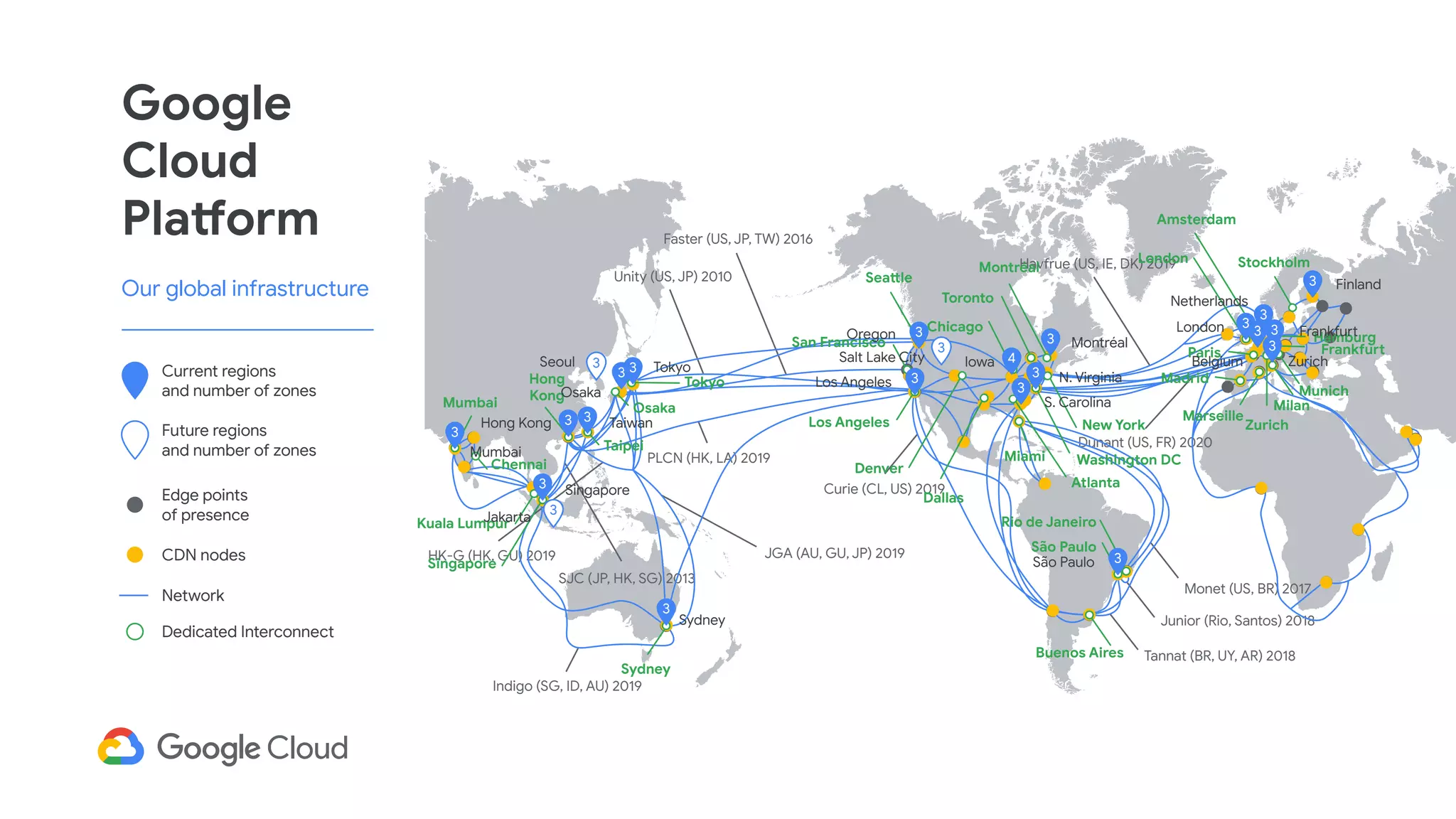
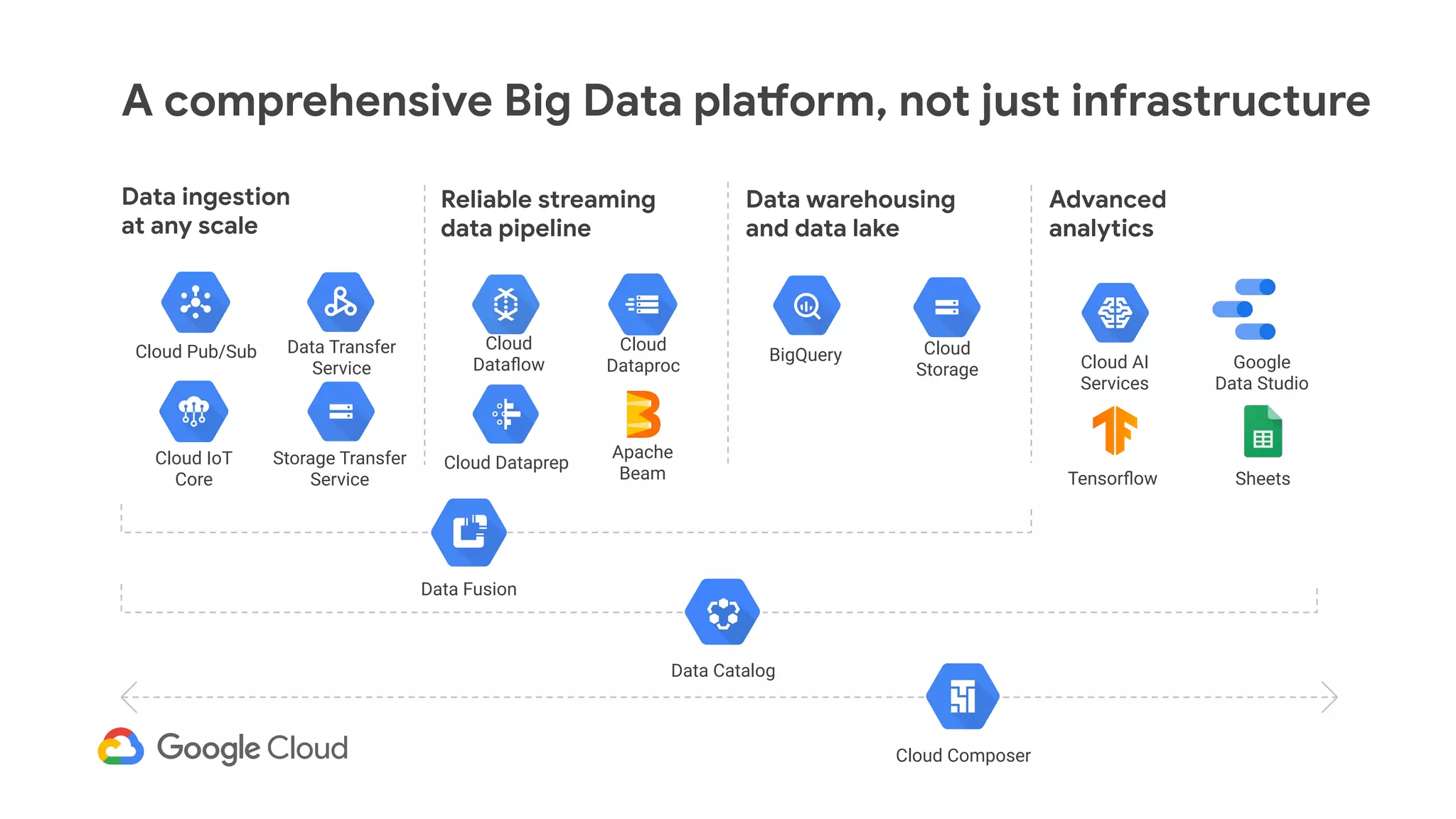
