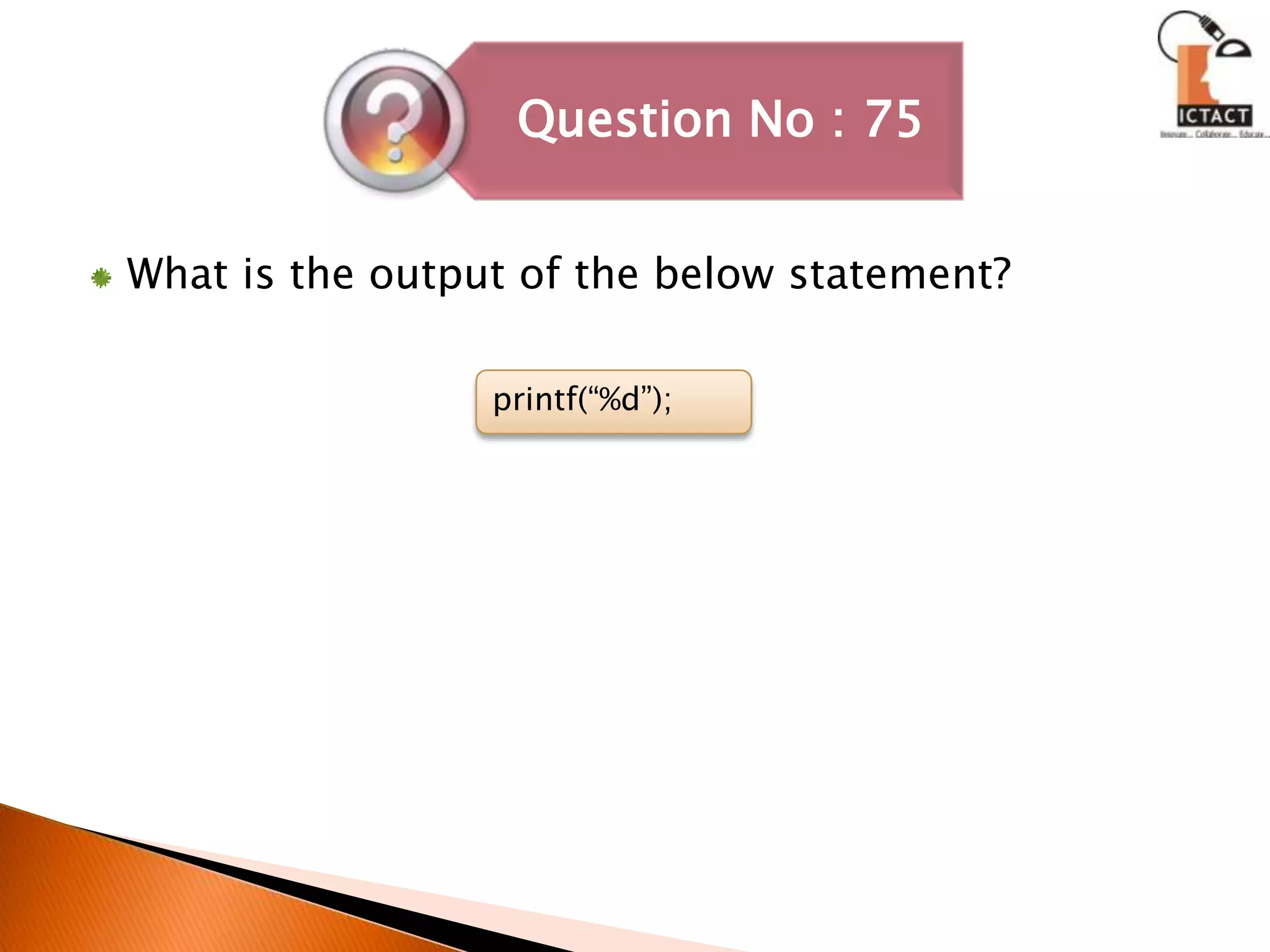
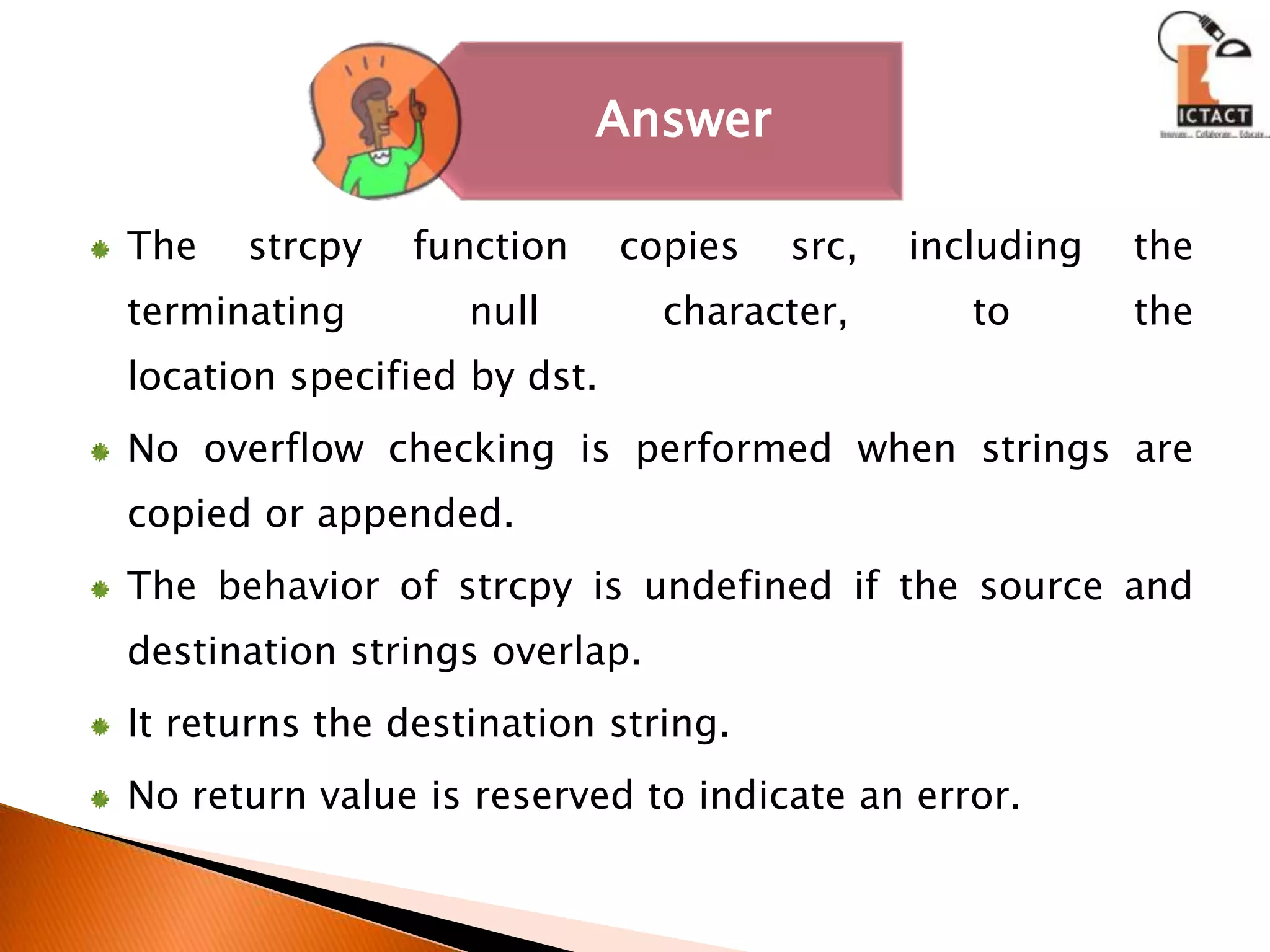
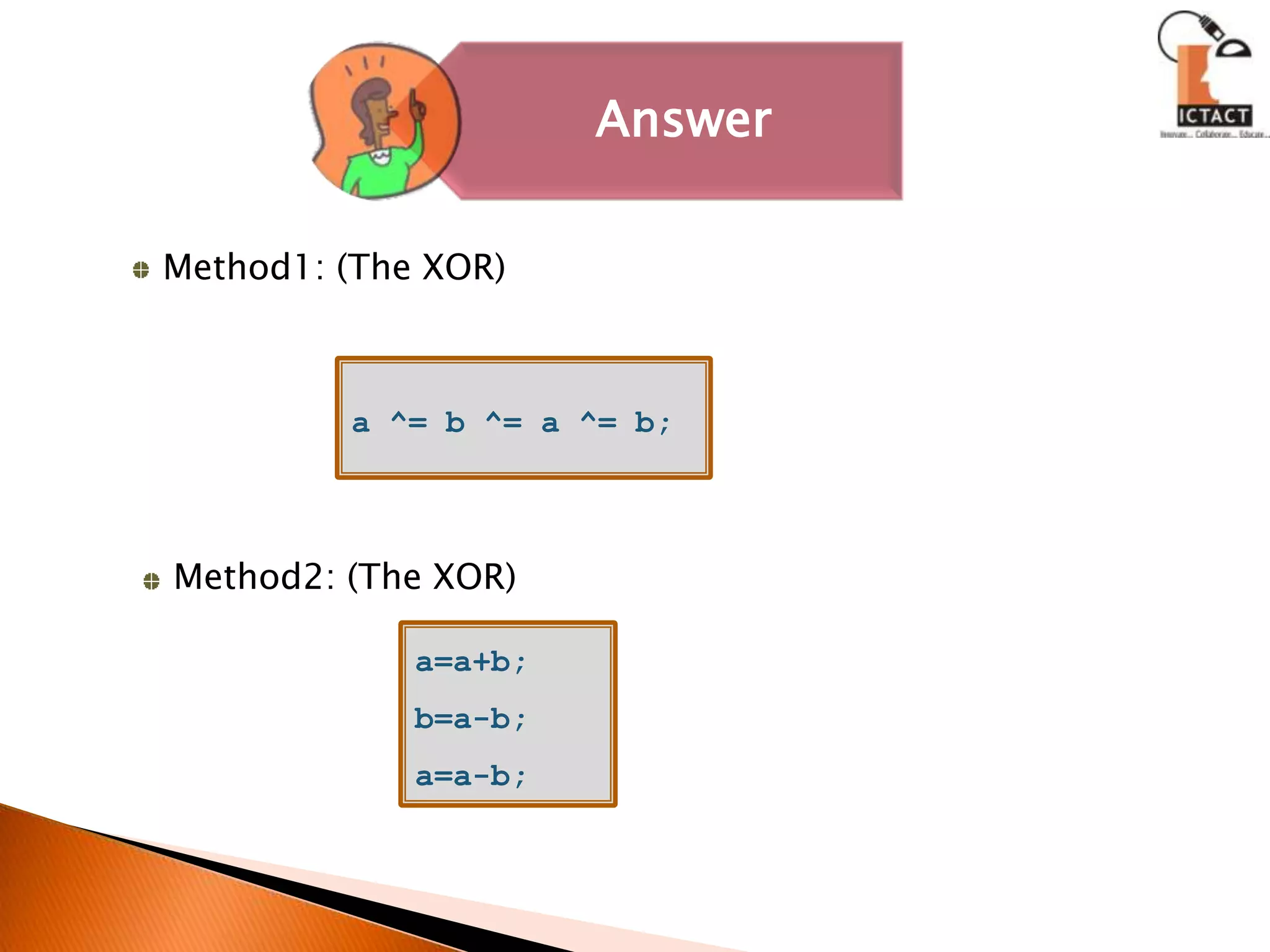
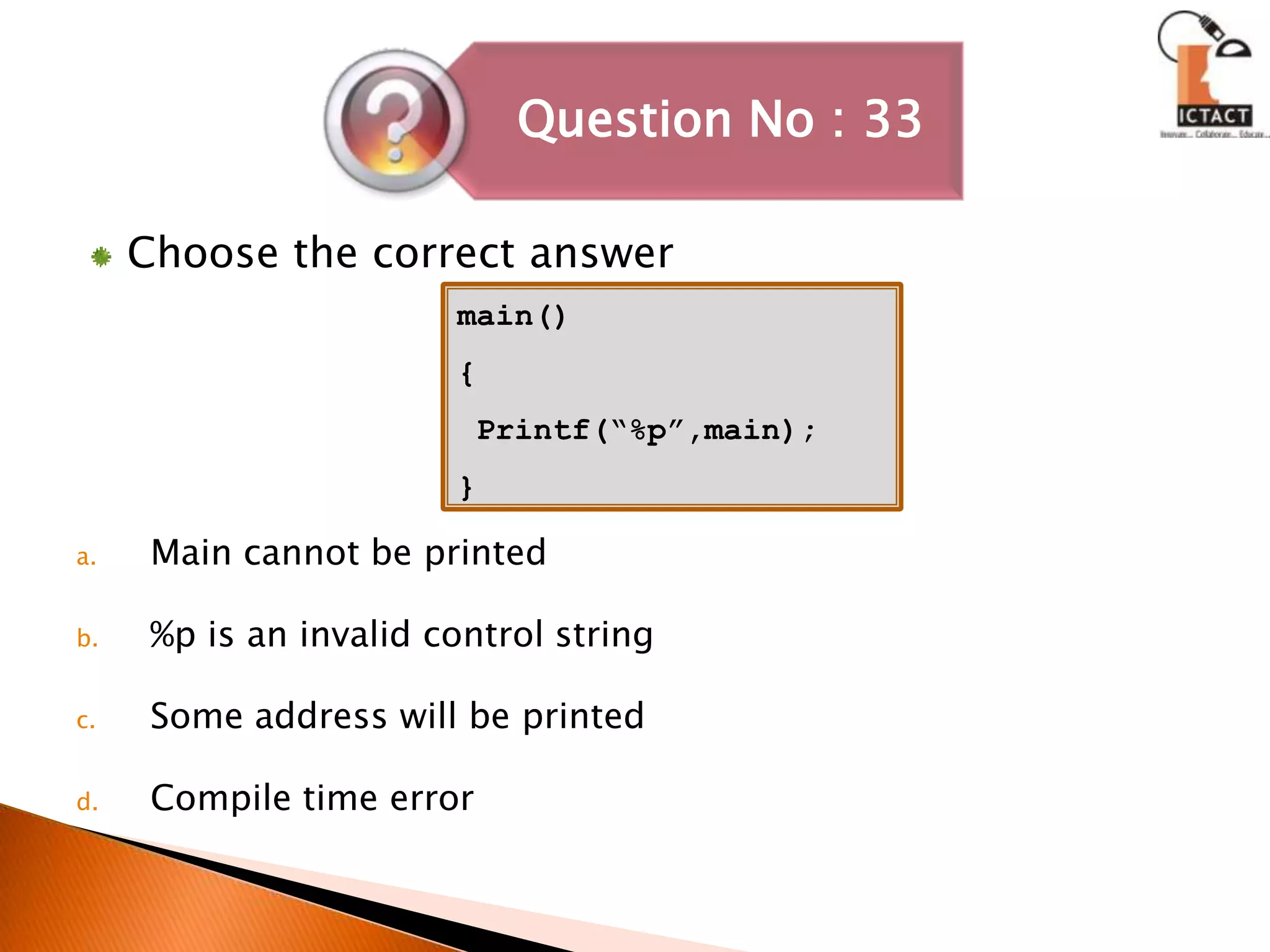
The document discusses C programming concepts like strcpy() function implementation, data types, operators, functions, pointers, arrays, strings and more. It provides code snippets to demonstrate various C programming techniques like implementing string copy functions, converting numbers to different bases, evaluating polynomials, swapping variables, reversing strings, matrix multiplication and more. It also answers questions about common C programming topics to test understanding.




