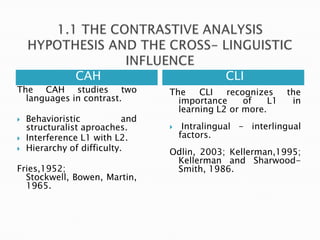
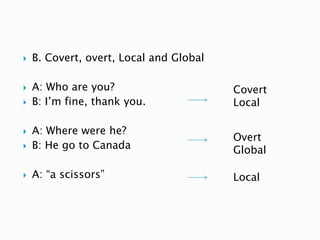
This document discusses linguistic factors that influence learner language such as cross-linguistic transfer between a learner's first and second languages. It covers key concepts like error analysis, the contrastive analysis hypothesis, and cross-linguistic influence. Error analysis describes and explains why learners make errors, categorizing errors into omission, addition, substitution, and ordering. Errors can be covert or overt, local or global. The document also discusses implications for error correction and conclusions about errors providing feedback on teaching.