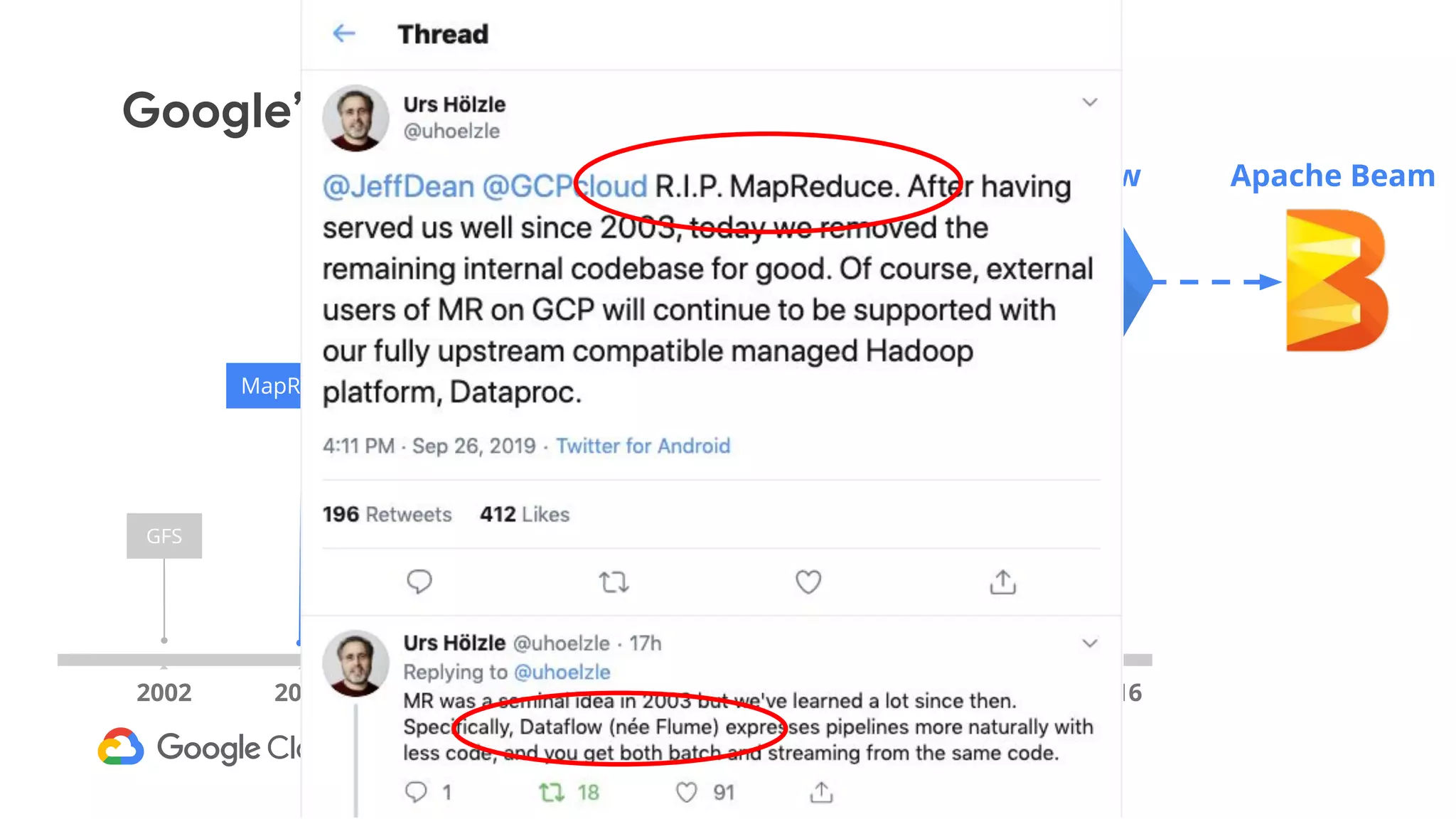
