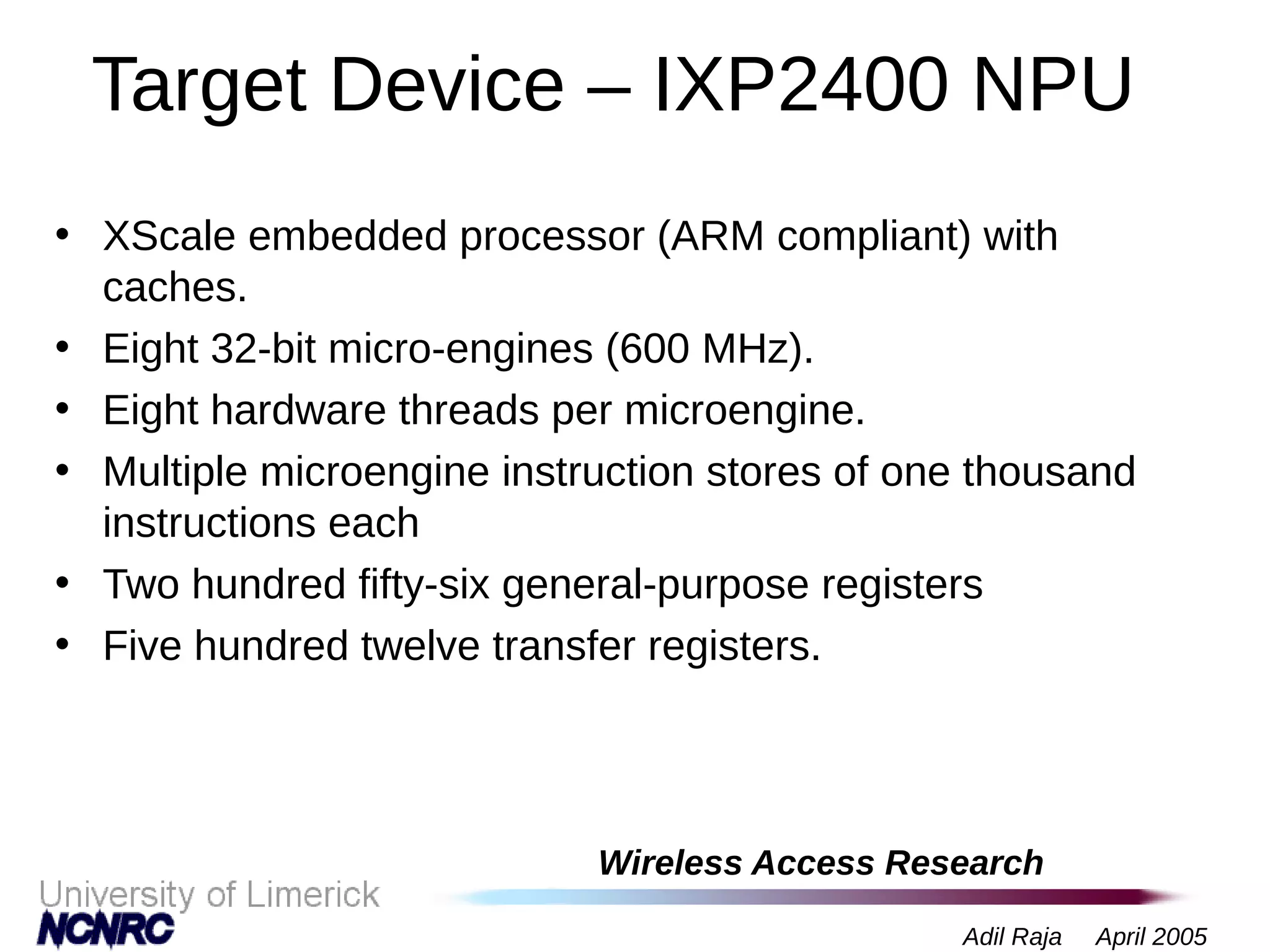
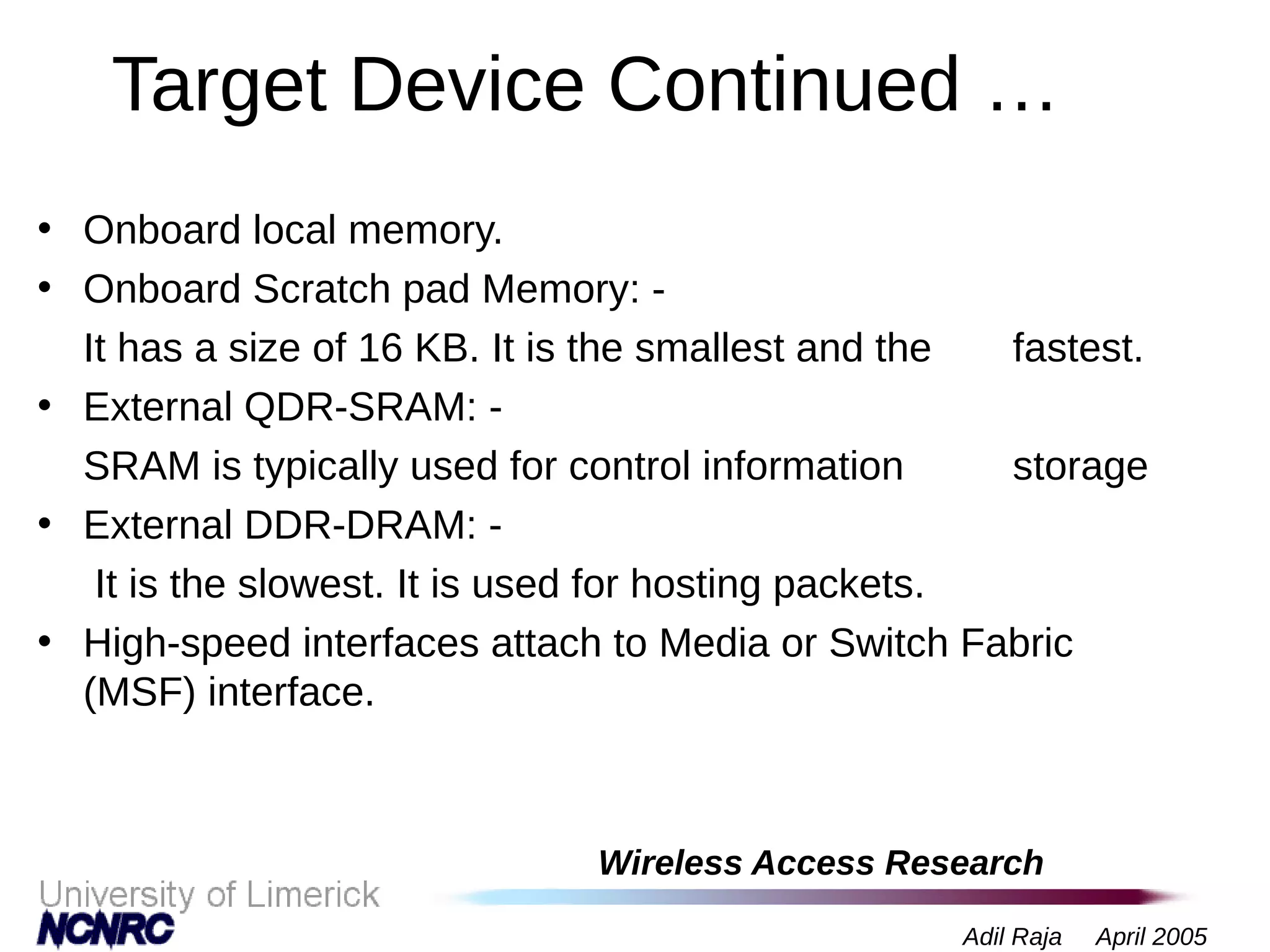
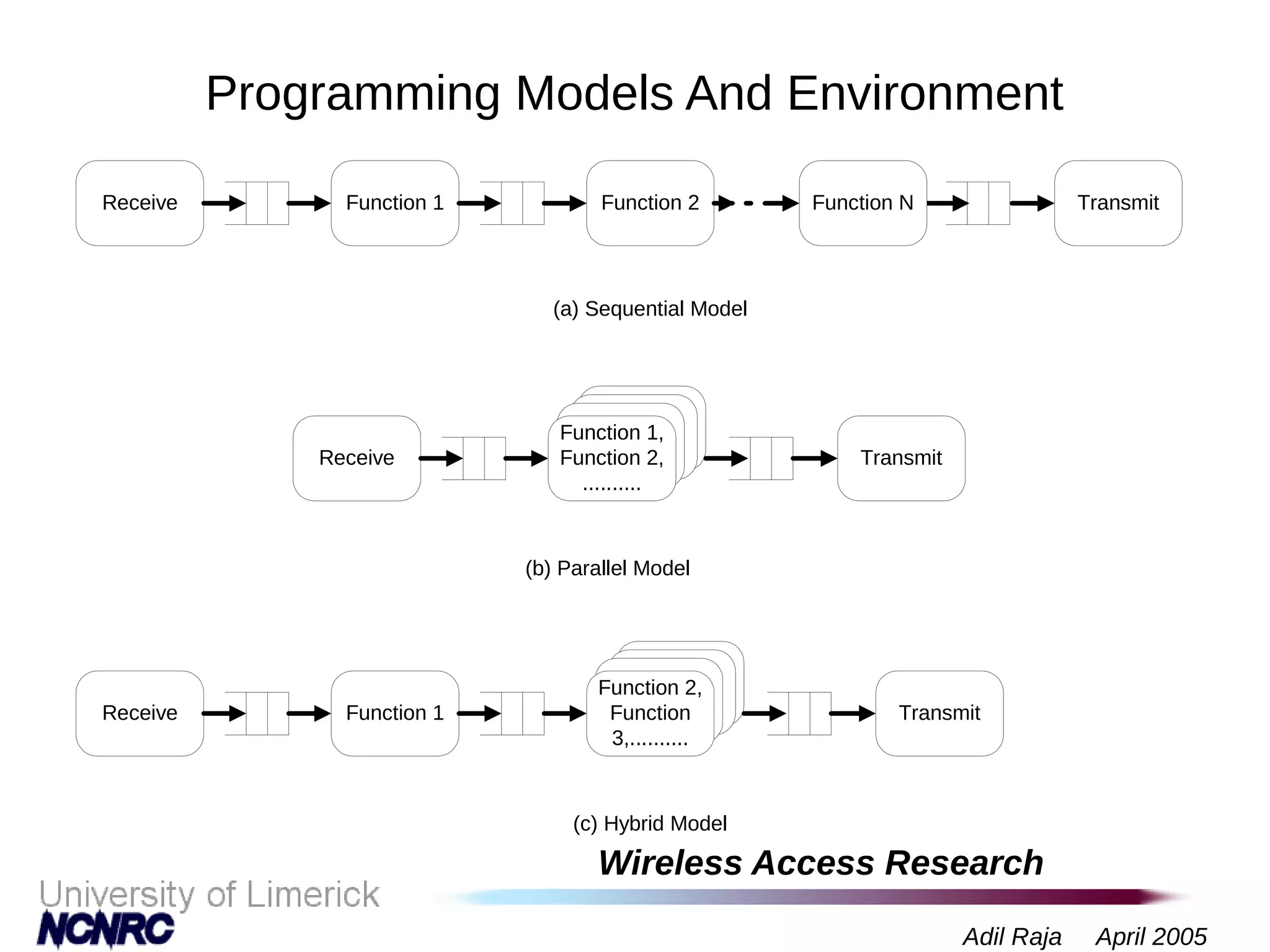
