The document discusses the advanced features of FluxQL, a functional data scripting language for querying and analyzing time-series data within InfluxDB 2.0. It covers the deployment options, the differences between Flux and InfluxQL, and highlights the capabilities of InfluxDB's architecture, including clustering, data ingestion, and integration with other data sources. The text is aimed at presenting the tools available for real-time performance monitoring, analytics, and machine learning in various scenarios.







![Nov 20-21, 2020
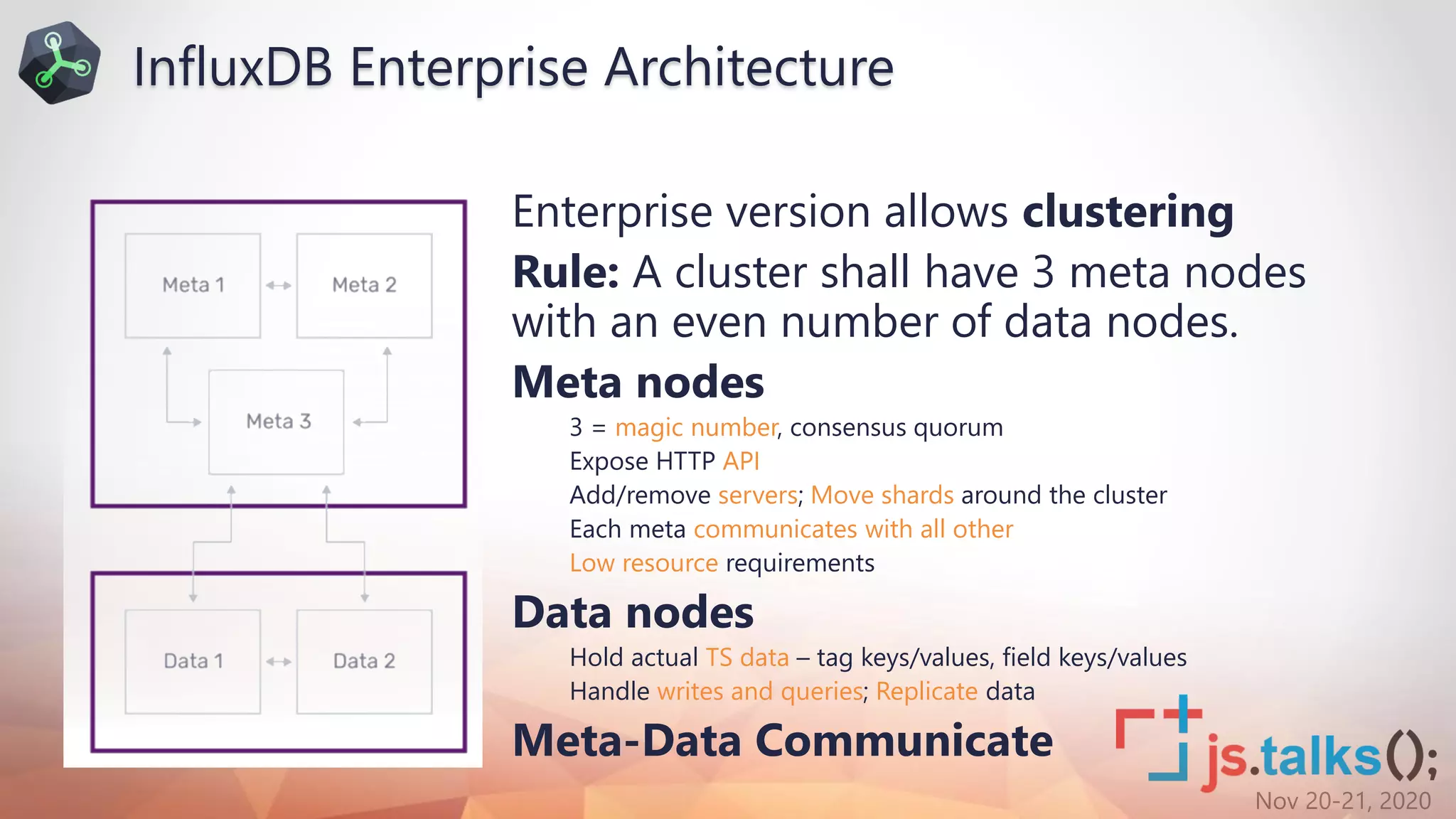
• 4th gen programming language (since July 2018)
• Why a new Language?