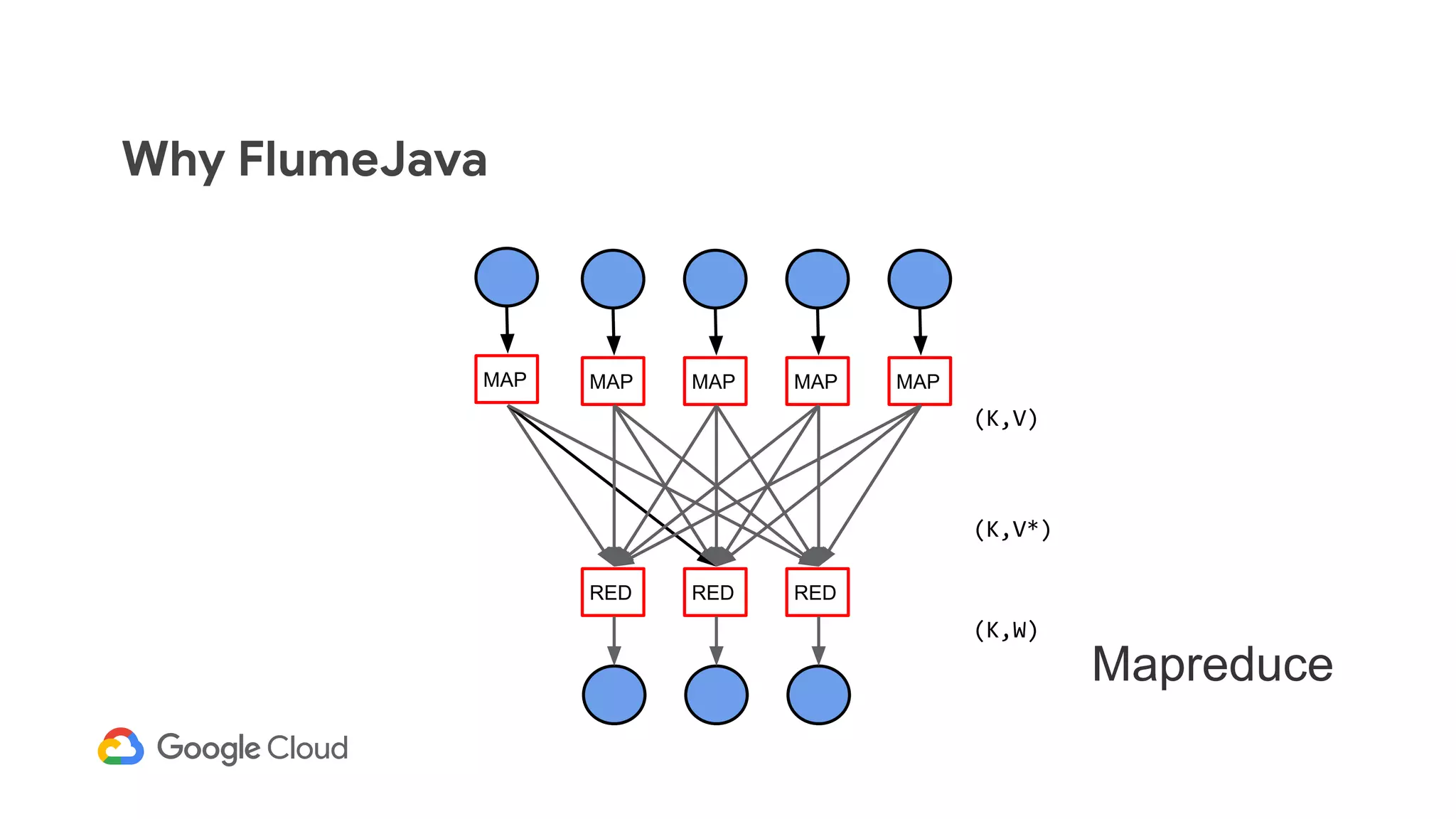
