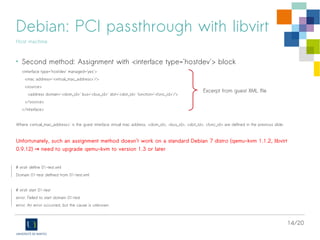
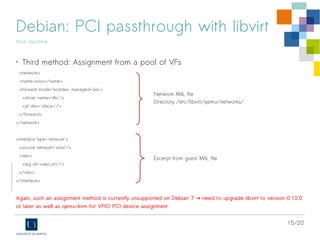
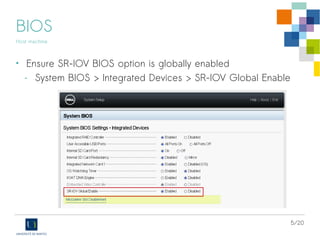
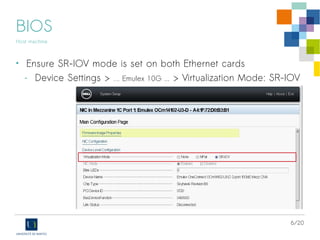
The document discusses the virtualization of high-performance servers and firewalls using Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) with Emulex OneConnect 10Gbps cards on Debian GNU/Linux. It outlines prerequisites for SR-IOV, including hardware support, BIOS settings, and kernel requirements, as well as steps to configure virtual functions for network interfaces. Additionally, it explains PCI passthrough methods with libvirt and specifies compatibility issues with older versions of Debian and QEMU/KVM software.





![8/20
Debian: Starting with SR-IOV
Host machine
• Check for SR-IOV hardware support:
# lspci -v
…
04:00.0 Ethernet controller: Emulex Corporation OneConnect NIC (Skyhawk) (rev 10)
...
Capabilities: [180 v1] Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV)
...
Initial VFs: 64, Total VFs: 64, Number of VFs: 64, Function Dependency Link: 00
Kernel driver in use: be2net
04:00.1 Ethernet controller: Emulex Corporation OneConnect NIC (Skyhawk) (rev 10)
...
Capabilities: [180 v1] Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV)
Kernel driver in use: be2net
eth2
eth3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sr-iov-emulex-debian-1-141226044757-conversion-gate01/85/SR-IOV-KVM-and-Emulex-OneConnect-10Gbps-cards-on-Debian-Stable-8-320.jpg)