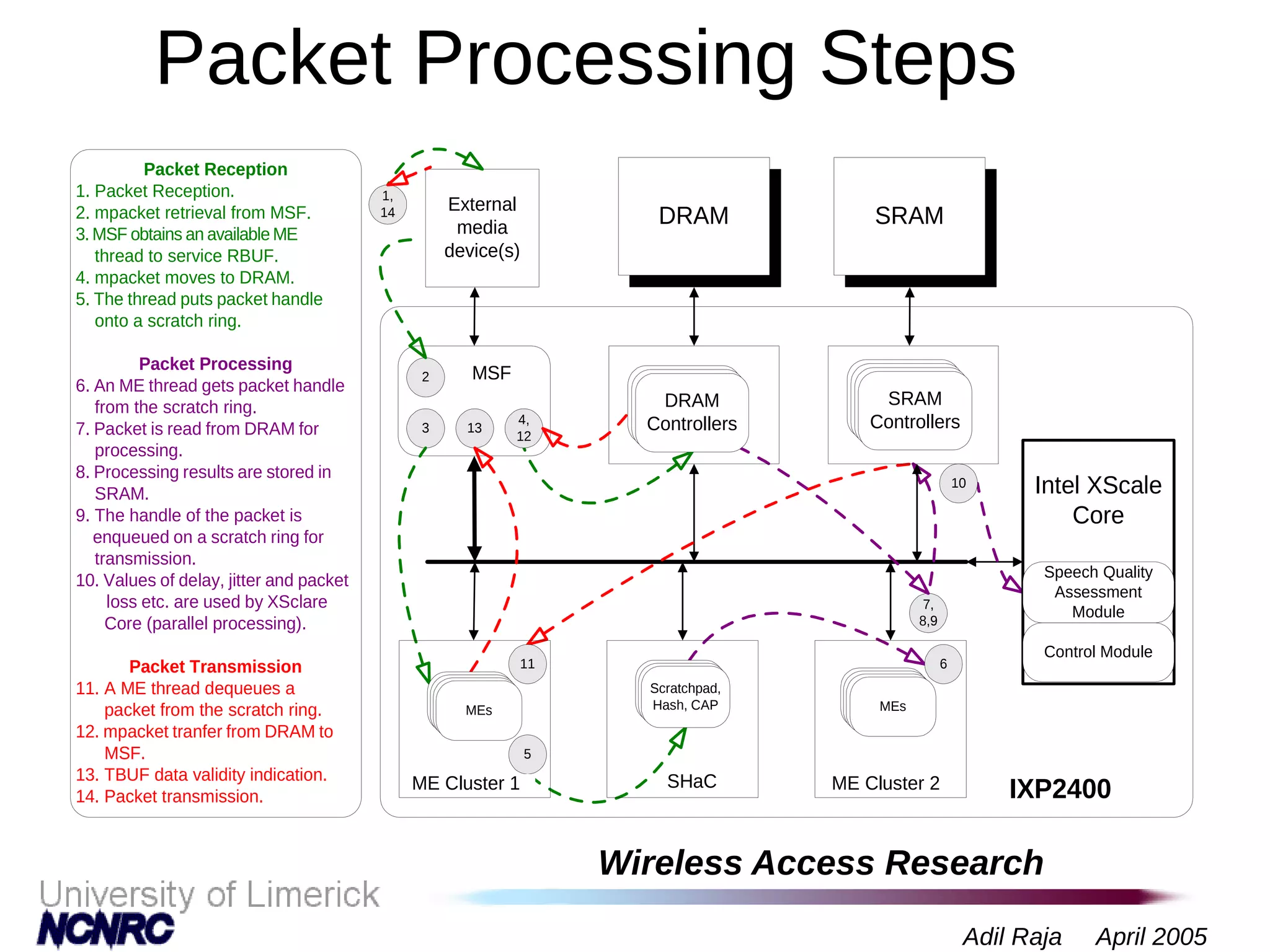
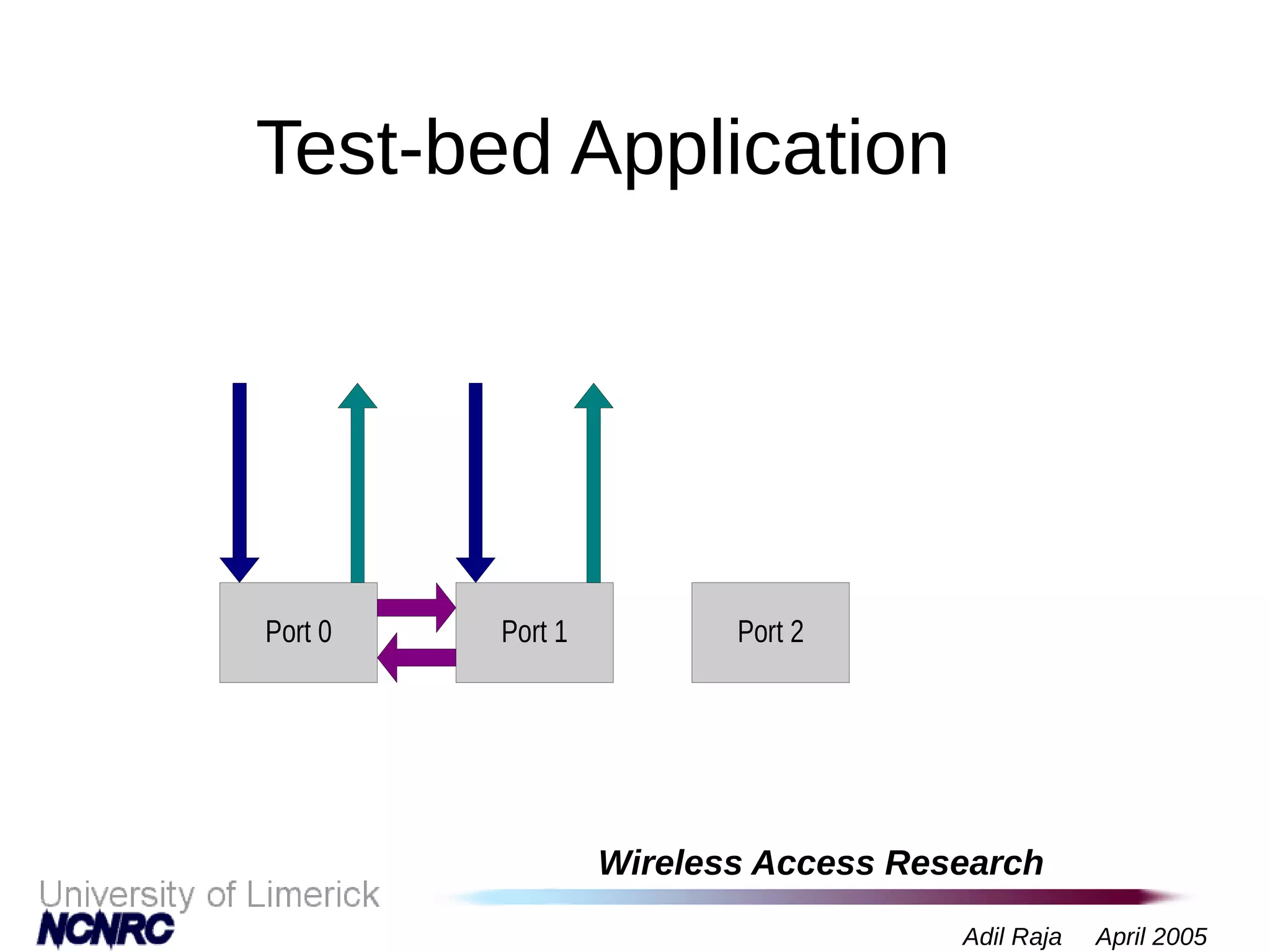
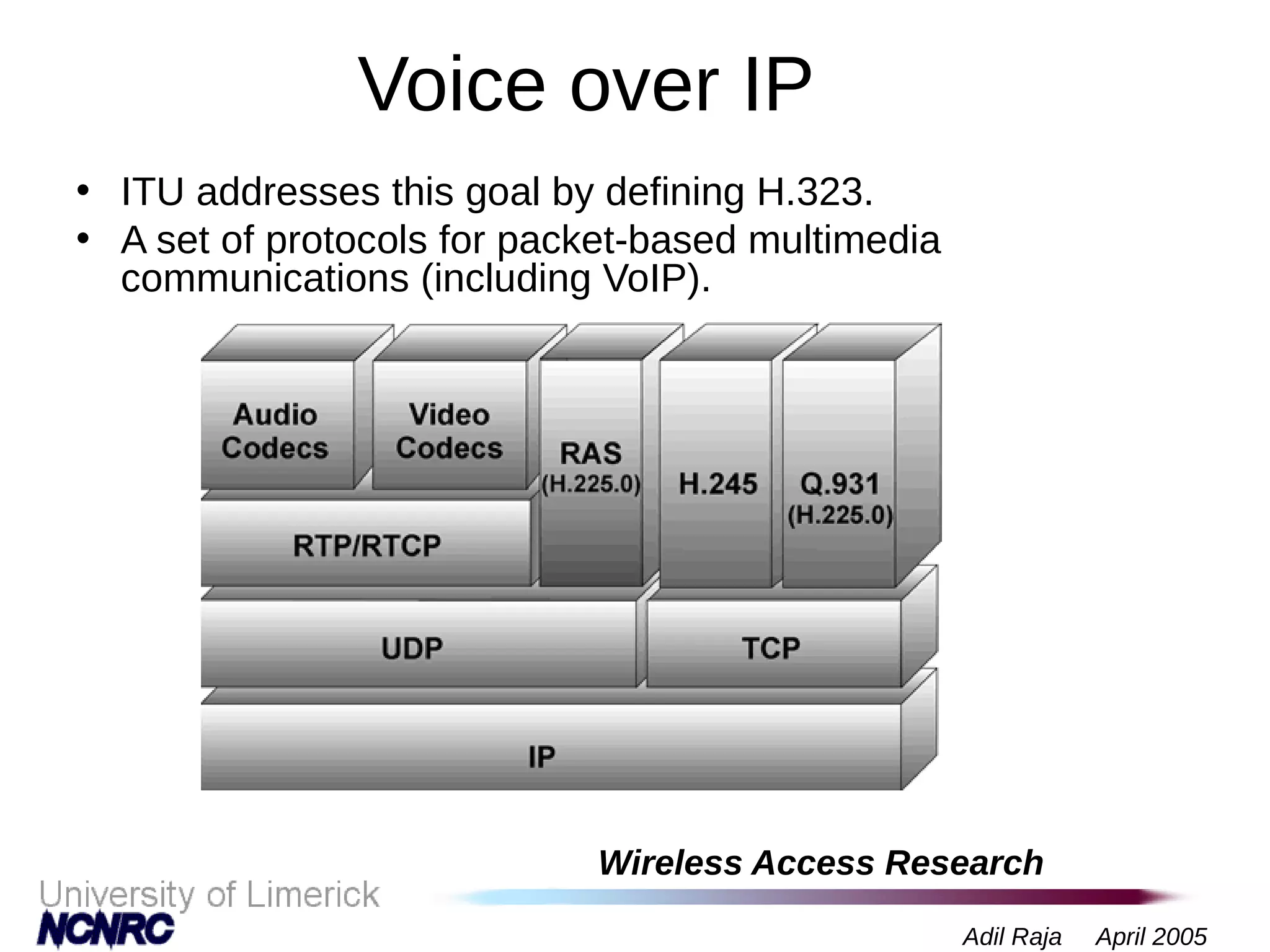