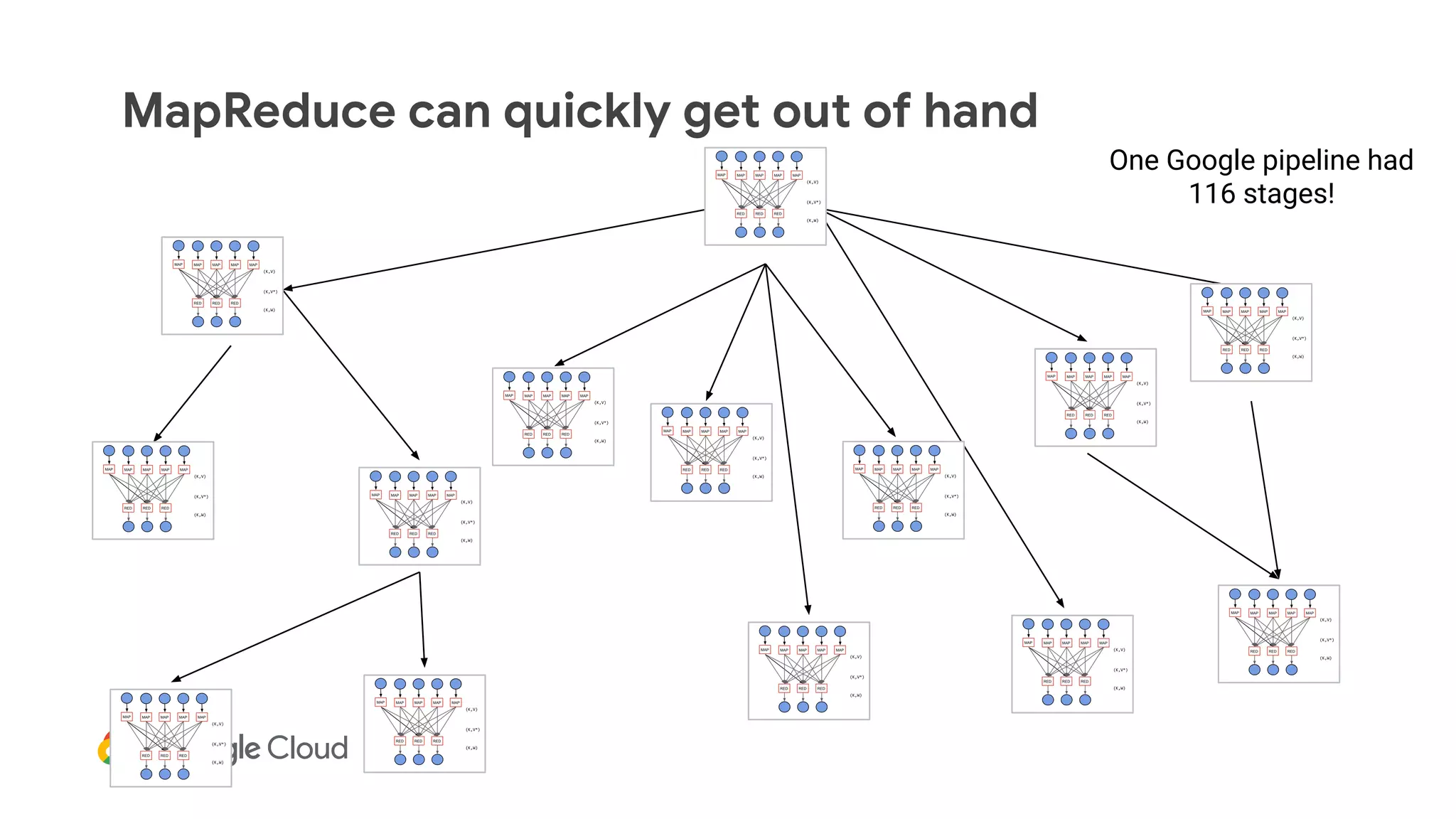
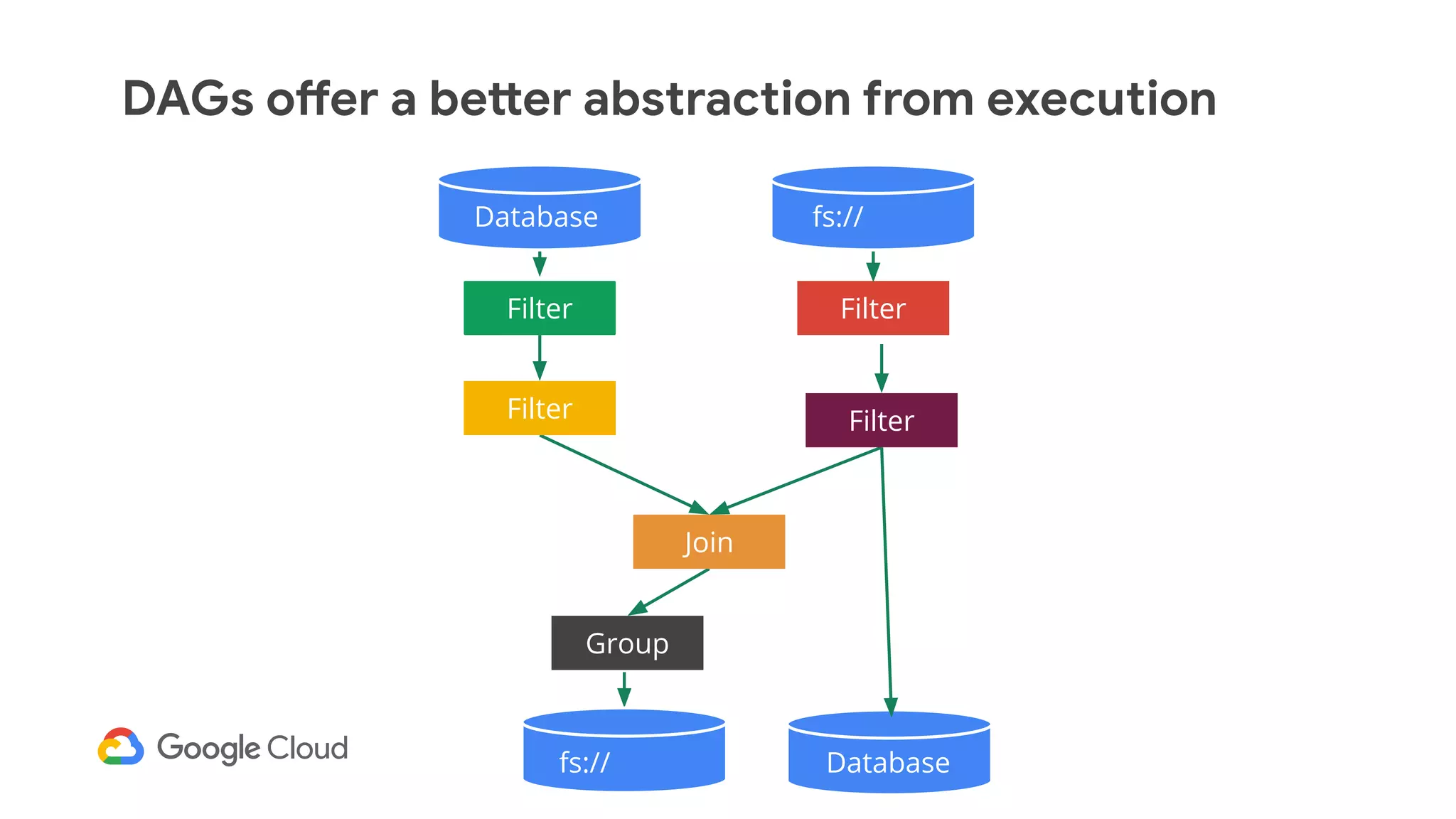
