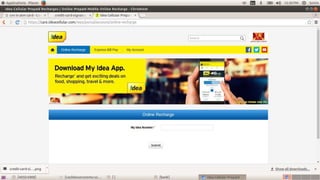
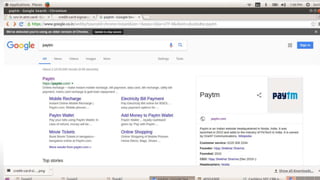
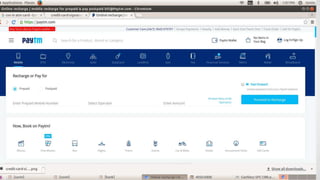
The document discusses the benefits and challenges of moving to a cashless economy in India. It notes that demonetization in India helped reduce black money held in cash form, but some black money is still kept in gold, real estate, and cash. A cashless economy would involve all electronic payments instead of cash or checks. This could help reduce illegal activities that use cash but may also raise security and privacy concerns. The document outlines various electronic payment methods like e-wallets, debit/credit cards, digital currencies, and their benefits and risks in a cashless system.