• Features
• Highly Readable – piping, instead of nesting, clear data origin
• Useable – aids productivity, shorter code to express the same
• Readable – derived from something common (JS)
• Testable – Flux functions can be tested in isolation from the outside world(unlike SQL)
• Shareable – community defines functions, creates libraries
• Decouples query engine from storage tier
Why the Trouble of a New Language?
d1=from(bucket: "industry4sme")
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "telemetry")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["SensorID"] == "M186")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["Type"] == "S1load")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluxql-nextgenmanagementoftimeseriesinspiredbyjs-201209204358/75/Flux-QL-Nexgen-Management-of-Time-Series-Inspired-by-JS-12-2048.jpg)
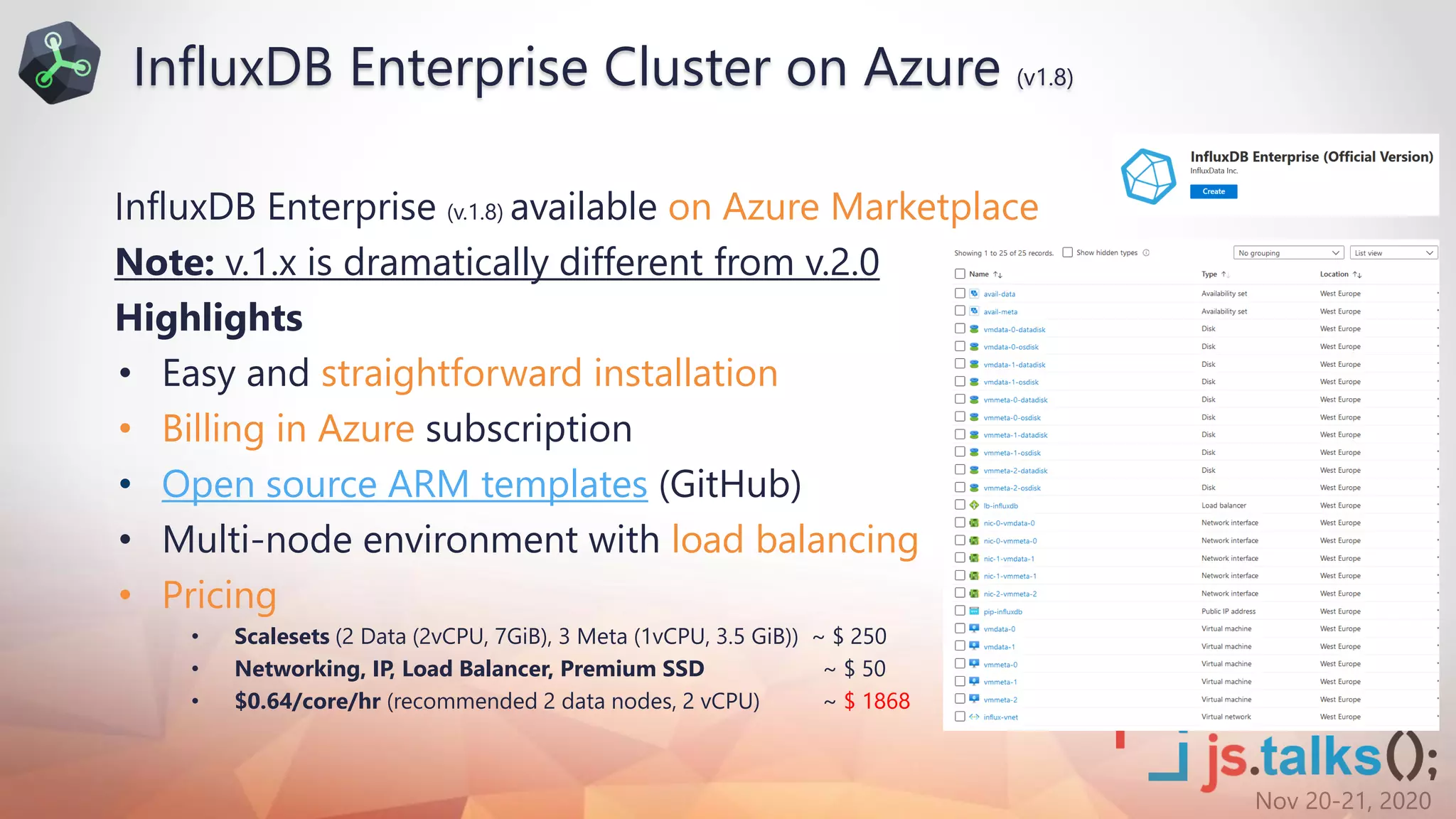
![Nov 20-21, 2020
• Joins – from any bucket, measurement and on any columns
• Math across measurements - run calculations using data from separate measurements
• Sort on tags – Order by time only was supported in InfluxQL
• Group by any column – InfluxQL allows grouping on tags and time only
• Multiple datasources – Flux query data from datasources like CSV, SQL and BigTable packages
• Custom functions – define custom auxiliary functions