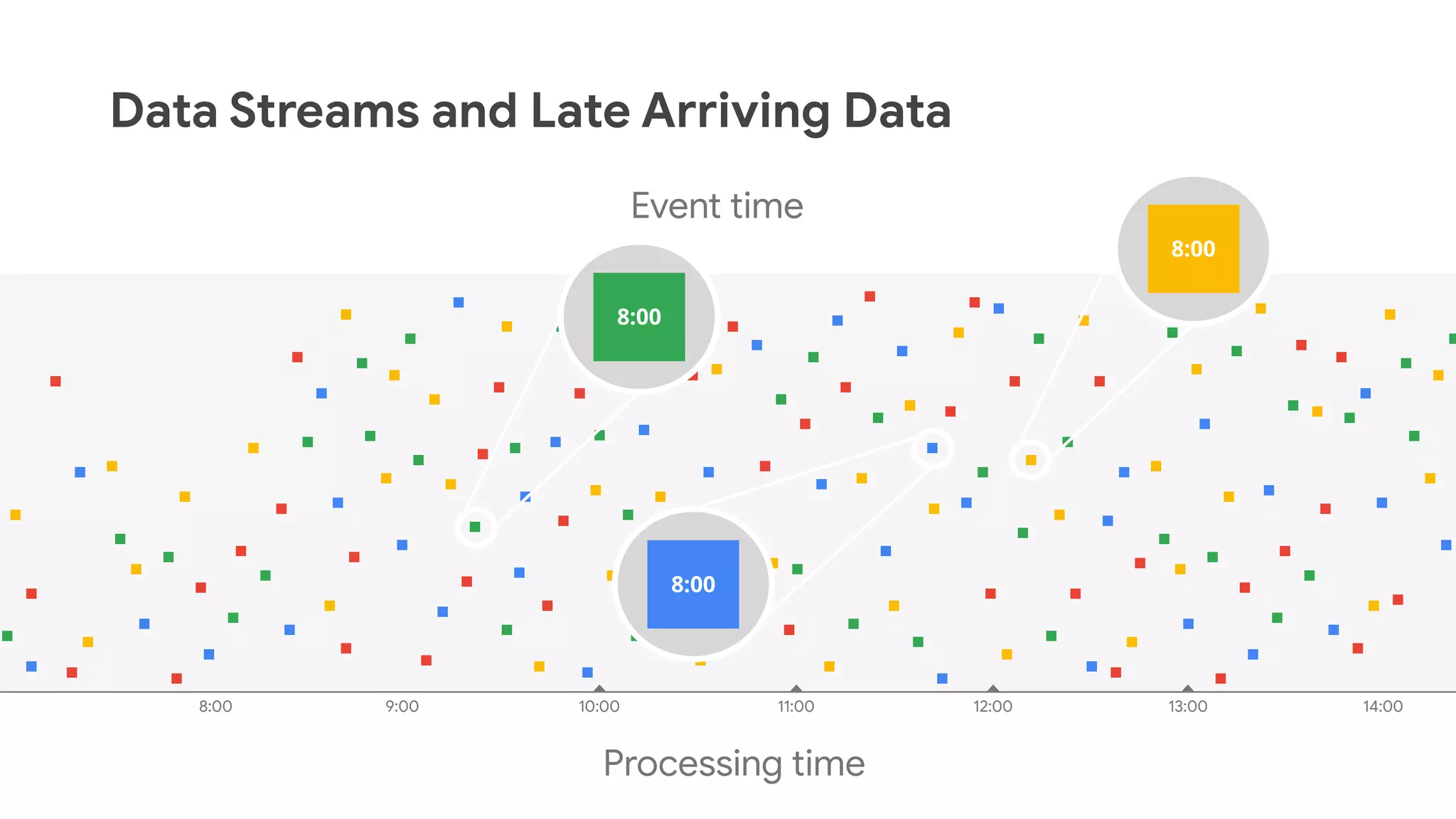
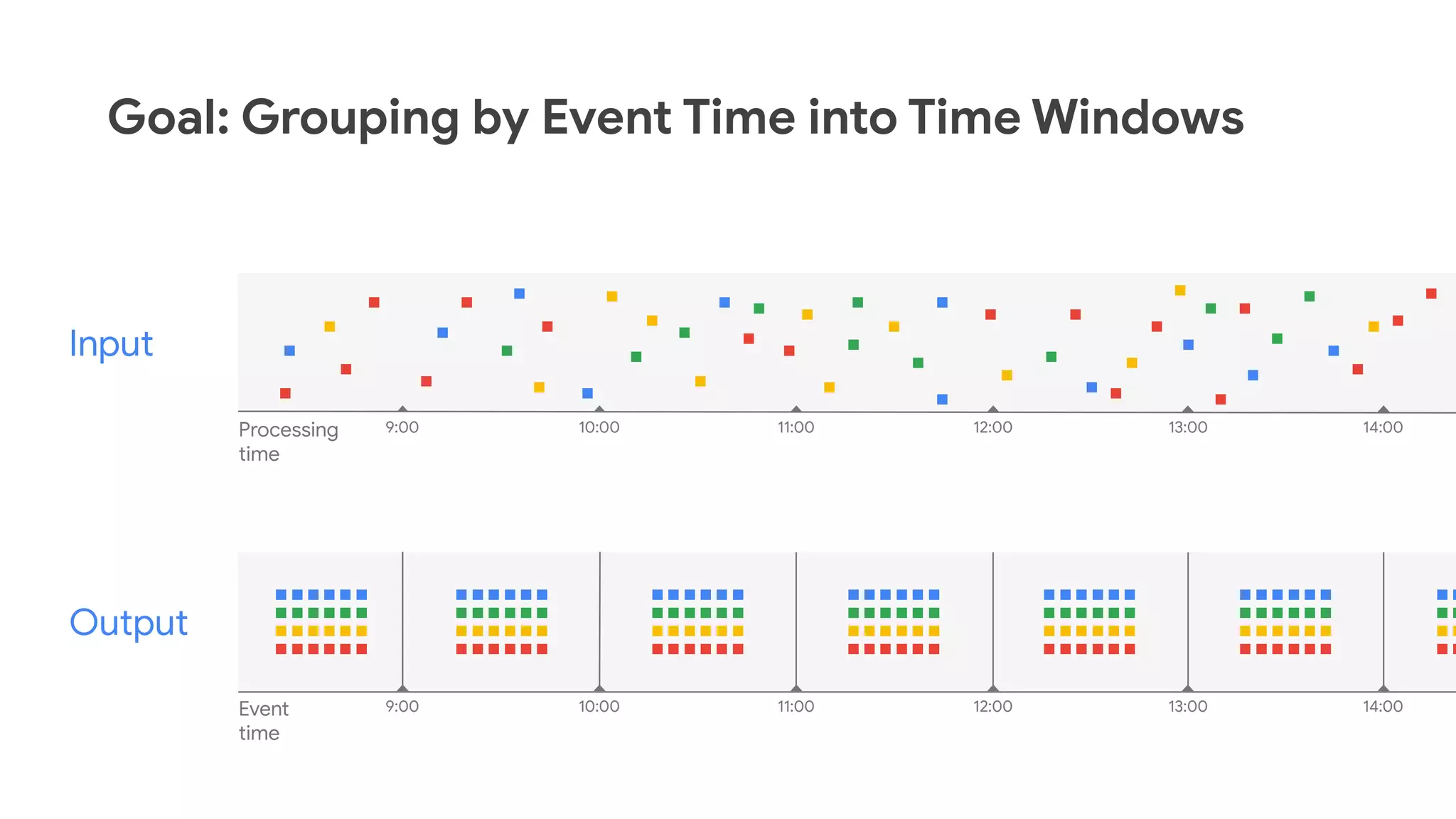
