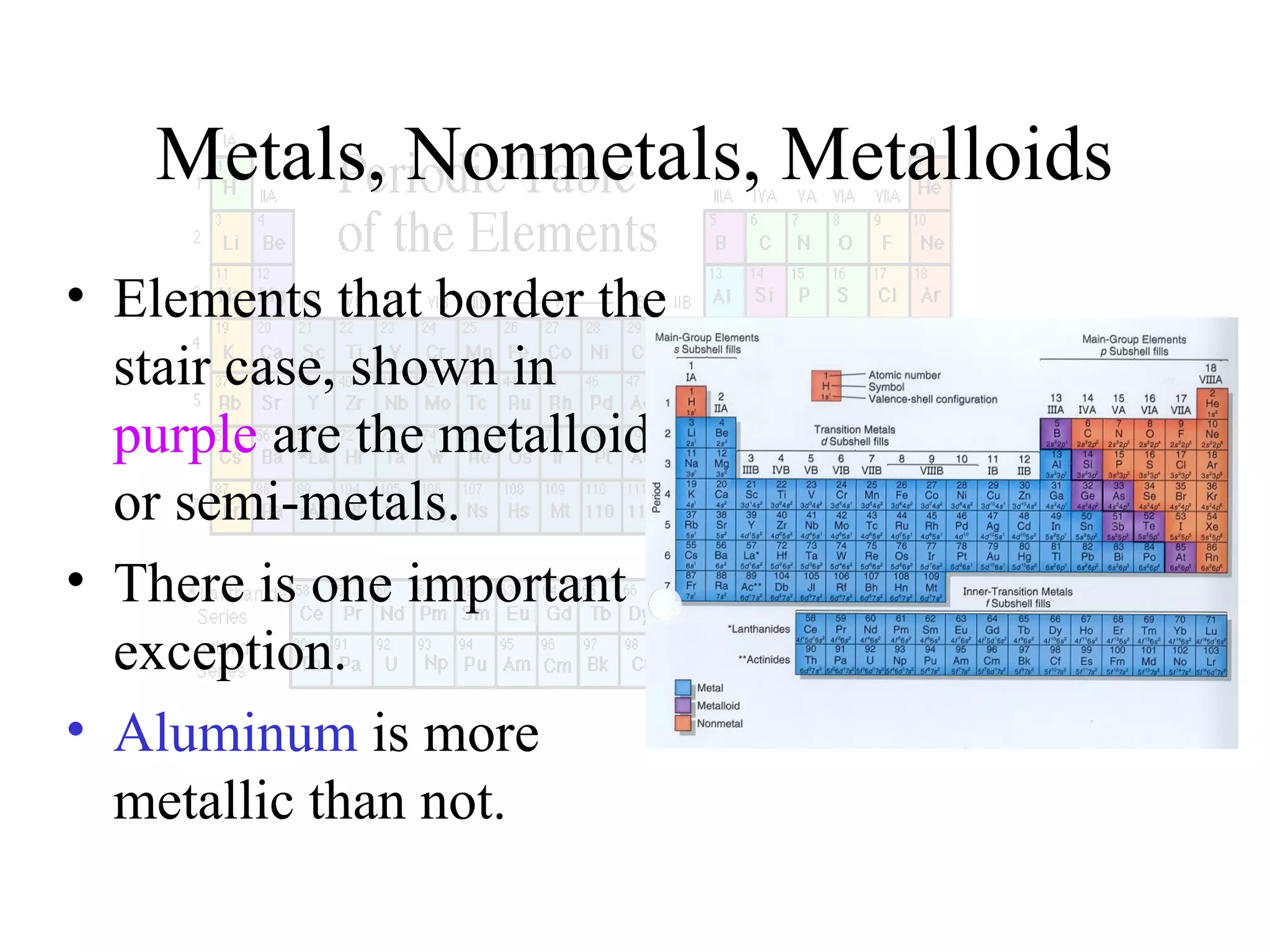
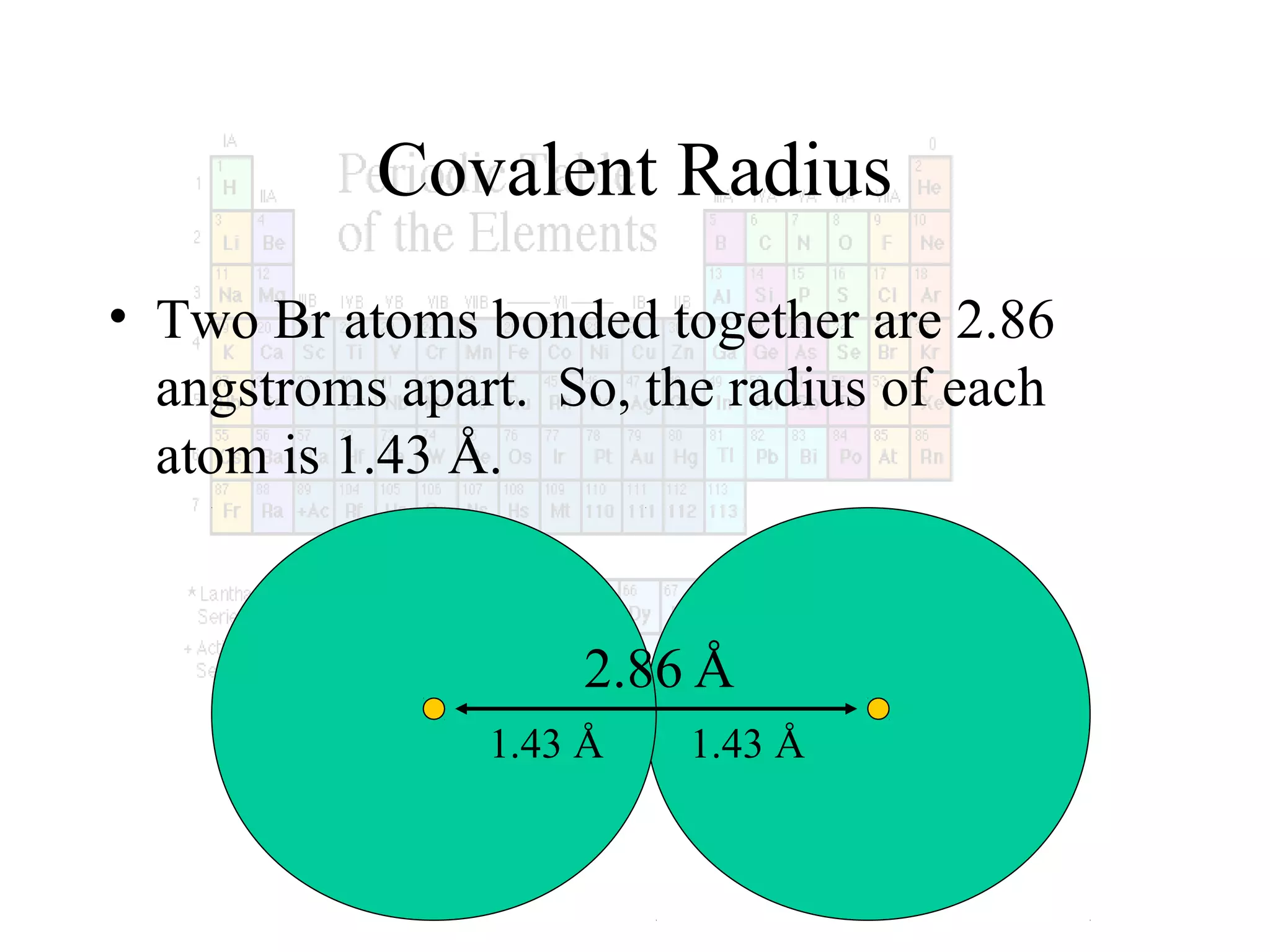
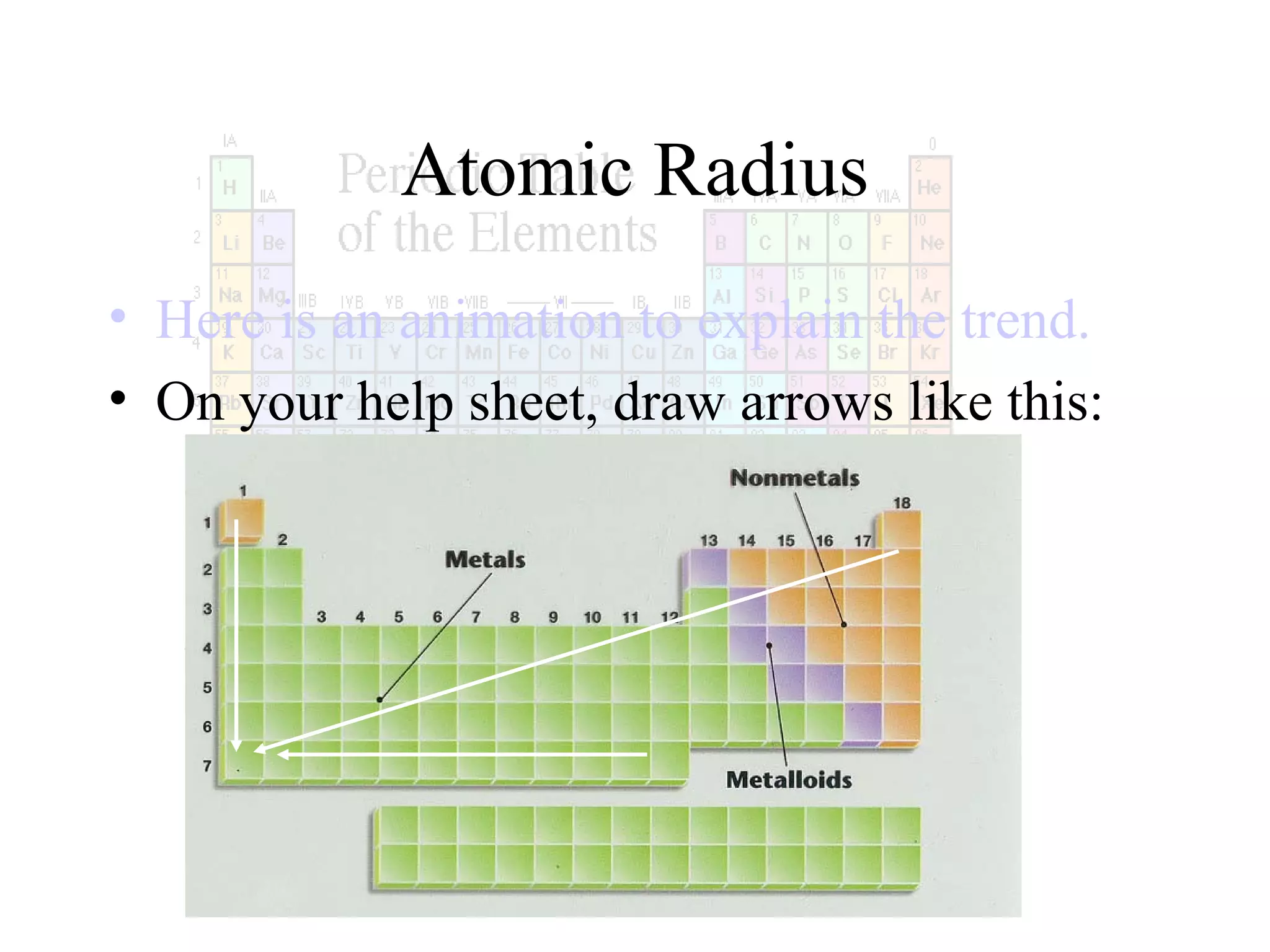
