Vsepr theory
- 2. Vsepr theory says that bonded atoms in aVsepr theory says that bonded atoms in a molecule adopt that particular arrangement inmolecule adopt that particular arrangement in space around the central atom which keepsspace around the central atom which keeps them as far apart as possible.them as far apart as possible. The premise of VSEPR is that the valenceThe premise of VSEPR is that the valence electron pairs surrounding an atom tend toelectron pairs surrounding an atom tend to repel each other and will, therefore, adopt anrepel each other and will, therefore, adopt an arrangement that minimizes this repulsion, thusarrangement that minimizes this repulsion, thus determining the molecule's geometry.determining the molecule's geometry. The state will have minimum repulsions andThe state will have minimum repulsions and thus corresponds to a state of minimumthus corresponds to a state of minimum repulsion, energy and maximum stability.repulsion, energy and maximum stability.
- 3. PostulatesPostulates The shape of a molecule depends upon the number of valence shellThe shape of a molecule depends upon the number of valence shell electron pairs (bonded or non-bonded) around the central atom.electron pairs (bonded or non-bonded) around the central atom. Pairs of electrons in the valence shell tend to repel each other as theirPairs of electrons in the valence shell tend to repel each other as their electron clouds are negatively charged.electron clouds are negatively charged. The electron pairs tend to occupy those positions in space, whichThe electron pairs tend to occupy those positions in space, which minimize repulsions and thus maximize distance from one another.minimize repulsions and thus maximize distance from one another. The valence shell is taken as a sphere with the electron pairsThe valence shell is taken as a sphere with the electron pairs localizing on the spherical surface at maximum distance from onelocalizing on the spherical surface at maximum distance from one another.another. A multiple bond is treated as a single electron pair and the two orA multiple bond is treated as a single electron pair and the two or three electron pairs of a multiple bond are treated as a single superthree electron pairs of a multiple bond are treated as a single super pair.pair. The VSEPR model is applicable to any such structure where two orThe VSEPR model is applicable to any such structure where two or more resonance structures can represent a molecule.more resonance structures can represent a molecule. Decreasing order of repulsive interaction of electron pairs:Decreasing order of repulsive interaction of electron pairs: Lone pair (lp) − Lone pair (lp) > Lone pair (lp) − Bond pair (bp) > BondLone pair (lp) − Lone pair (lp) > Lone pair (lp) − Bond pair (bp) > Bond pair (bp) − Bond pair (bp).pair (bp) − Bond pair (bp). Repulsive forcesRepulsive forces decrease sharply with increasing angle betweendecrease sharply with increasing angle between electron pairs. They areelectron pairs. They are strong at 90˚, weaker at 120˚ and weakest atstrong at 90˚, weaker at 120˚ and weakest at 180180˚.˚.
- 4. Reason for lone pair-loneReason for lone pair-lone pair having the mostpair having the most repulsionrepulsion The orbital of bonded electron pair is under theThe orbital of bonded electron pair is under the influence of two nuclei and most of the electron cloud isinfluence of two nuclei and most of the electron cloud is oriented between the nuclei of the two atoms. On theoriented between the nuclei of the two atoms. On the other hand, the lone pair of electrons is under theother hand, the lone pair of electrons is under the influence of only one nucleus and therefore its electroninfluence of only one nucleus and therefore its electron cloud is spread out and tends to occupy more space.cloud is spread out and tends to occupy more space. Since the lone pair is flatter and occupies more spaceSince the lone pair is flatter and occupies more space around the central atom, it can interact more and willaround the central atom, it can interact more and will repel the electron pairs in the neighbouring orbitalsrepel the electron pairs in the neighbouring orbitals strongly than do the electrons in the boned orbital.strongly than do the electrons in the boned orbital. Obviously, the repulsion between two lone pairs wouldObviously, the repulsion between two lone pairs would be the largest. It will be lesser if one of them is bondbe the largest. It will be lesser if one of them is bond pair and least if both are bond pairspair and least if both are bond pairs..
- 5. Geometries ofGeometries of molecules based onmolecules based on VSEPR theoryVSEPR theory Molecules are classified into theMolecules are classified into the following two categories to predict thefollowing two categories to predict the geometrical shapes of molecules usinggeometrical shapes of molecules using VSEPR theory.VSEPR theory. 1.1. Molecules in which the central atom has noMolecules in which the central atom has no lone pair (bond pairs only)lone pair (bond pairs only) 2.2. Molecules in which the central atom hasMolecules in which the central atom has one or more lone pairs (bond pair and loneone or more lone pairs (bond pair and lone pair)pair)
- 6. 1.1.Shape of moleculesShape of molecules containing bond pairscontaining bond pairs onlyonly In case of two electron pairsIn case of two electron pairs around the central atom, thearound the central atom, the only way to keep them as faronly way to keep them as far apart as possible is to arrangeapart as possible is to arrange them at an angle of 180˚ tothem at an angle of 180˚ to each othereach other . This is. This is linear geometry.linear geometry. Eg:BeFEg:BeF22
- 7. Similarly for three electron pairs aroundSimilarly for three electron pairs around the central atom, the molecule adoptsthe central atom, the molecule adopts trigonal planartrigonal planar geometry with 120˚geometry with 120˚ between each bond and four electronbetween each bond and four electron pairs adoptpairs adopt tetrahedraltetrahedral geometry withgeometry with 109.5 ˚.109.5 ˚. Trigonal planar TetrahedralTrigonal planar Tetrahedral
- 8. When five electron are present,When five electron are present, all bond angles and bond lengthsall bond angles and bond lengths are not equal. Three electron pairsare not equal. Three electron pairs are in the same plane at an angleare in the same plane at an angle of 120˚ while other two areof 120˚ while other two are perpendicular to the plane, bothperpendicular to the plane, both making an angle of 90˚ with themaking an angle of 90˚ with the plane.plane. This type of geometry isThis type of geometry is trigonal bipyramidaltrigonal bipyramidal.. Even the bond lengths are not equal. The three bondsEven the bond lengths are not equal. The three bonds lying in the trigonal plane are called equatorial bonds.lying in the trigonal plane are called equatorial bonds. The remaining two bonds are called axial bonds. It hasThe remaining two bonds are called axial bonds. It has been observed that axial bonds are slightly longer thanbeen observed that axial bonds are slightly longer than equatorial bonds.equatorial bonds. As the molecule is unsymmentrical, it is less stable andAs the molecule is unsymmentrical, it is less stable and highly reactive.highly reactive.