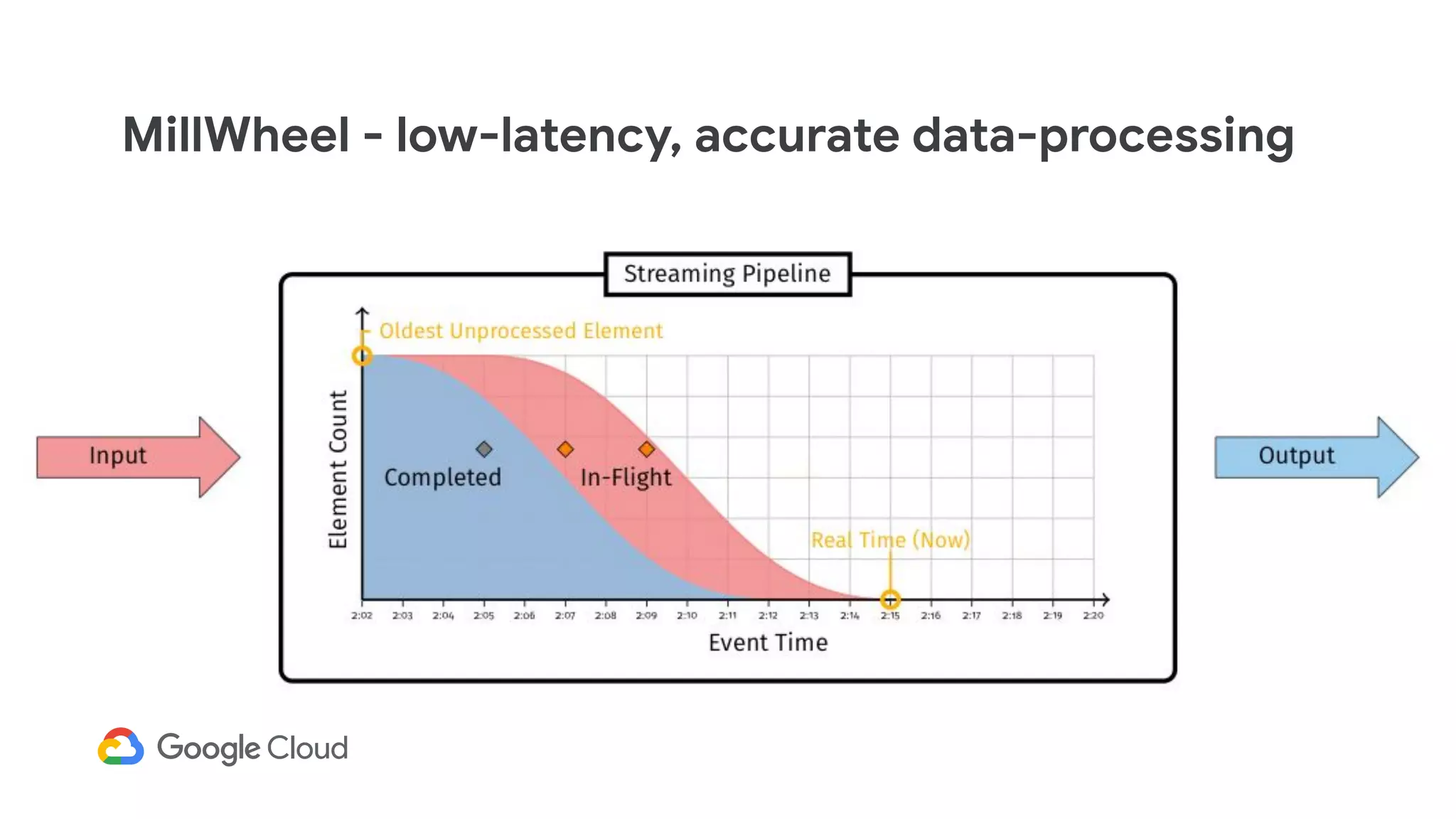
