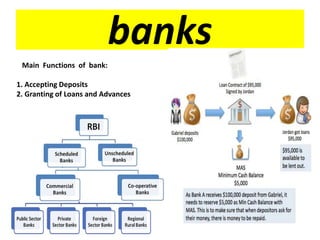
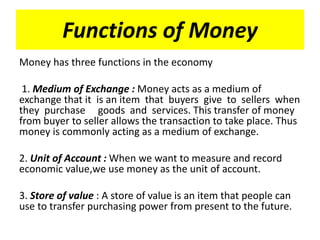
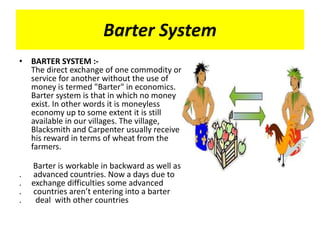
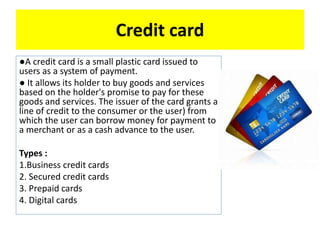
Money functions as a medium of exchange, unit of account, and store of value. There are different forms of money including commodity money, fiat money, fiduciary money, and commercial bank money. The traditional barter system was replaced by money to overcome limitations like the lack of a double coincidence of wants. Demonetization in India in 2016 aimed to reduce corruption and black money but also caused short-term cash shortages and economic difficulties.










![BITCOIN
• Bitcoin (₿) is a cryptocurrency, a form of electronic
cash. It is a decentralized digital currency without
a central bank or single administrator that can be
sent from user to user on the peer-to-peer bitcoin
network without the need for intermediaries.[8]
• Bitcoin was invented by an unknown person or
group of people using the name, Satoshi Nakamoto
Advantages:
●Freedom in Payment
●Control and Security
●Information is Transparent
●Very Low Fees
Disadvantages:
●Lack of Awareness & Understanding
●Risk and Volatility
●Still Developing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/money-190512190022/85/Money-16-320.jpg)