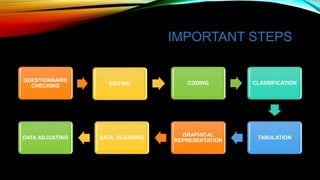
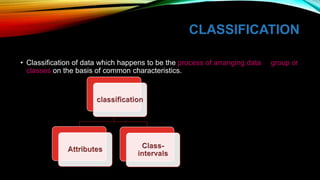
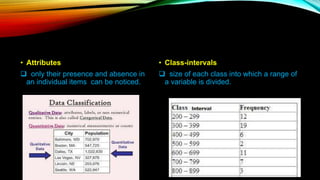
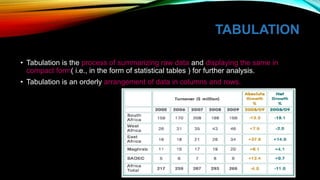
This document discusses research methodology and the processing of data. It outlines important steps in preparing raw data for analysis, including questionnaire checking, editing, coding, classification, tabulation, and graphical representation. The document also covers data cleaning and adjusting to ensure consistency and handle missing values, improving the quality of analysis. Proper data preparation through these steps is necessary to obtain reliable results from the analysis.