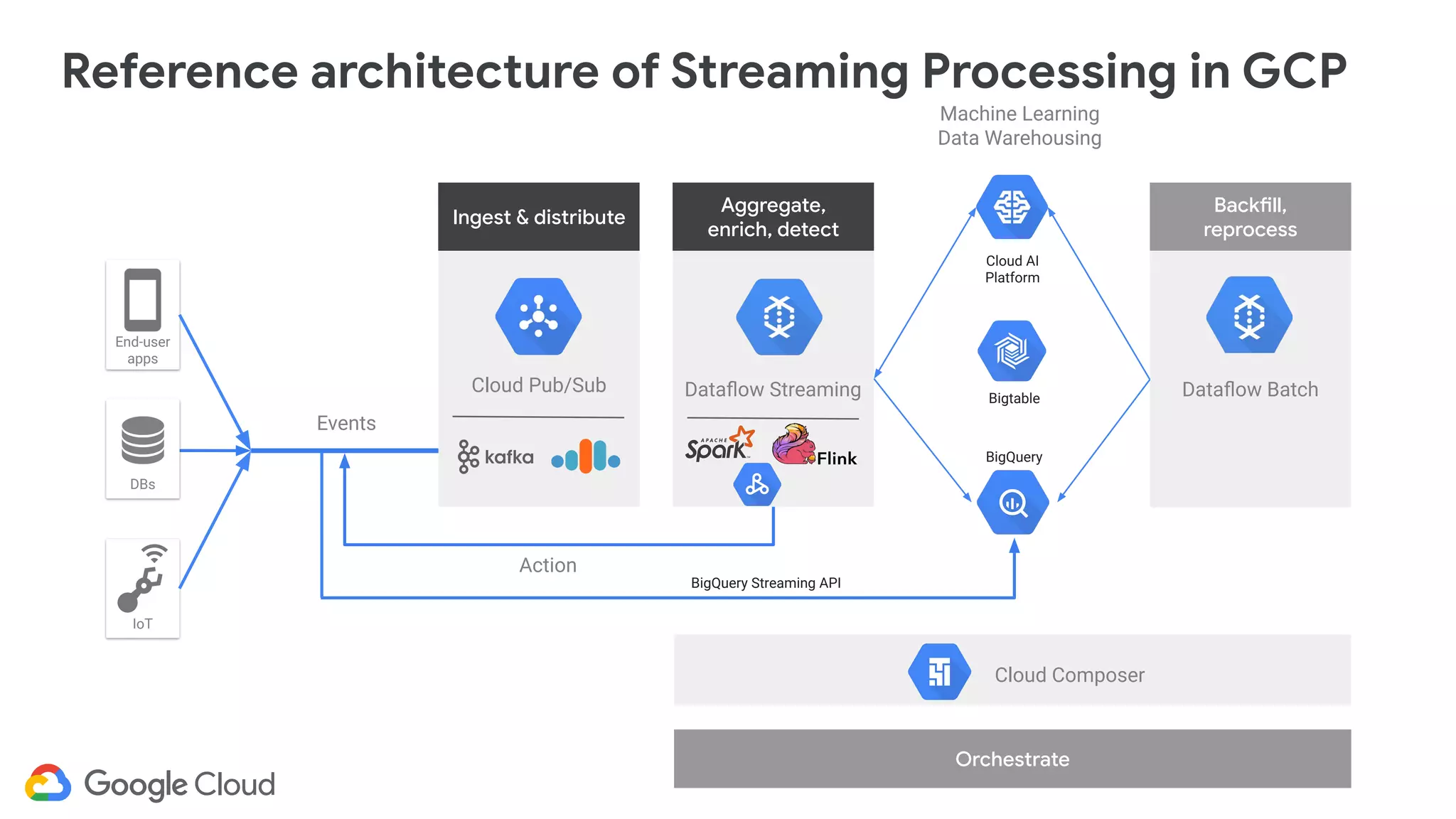
