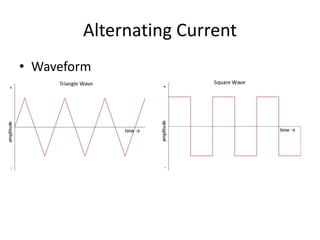
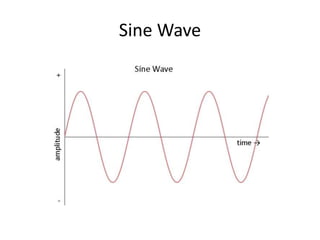
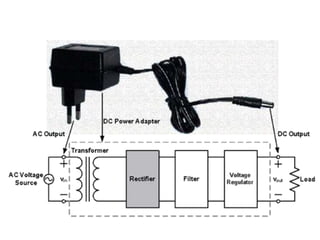
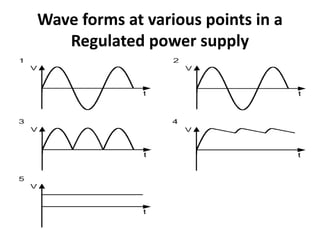
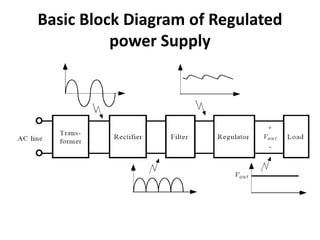
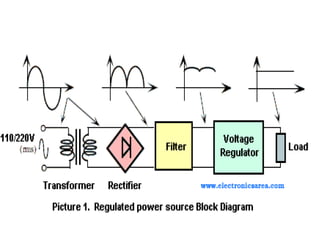
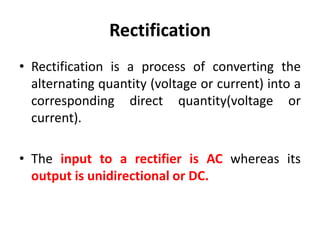
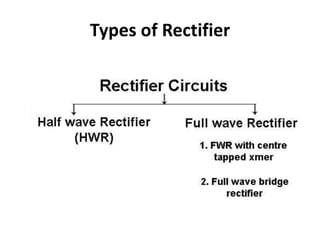
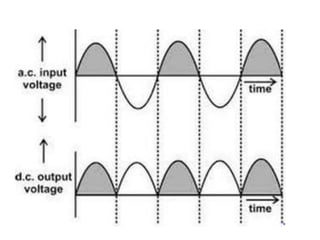
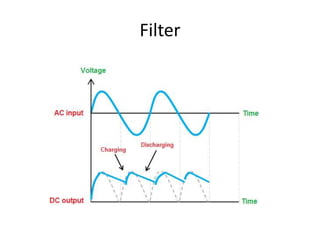
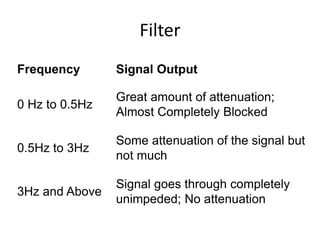
A power supply converts electrical current from a source to the correct voltage, current and frequency to power electrical loads. It first uses a transformer to reduce alternating current (AC) voltage from the source, then a rectifier converts it to direct current (DC). Filters are used to remove any remaining ripple or unwanted AC components, producing a smooth DC output. Voltage regulators then maintain a constant DC voltage level.