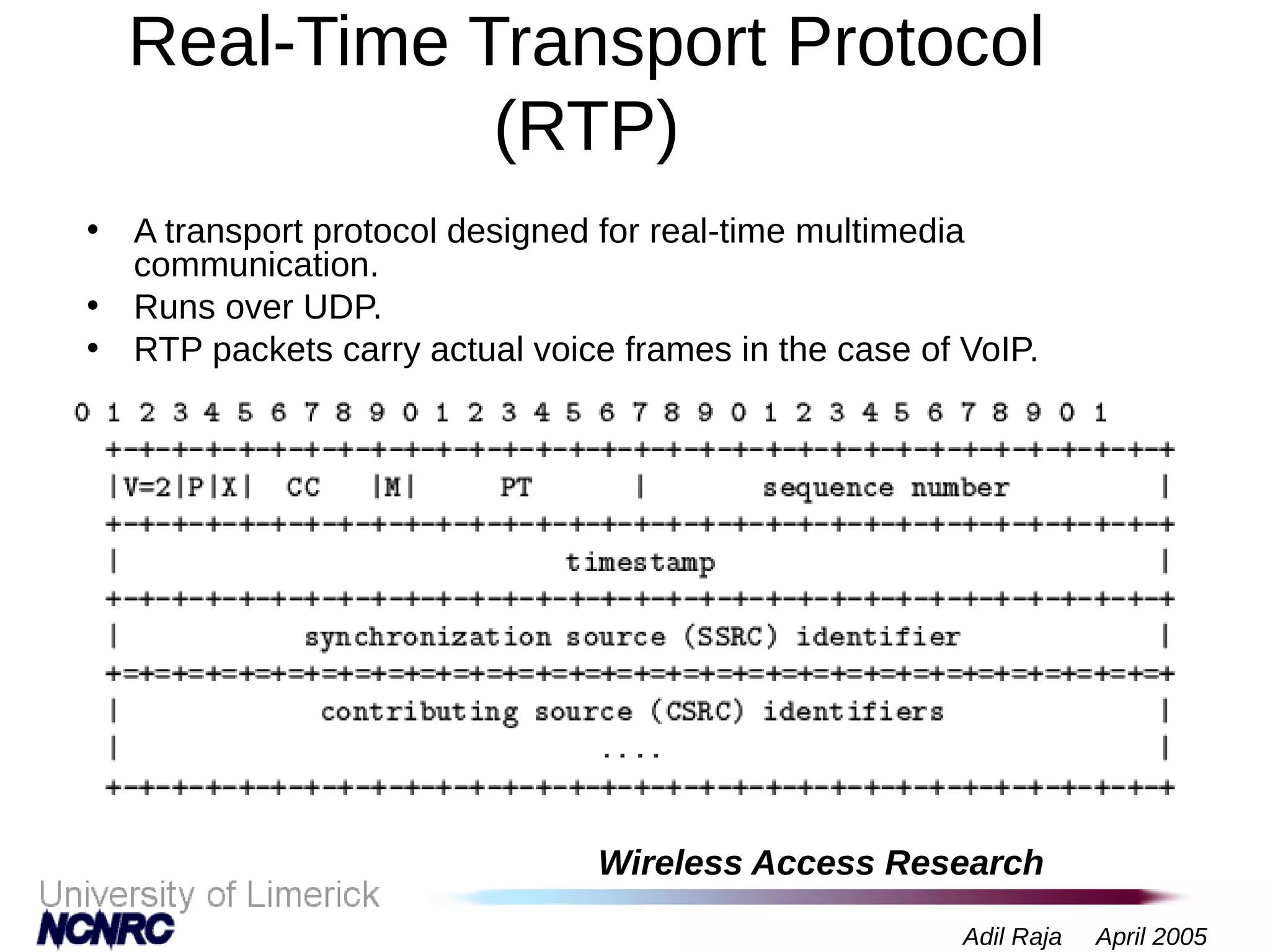
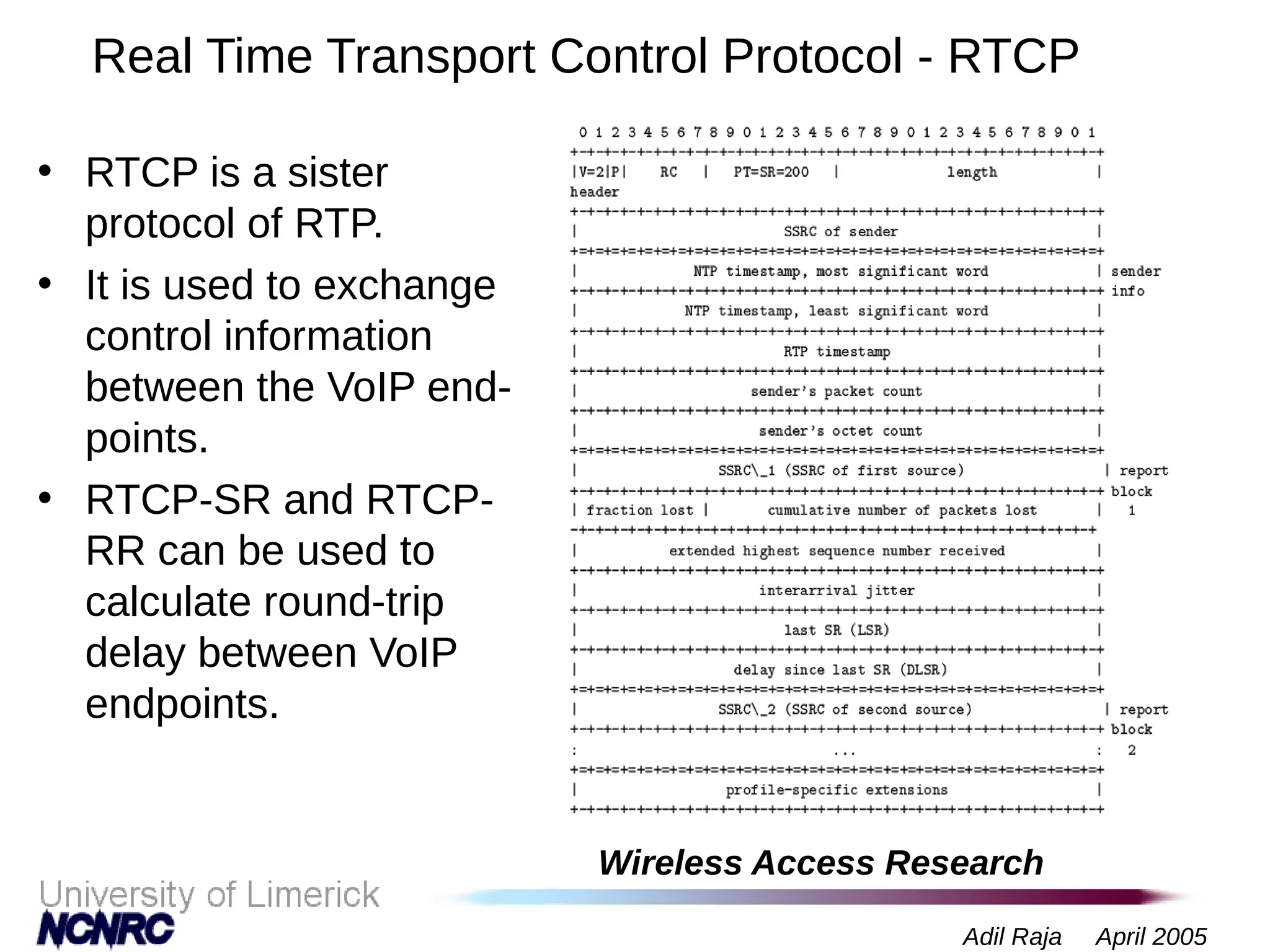
