Embed presentation
Download as PPSX, PPTX
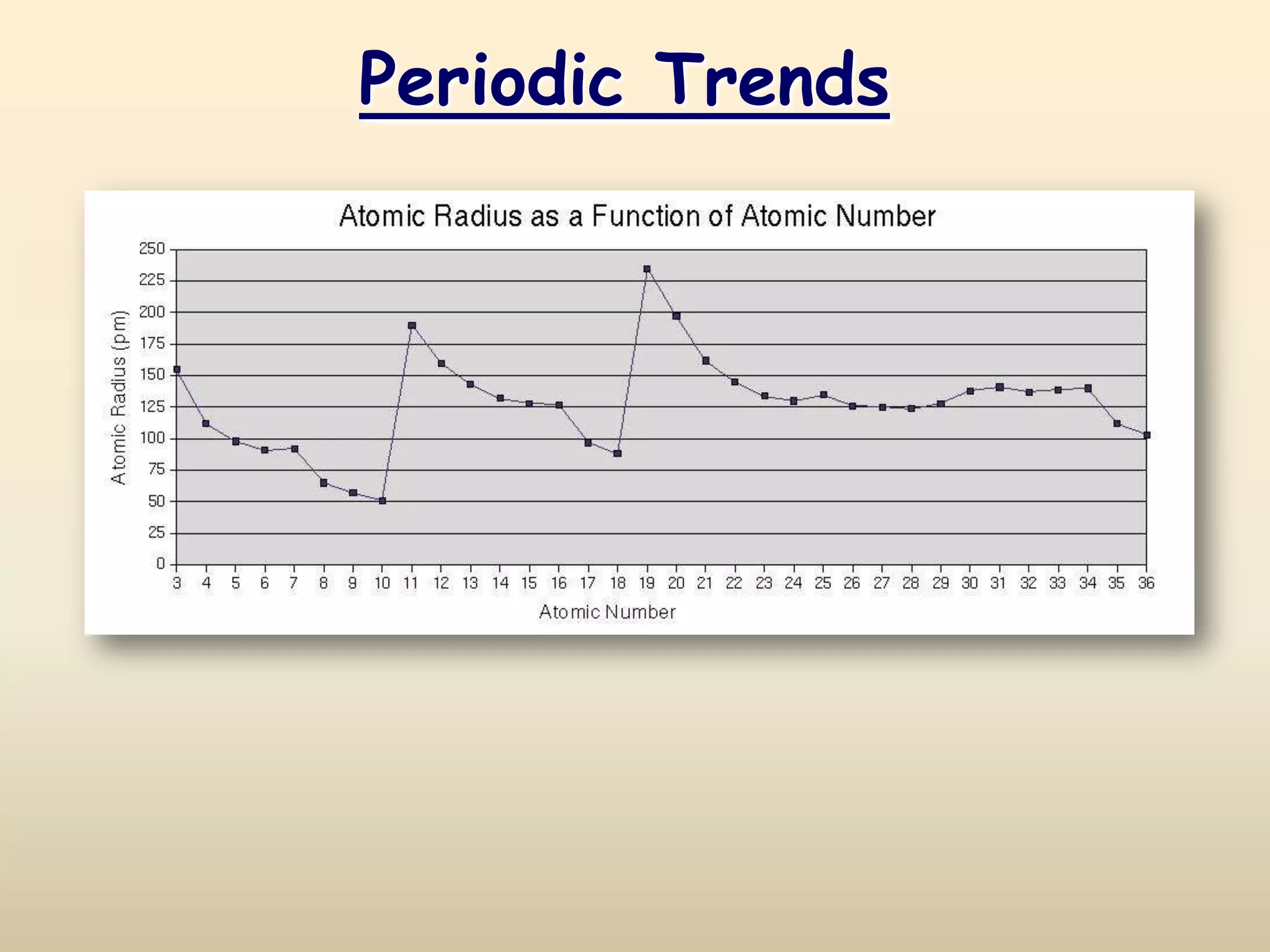



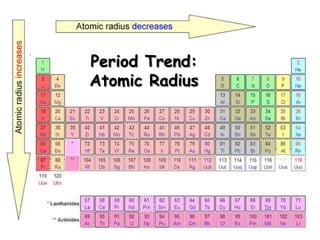

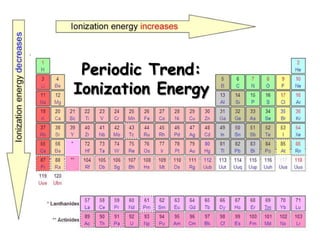

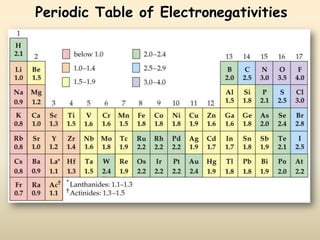
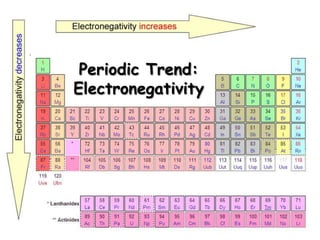
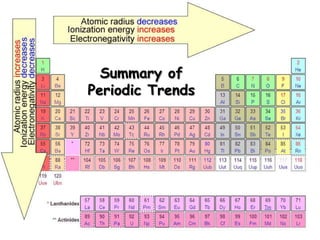

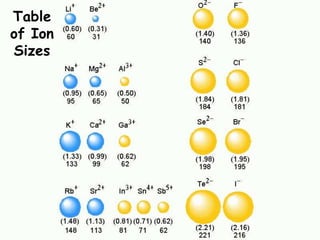
The document discusses periodic trends in atomic properties according to the periodic table. It explains that atomic radius decreases across a period as effective nuclear charge increases due to shielding effects, while radius increases down a group as each row adds a new shell. Ionization energy tends to increase across a period as removal of electrons becomes more difficult, and decreases down a group as outer electrons are farther from the nucleus. Electronegativity also increases across a period but decreases or stays the same down a group as distance from the nucleus increases. Positively charged cations are smaller than their parent atoms, while negatively charged anions are larger.