![Method2:char *my_strcpy(char dest[], const char source[]){ int i = 0; while (source[i] != '\0') {dest[i] = source[i]; i++; }dest[i] = '\0'; return(dest);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-6-2048.jpg)



















![Declare it this waychar *(*(*a[N])())();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-27-2048.jpg)










![int pow(int x, int y) { if(y == 1) return x ; return x * pow(x, y-1) ;}Divide and Conquer C program#include <stdio.h>int main(int argc, char*argv[]) { printf("\n[%d]\n",pow(5,4));} printf("\n[%d]\n",pow(5,4));}int pow(int x, int n) { if(n==0)return(1); else if(n%2==0) {return(pow(x,n/2)*pow(x,(n/2)));}else { return(x*pow(x,n/2)*pow(x,(n/2))); }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-38-2048.jpg)






![#include <stdio.h>#include <conio.h>void decimal_to_anybase(int,int);void main() {decimal_to_anybase(10, 2);decimal_to_anybase(255, 16); getch();}void decimal_to_anybase(int n, int base) { int i, m, digits[1000], flag; i=0; printf("\n\n[%d] converted to base [%d] : ", n, base);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-45-2048.jpg)
![while(n) { m=n%base; digits[i]="0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"[m]; n=n/base; i++;}//Eliminate any leading zeroesfor(i--;i>=0;i--) { if(!flag && digits[i]!='0')flag=1; if(flag)printf("%c",digits[i]); }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-46-2048.jpg)



![# include<stdio.h>void main(){ int num=123456; int sum=0; for(;num>0;sum+=num%10,num/=10); // This is the "single line". printf("\nsum = [%d]\n", sum);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-50-2048.jpg)

![#include <stdio.h>#include <conio.h>int isSubset(char *a, char *b);int main(){ char str1[]="defabc"; char str2[]="abcfed"; if(isSubset(str1, str2)==0){ printf("\nYes, characters in B=[%s] are a subset of characters in A=[%s]\n",str2,str1); } else { printf("\nNo, characters in B=[%s] are not a subset of characters in A=[%s]\n",str2,str1); } getch(); return(0); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-52-2048.jpg)
![// Function to check if characters in "b" are a subset// of the characters in "a“int isSubset(char *a, char *b) { int letterPresent[256]; int i; for(i=0; i<256; i++)letterPresent[i]=0; for(i=0; a[i]!='\0'; i++)letterPresent[a[i]]++; for(i=0; b[i]!='\0'; i++) if(!letterPresent[b[i]]) return(1); return(0);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-53-2048.jpg)

![void printUp(int startNumber, int endNumber){ if (startNumber > endNumber) return; printf("[%d]\n", startNumber++);printUp(startNumber, endNumber);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-55-2048.jpg)





![First reverse the whole string and then individually reverse the words#include <stdio.h>void rev(char *l, char *r);int main(int argc, char *argv[]){ char buf[] = "the world will go on forever"; char *end, *x, *y;// Reverse the whole sentence first.. for(end=buf; *end; end++); rev(buf,end-1);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-61-2048.jpg)



![// Matrix A (m*n)// Matrix B (n*k)// Matrix C (m*k)for(i=0; i<m; i++) { for(j=0;j<k;j++) { c[i][j]=0; for(l=0;l<n;l++) c[i][j] += a[i][l] * b[l][j]; }}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-65-2048.jpg)


























![What is the output of the below code?main(){ char str1[] = ”some”; char str2[] =”some”; if (strcmp(str1,str2)) printf(“Strings are not equal\n”);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-93-2048.jpg)