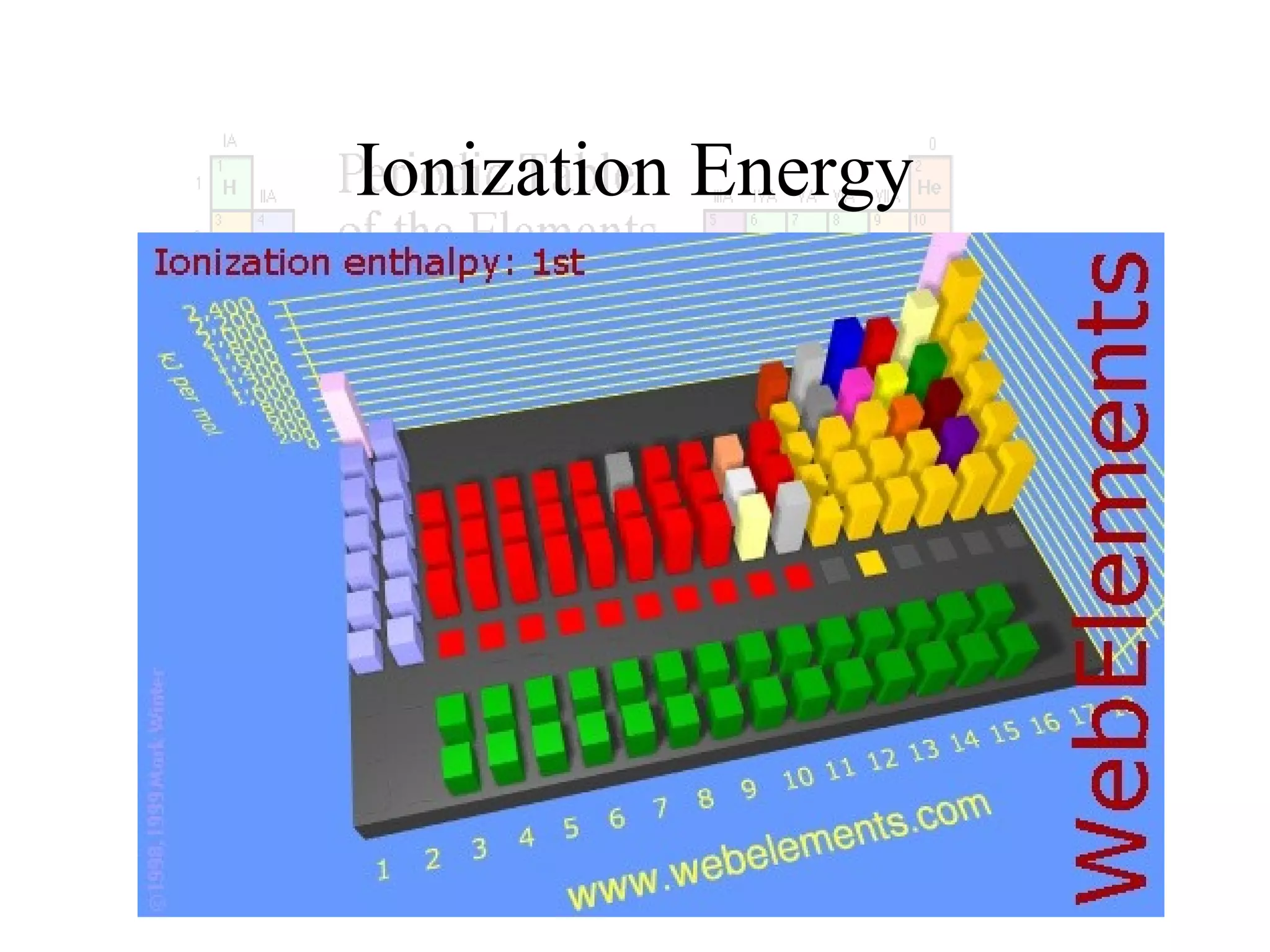
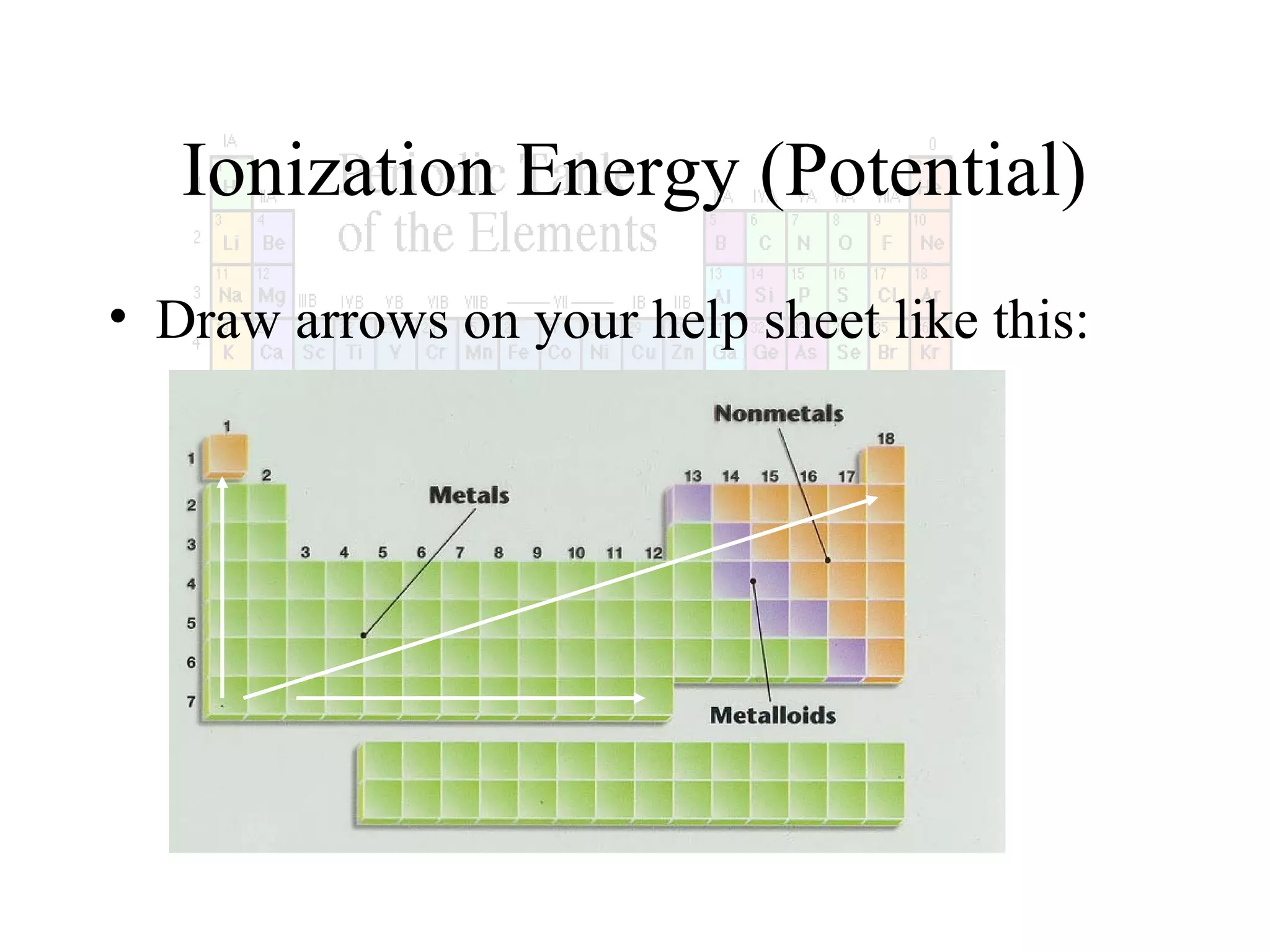
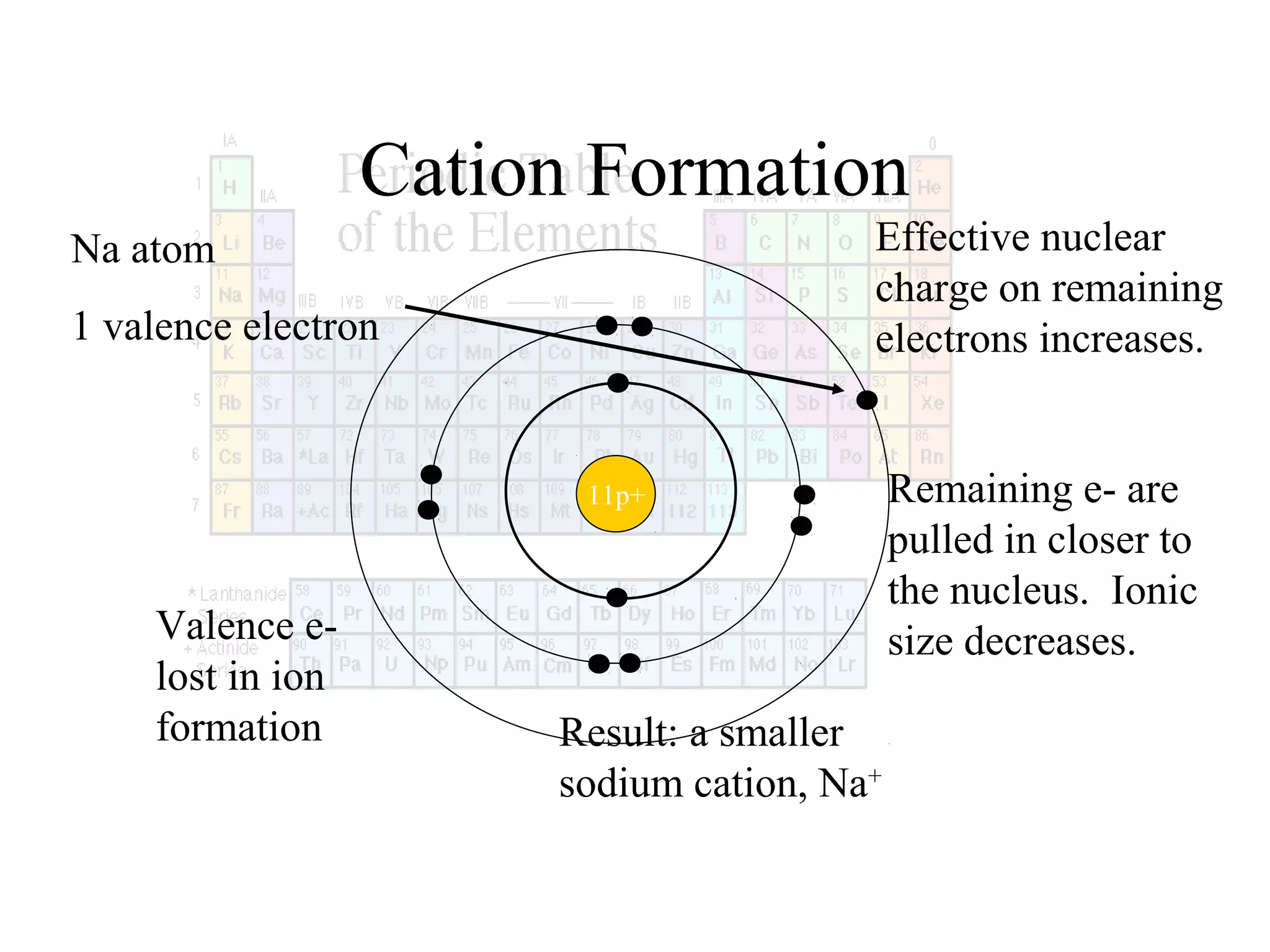
This document provides information about the periodic table and periodic trends. It discusses the organization of the periodic table into rows (periods) and columns (groups/families) and explains how elements in the same group have similar properties based on their electron configuration. Periodic trends are covered, including how atomic radius decreases across a period as effective nuclear charge increases, and how ionization energy and electron affinity vary periodically. Metals, nonmetals, and metalloids are defined based on their characteristic properties.