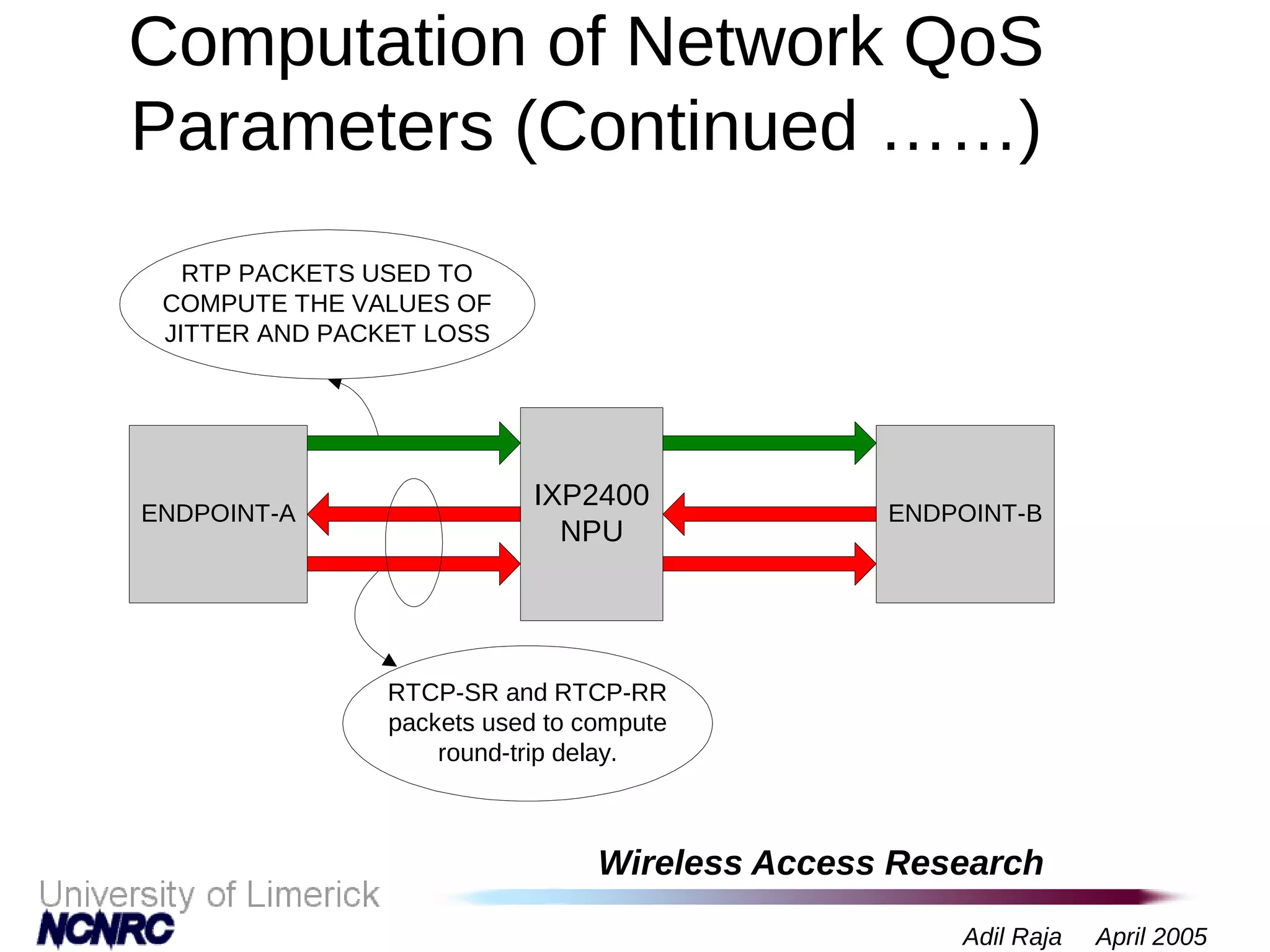
The document presents a research on a non-intrusive speech quality assessment tool for VoIP communications, highlighting the need for objective quality testing over subjective methods. It discusses the implementation of various features such as packet loss, jitter, and round-trip delay metrics computed on the IXP2400 network processor, focusing on speech processing methodologies. The results indicate successful computation of packet loss and jitter, although challenges with RTCP implementation for round-trip delay calculations are noted.