![What is the output of the below code?main(){ char p[ ]="%d\n"; p[1] = 'c'; printf(p,65);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-95-2048.jpg)
![AExplanation:Due to the assignment p[1] = ‘c’ the string becomes, “%c\n”. Since this string becomes the format string for printf and ASCII value of 65 is ‘A’, the same gets printed.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-96-2048.jpg)


![What is the output of the following code?main(){ int a[5] = {2,3}; printf(" "\n%d %d d"",a[2],a[3],a[4]);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-99-2048.jpg)











![Which of the following is the correct output for the given program?dAbcdefgheCompile time errorvoid main(){printf("%c","abcdefgh"[4]);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-111-2048.jpg)









![Write down the equivalent pointer expression for referring element a[i][j][k][l] ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-121-2048.jpg)
![a[i] == *(a+i)a[i][j] == *(*(a+i)+j)a[i][j][k] == *(*(*(a+i)+j)+k)a[i][j][k][l] == *(*(*(*(a+i)+j)+k)+l)Hence Final output is *(*(*(*(a+i)+j)+k)+l)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-122-2048.jpg)


![What is the output of the below code?Syntax ErrorNo OutputCompiler Errorhello#include main(){ struct xx { int x=3; char name[]=”hello”; };struct xx *s;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-125-2048.jpg)





![#include<stdio.h>main(){char line[80];scanf("%[^n]",line);printf("%s",line);}what will scanf do ?Compiler errorterminates reading input into variable line after newlineterminates reading input into variable line after entering ^n](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-131-2048.jpg)

![What is the output of the below code?void main(){ char s[ ]="Welcome"; int i; for(i=0;s[ i ];i++) printf("\n%c%c%c%c",s[ i ],*(s+i),*(i+s),i[s]);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-133-2048.jpg)

![Explanation:s[i], *(i+s), *(s+i), i[s] are all different ways of expressing the same idea.Generally array name is the base address for that array. Here s is the base address. i is the index number/displacement from the base address. So, indirecting it with * is same as s[i]. i[s] may be surprising. But in the case of C it is same as s[i].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-135-2048.jpg)





![In the order, first construct the main objects, and then construct the internal objectsAllocationchar** pp = new char*[10]; for(int i=0;i<10;i++) char*[i]=new char[100];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-141-2048.jpg)
![In the reverse order, first destruct the internal objects, then destruct the main objectDeallocation for(int i=0;i<10;i++) delete [] char*[i]; delete[] pp;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-142-2048.jpg)