• Datepart queries –only data within a specified hour range (i.e. work hours), for a large period
• Pivot - pivot data tables by specifying rowKey, columnKey
• Histograms - generate a cumulative histogram in buckets [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
• Covariance - covariance() function calculates the covariance between two columns
Flux vs InfluxQL](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluxql-nextgenmanagementoftimeseriesinspiredbyjs-201209204358/75/Flux-QL-Nexgen-Management-of-Time-Series-Inspired-by-JS-13-2048.jpg)

![Nov 20-21, 2020
$ wget https://dl.influxdata.com/influxdb/releases/influxdb_2.0.0-beta.16_linux_amd64.tar.gz
$ tar xvzf influxdb_2.0.0-beta.16_linux_amd64.tar.gz
• MacOS, Linux, Docker…No Windows? (see Docker)
• Create a VM (i.e. Standard B2s (2 vcpus, 4 GiB memory, Standard SSD))
• Connect with SSH client of choice (i.e. Putty)
• Download and Unzip
• Setup as Service
$ sudo cp influxdb_2.0.0-beta.16_linux_amd64/{influx,influxd}
/usr/local/bin/
$ sudo useradd -rs /bin/false influxdb
$ sudo mkdir /home/influxdb
$ sudo chown influxdb /home/influxdb
$ sudo vi /lib/systemd/system/influxdb2.service
(Add the InfluxDB service file content)
$ sudo systemctl enable influxdb2
$ sudo systemctl start influxdb2
$ sudo systemctl status influxdb2
InfluxDB service file
[Unit]
Description=InfluxDB 2.0 service file.
