2.4 & 7.3 Notes
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
1 like•1,040 views
Guided notes covering material from Topics 2.4 and 7.3 of the updated IB Biology syllabus for 2016 exams. Notes sequence and prompts are based on the Oxford IB Biology textbook by Allott and Mindorff.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Recommended
More Related Content
What's hot
What's hot (20)
Biology 12 - Chemistry of Carbohydrates - Section 2-5 and 2-6

Biology 12 - Chemistry of Carbohydrates - Section 2-5 and 2-6
Biology 12 - Chemistry of Water and Carbon - Section 2-3 and 2-4

Biology 12 - Chemistry of Water and Carbon - Section 2-3 and 2-4
B.sc. biochemistry sem 1 introduction to biochemistry unit 2 biomolecules

B.sc. biochemistry sem 1 introduction to biochemistry unit 2 biomolecules
Cell Biology (Bio 108) - The Chemistry of the Cell

Cell Biology (Bio 108) - The Chemistry of the Cell
Viewers also liked
Viewers also liked (20)
IB DNA Structure & Replication Review Key (2.6-2.7-7.1)

IB DNA Structure & Replication Review Key (2.6-2.7-7.1)
Similar to 2.4 & 7.3 Notes
Similar to 2.4 & 7.3 Notes (20)
Protein metabolism and nitrogen fixation and metabolism

Protein metabolism and nitrogen fixation and metabolism
More from Jacob Cedarbaum
More from Jacob Cedarbaum (14)
IB DNA Structure & Replication Review (2.6-2.7-7.1)

IB DNA Structure & Replication Review (2.6-2.7-7.1)
Recently uploaded
https://app.box.com/s/7hlvjxjalkrik7fb082xx3jk7xd7liz3TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? webinar
Thursday 2 May 2024
A joint webinar created by the APM Enabling Change and APM People Interest Networks, this is the third of our three part series on Making Communications Land.
presented by
Ian Cribbes, Director, IMC&T Ltd
@cribbesheet
The link to the write up page and resources of this webinar:
https://www.apm.org.uk/news/making-communications-land-are-they-received-and-understood-as-intended-webinar/
Content description:
How do we ensure that what we have communicated was received and understood as we intended and how do we course correct if it has not.Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...Association for Project Management
Recently uploaded (20)
Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx

Basic Civil Engineering first year Notes- Chapter 4 Building.pptx
TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...

TỔNG ÔN TẬP THI VÀO LỚP 10 MÔN TIẾNG ANH NĂM HỌC 2023 - 2024 CÓ ĐÁP ÁN (NGỮ Â...
General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...

General Principles of Intellectual Property: Concepts of Intellectual Proper...
Interdisciplinary_Insights_Data_Collection_Methods.pptx

Interdisciplinary_Insights_Data_Collection_Methods.pptx
Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf

Unit 3 Emotional Intelligence and Spiritual Intelligence.pdf
UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf

UGC NET Paper 1 Mathematical Reasoning & Aptitude.pdf
Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx

Unit-V; Pricing (Pharma Marketing Management).pptx
Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...

Making communications land - Are they received and understood as intended? we...
2.4 & 7.3 Notes
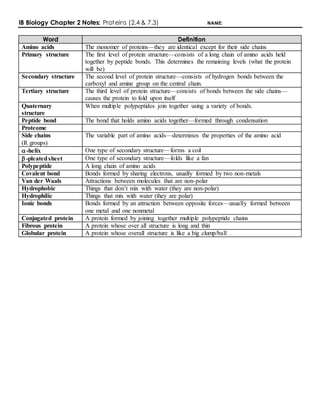
- 1. IB Biology Chapter 2 Notes: Proteins (2.4 & 7.3) NAME: Word Definition Amino acids The monomer of proteins—they are identical except for their side chains Primary structure The first level of protein structure—consists of a long chain of amino acids held together by peptide bonds. This determines the remaining levels (what the protein will be) Secondary structure The second level of protein structure—consists of hydrogen bonds between the carboxyl and amine group on the central chain. Tertiary structure The third level of protein structure—consists of bonds between the side chains— causes the protein to fold upon itself Quaternary structure When multiple polypeptides join together using a variety of bonds. Peptide bond The bond that holds amino acids together—formed through condensation Proteome Side chains (R groups) The variable part of amino acids—determines the properties of the amino acid -helix One type of secondary structure—forms a coil -pleatedsheet One type of secondary structure—folds like a fan Polypeptide A long chain of amino acids Covalent bond Bonds formed by sharing electrons, usually formed by two non-metals Van der Waals Attractions between molecules that are non-polar Hydrophobic Things that don’t mix with water (they are non-polar) Hydrophilic Things that mix with water (they are polar) Ionic bonds Bonds formed by an attraction between opposite forces—usually formed between one metal and one nonmetal Conjugated protein A protein formed by joining together multiple polypeptide chains Fibrous protein A protein whose over all structure is long and thin Globular protein A protein whose overall structure is like a big clump/ball .
- 2. 2.4.1 Amino acids are linked togetherby condensation to form polypeptides. 2.4.11 Draw molecular diagrams showing the formation of a peptide bond. 2.4.2 There are twenty different amino acids in polypeptides synthesized on ribosomes. 2.4.3 Amino acids can be linked togetherin any sequence giving a huge range of possible polypeptides. 2.4.4 The amino acid sequence of polypeptides is coded for by genes. 2.4.5 A protein may consist of a single polypeptide or more than one polypeptide linked together. 2.4.6 The amino acid sequence determines the three dimensional conformation of a protein. 2.4.10 Explain the denaturation of proteins by heat or deviation of pH from the optimum. Draw formation of a peptide bond: What is different between each of the 20 amino acids? What are some of structuraland/or chemical differences between the different amino acids? Number of Polypeptides Example Description Lysozyme Collagen Hemoglobin Globular proteins (describe and give example): Fibrous proteins (describe and give example):
- 3. 2.4.7 Living organisms synthesize many different proteins with a wide range of functions. 2.4.9 Identify rubisco, insulin, immunoglobulins, rhodopsin,collagen, and spider silk as examples of the range of protein functions. 2.4.8 Every individual has a unique proteome. Protein Function Description Catalysis Muscle contraction Cytoskeleton Tensile strength Blood clotting Transport of nutrients/ gas Cell adhesion Membrane transport Hormones Receptors Packing DNA Immunity Protein Example Function Rubisco Insulin Immunoglobulin (Antibodies) Collagen Rhodopsin Spider silk Describe what is meant by a ‘proteome:’
- 4. 7.3.7 The sequence and number of amino acids in the polypeptide is the primary structure. 7.3.8 The secondary structure is the formation of alpha helices and beta pleated sheets stabilized by hydrogen bonds. 7.3.9 The tertiary structure is the further folding of the polypeptide stabilized by interactions between R groups (side-chains). 7.3.10 The quaternary structure exists in proteins with more than one polypeptide chain. What types of bonds form the secondary structure? What are the two secondary structures? What types of bonds/ interactions form the tertiary structure?