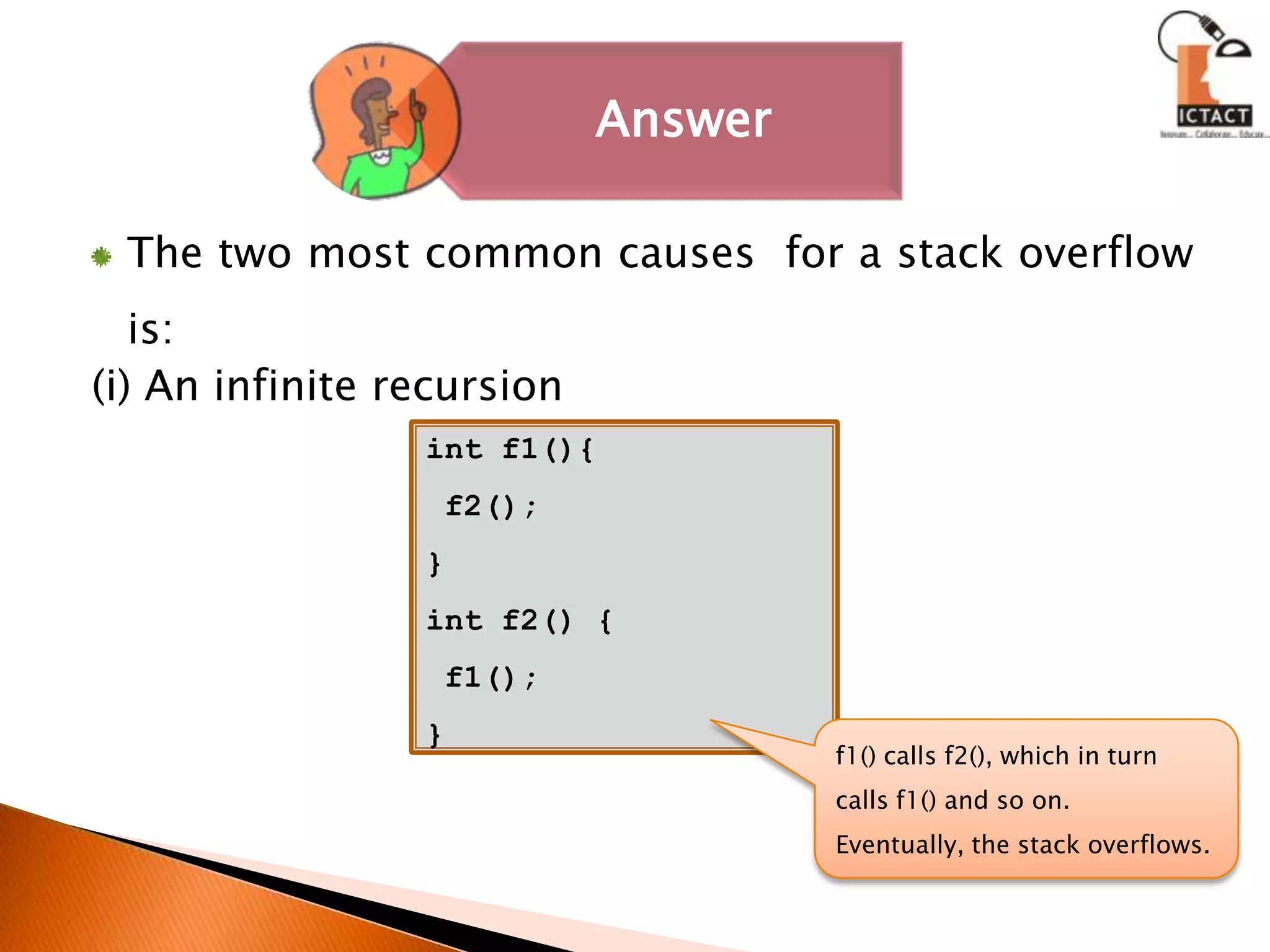
![(ii) An attempt to create a large array on the stack, for example:int main(){ int a[100000000]; // array is too large int b =0; //b's address exceeds the stack's limits, error}If our program crashes due to a stack overflow, we need to check for infinite recursion or too large local objects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-147-2048.jpg)




![What is the output of this program?#include <stdio.h>void main() { char s[20]; char *str = "SachinTendulker"; sscanf(str, "%s", s); printf("%s", s); sscanf(str+7, "%[duenTlk]", s); printf("%s", s); sscanf(str+15, "%[^Ganguly]", s); printf("%s\n", s); }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-152-2048.jpg)
![SachinTendulkerExplanation:The above statement captures Sachin only into S, because of white space character.The above statement captures Tendulker into S freshly. Because the format specifier has wildcard character [duenTlk], which means the scanning of string would be done as long as the character is one among the list of characters(starting from str+7).when it encounters a new character which is not there in the list the reading stops.sscanf(str, "%s", s);sscanf(str+7, "%[duenTlk]", s);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-153-2048.jpg)
![The above statement captures r into S freshly. Because the format specifier has wildcard character [^Ganguly], which means the scanning of string would be done as long as the character is not one among the list of characters(starting from str+15).when it encounters a new character which is there in the list(or when the null character occurs) the reading stops.sscanf(str+15, "%[^Ganguly]", s);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-154-2048.jpg)








![What would be the output of the following program if the array begins at the location 65472?main( ) { int a[3][4] = { 1,2,3, 4, 4,3,2,1, 7,8,9,0 }; printf( "\n %u %u ",a+1, &a+1);}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cprogramming-111011054818-phpapp02/75/C-programming-163-2048.jpg)