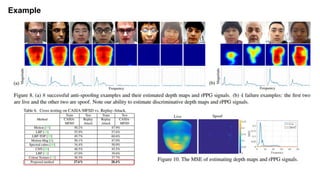
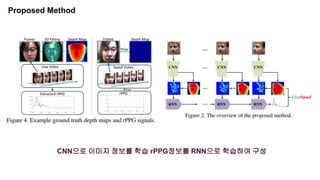
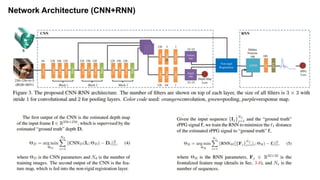
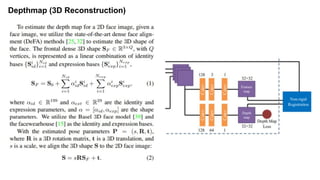
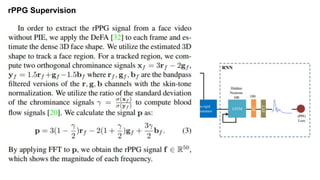
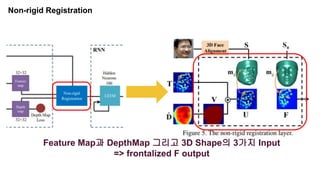
This document summarizes a research paper on face anti-spoofing using deep learning models. It discusses using auxiliary supervision from additional data sources like depth maps and remote photoplethysmography (rPPG) signals to improve spoof detection performance. The proposed method uses a CNN to extract image features and an RNN to model rPPG signals. It evaluates the approach on the Spoof in the Wild database containing live and spoof videos, and compares error rates to other databases. The document provides background on anti-spoofing, defines relevant terms like rPPG and error metrics, and references related works and datasets.

![Anti-Spoofing 관련 아래 논문을 바탕으로 설명
[논문]
Learning Deep Models for Face Anti-Spoofing: Binary or Auxiliary Supervision
In Proceeding of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2018), Salt Lake City, UT, Jun. 2018
http://cvlab.cse.msu.edu/pdfs/Liu_Jourabloo_Liu_CVPR2018.pdf
[Data]
Spoof in the Wild (SiW) Face Anti-spoofing Database
http://cvlab.cse.msu.edu/spoof-in-the-wild-siw-face-anti-spoofing-database.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperanti-spoofingforfacerecognition-210508093958/85/Paper-anti-spoofing-for-face-recognition-2-320.jpg)
![얼굴인식 실제 서비스로 이어지기 위해서는...
실재 얼굴과 Print,Phone(Galaxy,iPhone),
가면, 동영상등을 구분해야함
[출처] : http://biometrics.cse.msu.edu/projects/face_recog_spoofing.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperanti-spoofingforfacerecognition-210508093958/85/Paper-anti-spoofing-for-face-recognition-3-320.jpg)

![What is rPPG?
[출처] : https://www.noldus.com/facereader/remote-photoplethysmography-facereader](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperanti-spoofingforfacerecognition-210508093958/85/Paper-anti-spoofing-for-face-recognition-5-320.jpg)


![Experimental Comparison
Attack Presentation Classification Error Rate APCER
Bona Fide Presentation Classification Error Rate BPCER ACER =
(APCER+BPCER) / 2
Half Total Error Rate HTER
The HTER is half of the summation of the False Rejection Rate
(FRR) and the False Acceptance Rate (FAR)
Oulu protocols : OULU-NPU
a mobile face presentation attack database with real-world variations
[출처] : TDR/ FDR http://www.mohr-engineering.com/TDR_vs_FDR_Distance_to_Fault-A.php](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/paperanti-spoofingforfacerecognition-210508093958/85/Paper-anti-spoofing-for-face-recognition-14-320.jpg)