- 9. When six electron pairs are present, allWhen six electron pairs are present, all bond angles are of 90˚.bond angles are of 90˚. When seven electron pairs are present, fiveWhen seven electron pairs are present, five electron pairs are equatorial bonds in theelectron pairs are equatorial bonds in the same plane each having 72˚ bond anglesame plane each having 72˚ bond angle and two electro pairs are axial bondsand two electro pairs are axial bonds making 90˚ with the bond.making 90˚ with the bond.
- 11. 2.Shape of molecules2.Shape of molecules containing lone pairs andcontaining lone pairs and bond pairsbond pairs If the valence shell has 1 lone pair,2If the valence shell has 1 lone pair,2 bond pairs(3 electron pairs), then thebond pairs(3 electron pairs), then the geometry is slightly distorted fromgeometry is slightly distorted from trigonal planar geometry and has V-trigonal planar geometry and has V- shapes or angular shape.shapes or angular shape. Since the lone pair-lone pair repulsion isSince the lone pair-lone pair repulsion is more than bond pair-bond pair repulsion,more than bond pair-bond pair repulsion, the bonded pairs are pushed more closerthe bonded pairs are pushed more closer and angle decreases from 120˚ to 119.5˚.and angle decreases from 120˚ to 119.5˚.
- 13. Due to the presence of lone pairs, the geometry becomesDue to the presence of lone pairs, the geometry becomes distorted and the bond angle reduces as the lone pairdistorted and the bond angle reduces as the lone pair occupies more space and has more repulsion.occupies more space and has more repulsion. Sometimes, certain geometries can have two or moreSometimes, certain geometries can have two or more ways of arrangements here, the most stable one will beways of arrangements here, the most stable one will be taken. The most stable ones are usually when the lonetaken. The most stable ones are usually when the lone pairs are at the equatorial positionspairs are at the equatorial positions.. Example: when there are 3 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs,Example: when there are 3 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs, there are 3 ways to positionthere are 3 ways to position 1.Two lone pairs ar equatorial positions1.Two lone pairs ar equatorial positions 2.One lp on axial one lp on equatorial2.One lp on axial one lp on equatorial 3.Both lp on axial position.3.Both lp on axial position. Here, the adopted geometry is (1) since it is the mostHere, the adopted geometry is (1) since it is the most stable and has minimum repulsion.stable and has minimum repulsion. When there are 2 bp and 3 lp, the three lone pairs areWhen there are 2 bp and 3 lp, the three lone pairs are present at the corners of an equilateral plane, the netpresent at the corners of an equilateral plane, the net repulsion on the bonds due to lone pairs cance out and isrepulsion on the bonds due to lone pairs cance out and is zero. So the molecule adopts linear geometryzero. So the molecule adopts linear geometry
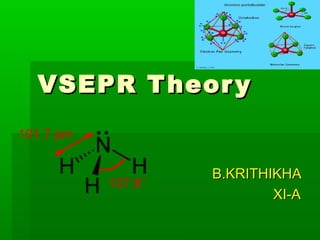
- 14. Few examplesFew examples Water (HWater (H22O):O): It is evident from theIt is evident from the Lewis structure of waterLewis structure of water molecule, there are twomolecule, there are two bond pairs and two lonebond pairs and two lone pairs in the valence shellpairs in the valence shell of oxygen. Hence itsof oxygen. Hence its structure is based onstructure is based on tetrahedral geometry.tetrahedral geometry. However its shape isHowever its shape is angular with two loneangular with two lone pairs on oxygen.pairs on oxygen.
- 15. SulfurSulfur tetrachloridetetrachloride (SCl(SCl44):): S(Z=16), Cl(Z=17)S(Z=16), Cl(Z=17) Since there are fourSince there are four bond pairs and one lonebond pairs and one lone pair around sulfur in itspair around sulfur in its valence shell, thevalence shell, the structure of SCl4 isstructure of SCl4 is based on trigonalbased on trigonal bipyramidal geometry. Itbipyramidal geometry. It has seesaw shape withhas seesaw shape with a lone pair occupying thea lone pair occupying the equatorial position.equatorial position.
- 16. LimitationLimitation It can’t explain the shape of molecules havingIt can’t explain the shape of molecules having very polar bonds, eg. Li2O should have thevery polar bonds, eg. Li2O should have the same structure as H2O but actually it is linear.same structure as H2O but actually it is linear. This fails to explain the shape of moleculesThis fails to explain the shape of molecules having extensive delocalized pi electronhaving extensive delocalized pi electron system.system. This theory is not able to predict the shape ofThis theory is not able to predict the shape of certain transition metal complexes.certain transition metal complexes. It does not help in determining the exact bondIt does not help in determining the exact bond angle.angle.