After=network-online.target
[Service]
User=influxdb
Group=influxdb
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/influxd
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
InfluxDB OSS 2.0 Installation (Azure VM)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluxql-nextgenmanagementoftimeseriesinspiredbyjs-201209204358/75/Flux-QL-Nexgen-Management-of-Time-Series-Inspired-by-JS-17-2048.jpg)
![Nov 20-21, 2020
• Configure
Add Firewall rule (allow incoming TCP port 9999)
Option 1(GUI)
Open http://[IPAddress]:9999
Option 2(CLI)
influx setup
Configure InfluxDB OSS 2.0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluxql-nextgenmanagementoftimeseriesinspiredbyjs-201209204358/75/Flux-QL-Nexgen-Management-of-Time-Series-Inspired-by-JS-18-2048.jpg)



![Nov 20-21, 2020
Export from InfluxDB 1.x
• Export to Influx line protocol
influx_inspect export -datadir “[influxRoot]data" -waldir "[influxRoot]meta" -out “[outFolder]"
-database [databaseName] -retention autogen -start "2020-10-01T00:00:00Z“
Note: Edit file and remove DDL statements (CREATE DATABASE [databaseName] WITH NAME autogen)
Import in InfluxDB 2
• Option 1 (GUI)
• Open InfluxDB home (http://[IPAddress]:9999/)
• Open Data Tab
• Find TS Data bucket
• 1.1 Line Protocol
• Drag file for import
• 1.2 Client Library
• Open IDE
• Reuse sample code
• Option 2 (CLI)
• Connect remotely (i.e. Putty)
• Upload files to VM over SFTP (i.e. WinSCP)
• Bucket must exist prior to import
influx write -b [bucket] -o [orgName] -p ns --
format=lp -f [filePath/filename] -t [token]
Migration to Flux](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluxql-nextgenmanagementoftimeseriesinspiredbyjs-201209204358/75/Flux-QL-Nexgen-Management-of-Time-Series-Inspired-by-JS-26-2048.jpg)

![Nov 20-21, 2020
Secrets
• Add Secrets
influx secret update -k [database.User] -v [userName] -o [orgName] -t [token]
influx secret update -k [database.Pass] -v [password] -o [orgName] -t [token]
• View Secrets
influx secret list -o [orgName] -t [token]
Note: Use ReadOnly user for security reasons; Enable access to SQL through the firewall
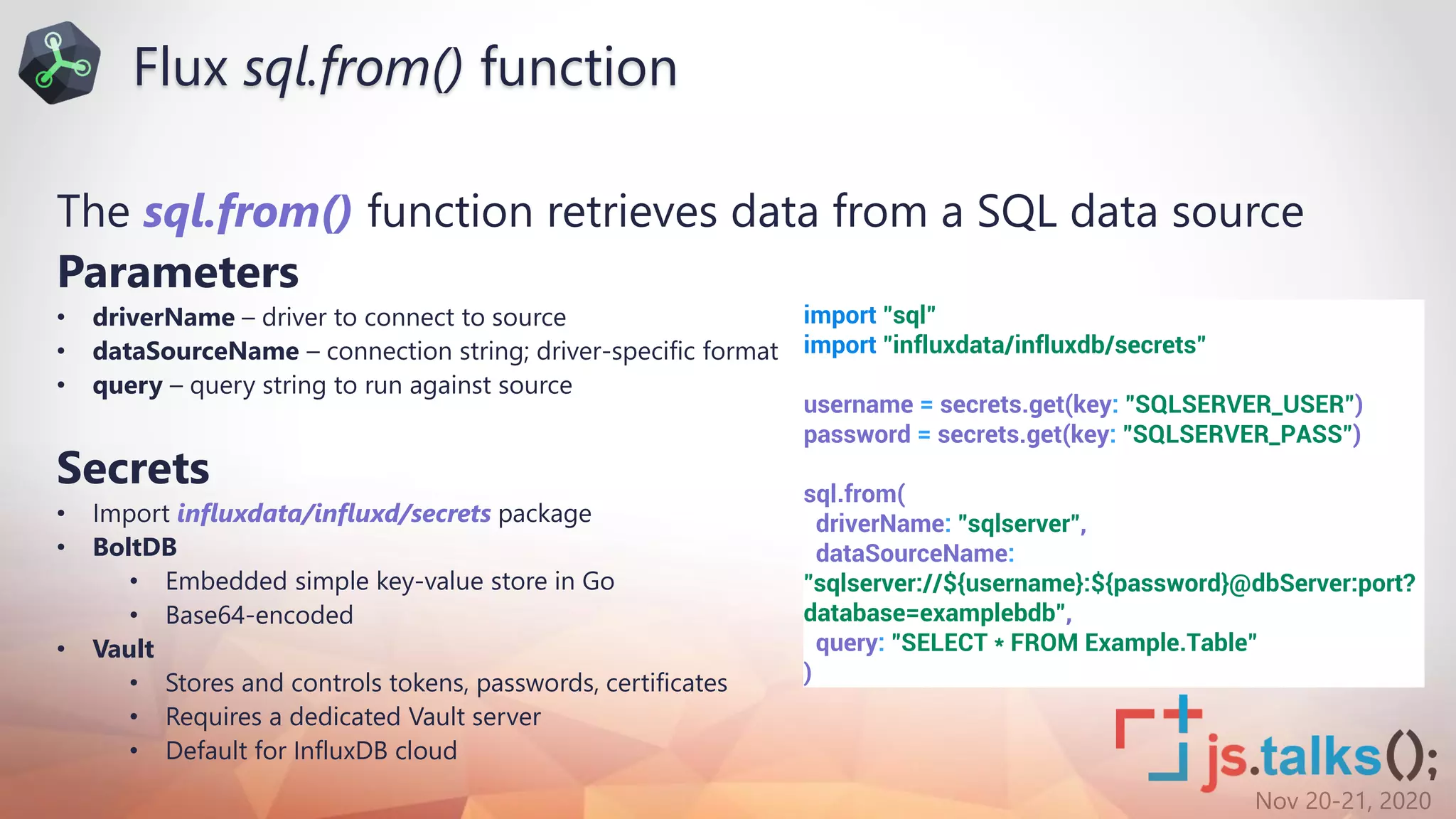
import "sql"
import "influxdata/influxdb/secrets"
username = secrets.get(key: "ConfigDB.User")
password = secrets.get(key: "ConfigDB.Pass")
configDB = secrets.get(key: "ConfigDB")
machineData = sql.from(
driverName: "sqlserver",
dataSourceName: "sqlserver://${username}:${password}@${configDB}?
database=ConfigurationDB",
query: "exec [org].[spRetrieveMachineList] 'grafana_admin@localhost', 'S
tatus', 'All', 'All'"
)
SQL Fluxsensordata = from(bucket: "industry4sme")
