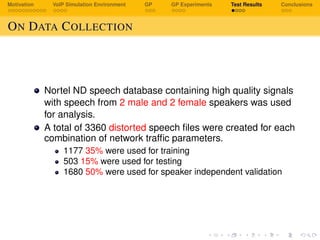
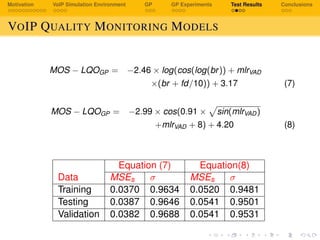
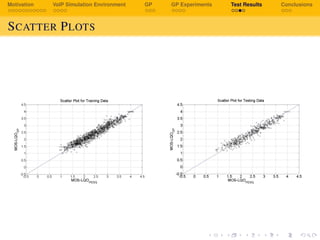
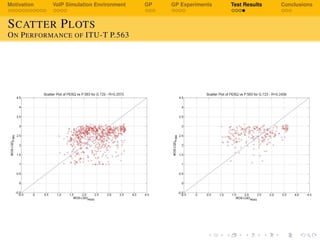
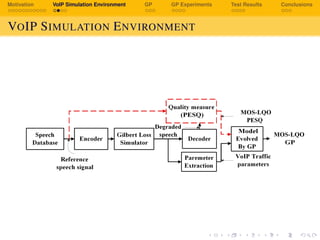
The document discusses using genetic programming to develop a non-intrusive model for evaluating voice over IP (VoIP) quality based on transport layer network metrics. It first provides background on VoIP and challenges with speech quality assessment. It then describes a VoIP simulation environment and genetic programming approach. The goal is to evolve an estimation model for VoIP listening quality as a function of packet loss rate, jitter, bitrate and other transport metrics using genetic programming, and validate it against PESQ (Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality) scores.























![Motivation VoIP Simulation Environment GP GP Experiments Test Results Conclusions
NETWORK TRAFFIC SCENARIOS
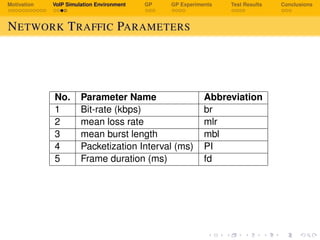
No. Parameter Range
1 br G.729 (8 kbps), G.723.1 (6.3 kbps),
AMR 7.4 and 12.2 kbps
2 mlr [0,2.5,3.5,. . . 15,20,25,. . . 40]%
3 mbl 10, 50, 60, 70 and 80%
4 PI 10-60 ms
5 fd 10, 20, 30 ms](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5o0up0byqlmxeoa3mfyl-140619004735-phpapp01/85/Realtime-Non-Intrusive-Evaluation-of-VoIP-Using-Genetic-Programming-29-320.jpg)



![Motivation VoIP Simulation Environment GP GP Experiments Test Results Conclusions
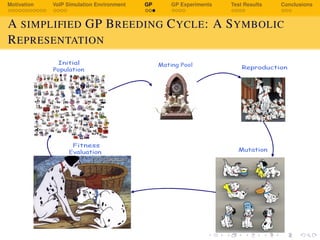
GP EXPERIMENTS
COMMON PARAMETERS
Parameter Value
Initial Population Size 300
Selection LPP Tournament
Tournament Size 2
Genetic Operators Crossover and Subtree Mutation
Initial Operator probabilities 0.5 initial, adaptive onwards
Survival Half Elitism
Function Set +, -, *, /, sin, cos, log2, log10,
loge, sqrt, power,
Terminal Set Random numbers [0.0 . . . 1.0]
Integers [2 . . . 10]. mlrVAD,
mblVAD, PI, br, fd](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5o0up0byqlmxeoa3mfyl-140619004735-phpapp01/85/Realtime-Non-Intrusive-Evaluation-of-VoIP-Using-Genetic-Programming-34-320.jpg)