The document discusses the 'toolbelt theory' for teaching students to analyze tasks, environments, and their skills, while empowering them to make informed decisions regarding tools for various situations. It emphasizes the importance of modern technology in schools to prepare students for future challenges, and advocates for an educational approach that encourages experimentation, acceptance of failure, and personalized learning. Ultimately, the aim is to foster independence and adaptability in students as they navigate an evolving technological landscape.


































































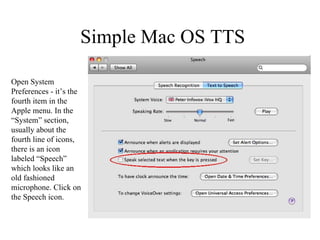
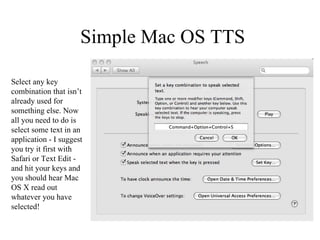







![http://speedchange.blogspot.com/ [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/toolbelttheory-090617184017-phpapp02/85/Toolbelt-Theory-76-320.jpg)