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "telemetry")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["SensorID"] == "M186" or r["SensorID"] == "M222"
)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["Type"] == "S1speed")
|> aggregateWindow(every: 5m, fn: mean, createEmpty: false)
Flux sql.from()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluxql-nextgenmanagementoftimeseriesinspiredbyjs-201209204358/75/Flux-QL-Nexgen-Management-of-Time-Series-Inspired-by-JS-28-2048.jpg)
![Nov 20-21, 2020
Join
• Join 2 data streams in a single table - InfluxDB query results with SQLServer query results
• Both tables must have all columns specified in this list.
• Columns renamed if having the same name i.e. Type_metric
Mapped table
• Build a new table, mapping existing columns to new ones.
• Aggregate the rows, grouping by interval and using Max as aggregation function
join(tables: {metric: sensordata, info: machineData}, on: ["SensorID"])
|> map(fn: (r) => ({
SensorID: r.SensorID,
Name: r.Name,
_value: r._value,
_time: r._time
})
)
|> aggregateWindow(every: 10m, fn: max)
Flux join()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluxql-nextgenmanagementoftimeseriesinspiredbyjs-201209204358/75/Flux-QL-Nexgen-Management-of-Time-Series-Inspired-by-JS-29-2048.jpg)
![Nov 20-21, 2020
cov()
• Computes the covariance between two streams by first joining the streams
Covariance
• Measures the extent of change in one variable compared to other (-∞;+∞)
• High covariance - strong relationship, low covariance - weak relationship
Pearsonr()
• Computes the Pearson R correlation coefficient between two streams by first joining the streams
Correlation
• How strongly two variables are related, scaled covariance [-1;+1] , 0.0-0.4 – low, 0.4-0.7 – moderate, 0.7-1.0 -
high
d1=from(bucket: "industry4sme")
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "telemetry")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["SensorID"] == "M186")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["Type"] == "S1load")
d2=from(bucket: "industry4sme")
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "telemetry")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["SensorID"] == "M186")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["Type"] == "S2load")
pearsonr(x: d2, y: d1, on:["_time", "SensorID"])
cov(x: d2, y: d1, on:["_time", "SensorID"])
Flux cov(), pearsonr()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fluxql-nextgenmanagementoftimeseriesinspiredbyjs-201209204358/75/Flux-QL-Nexgen-Management-of-Time-Series-Inspired-by-JS-30-2048.jpg)