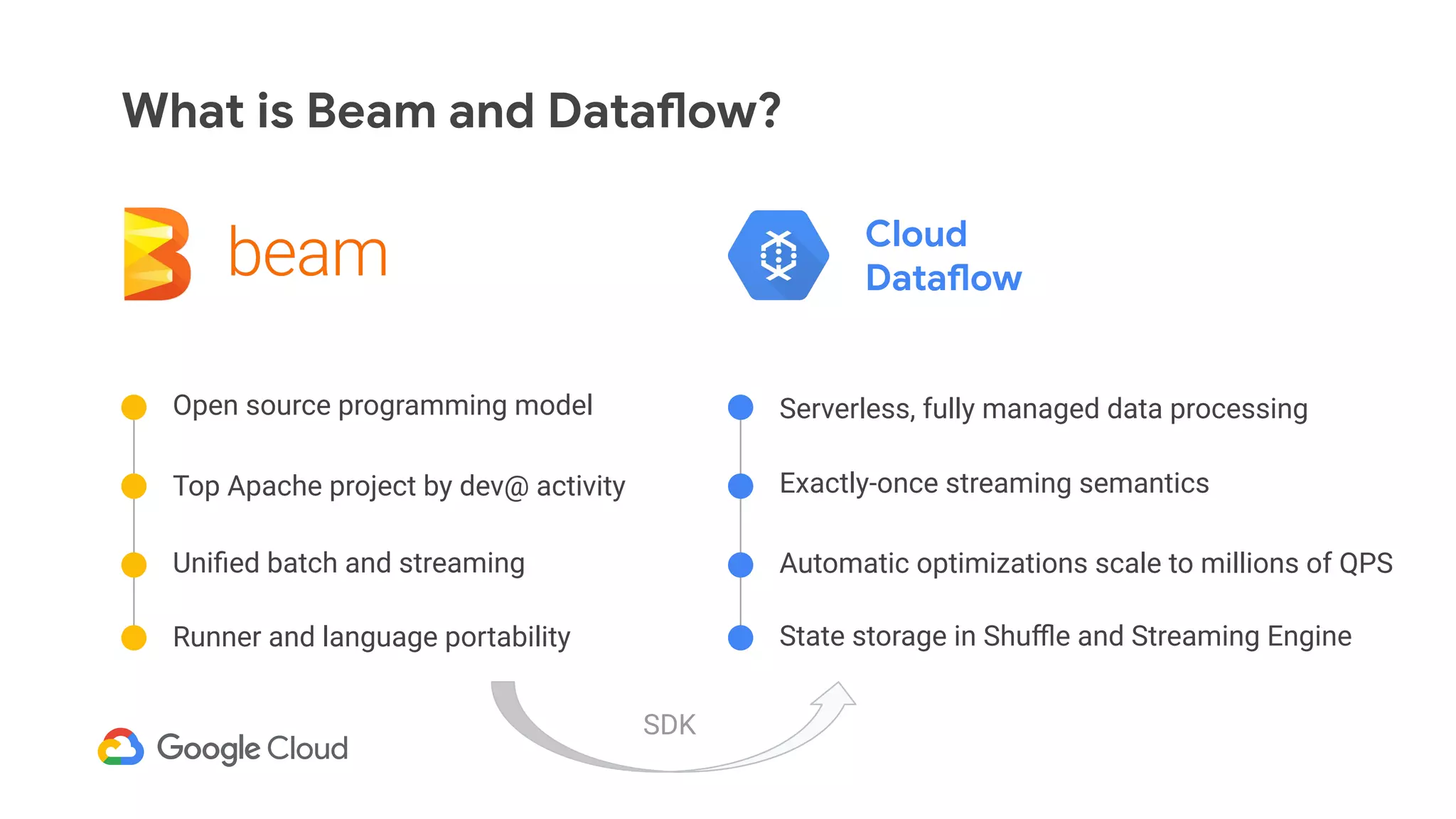
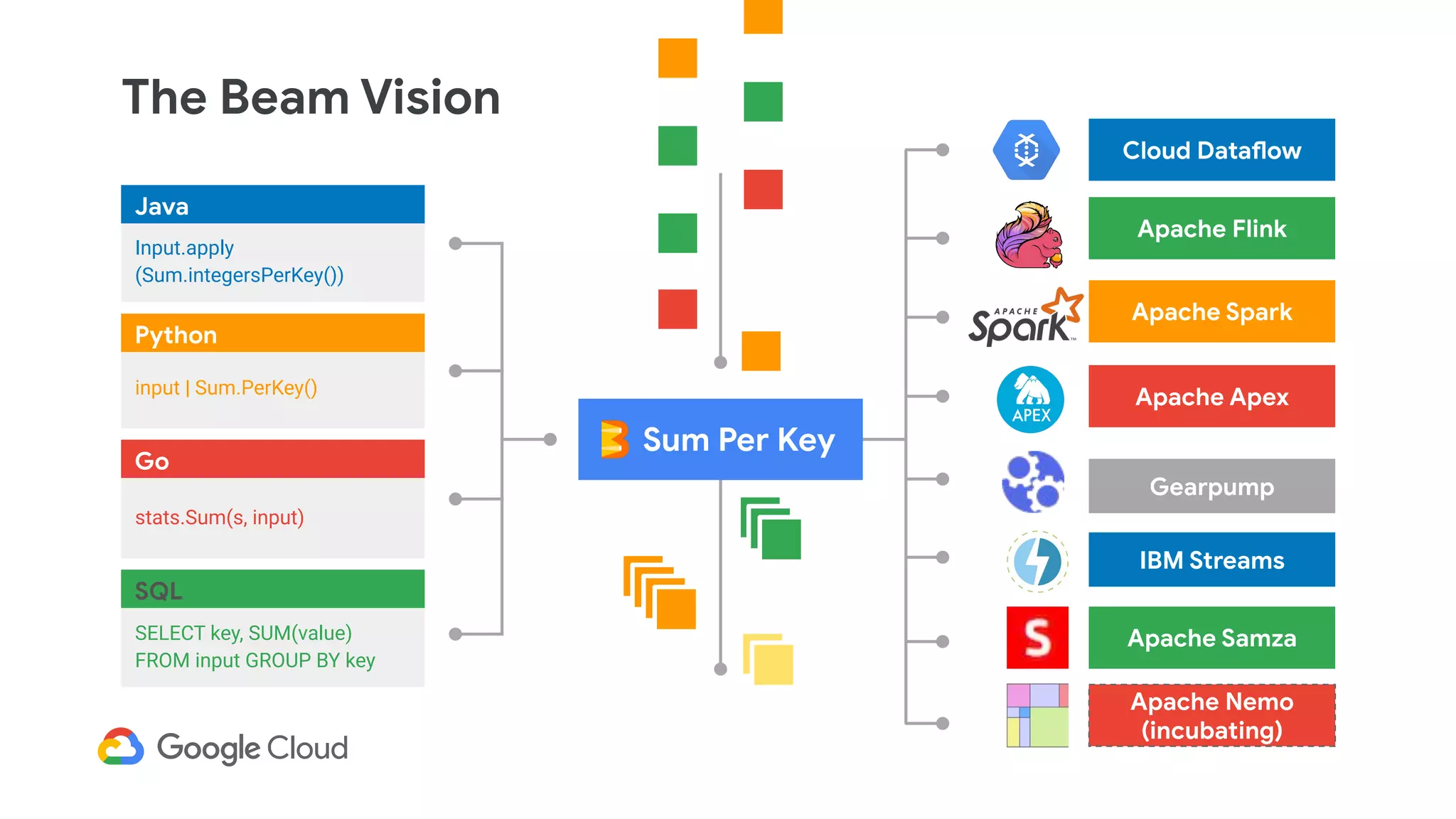
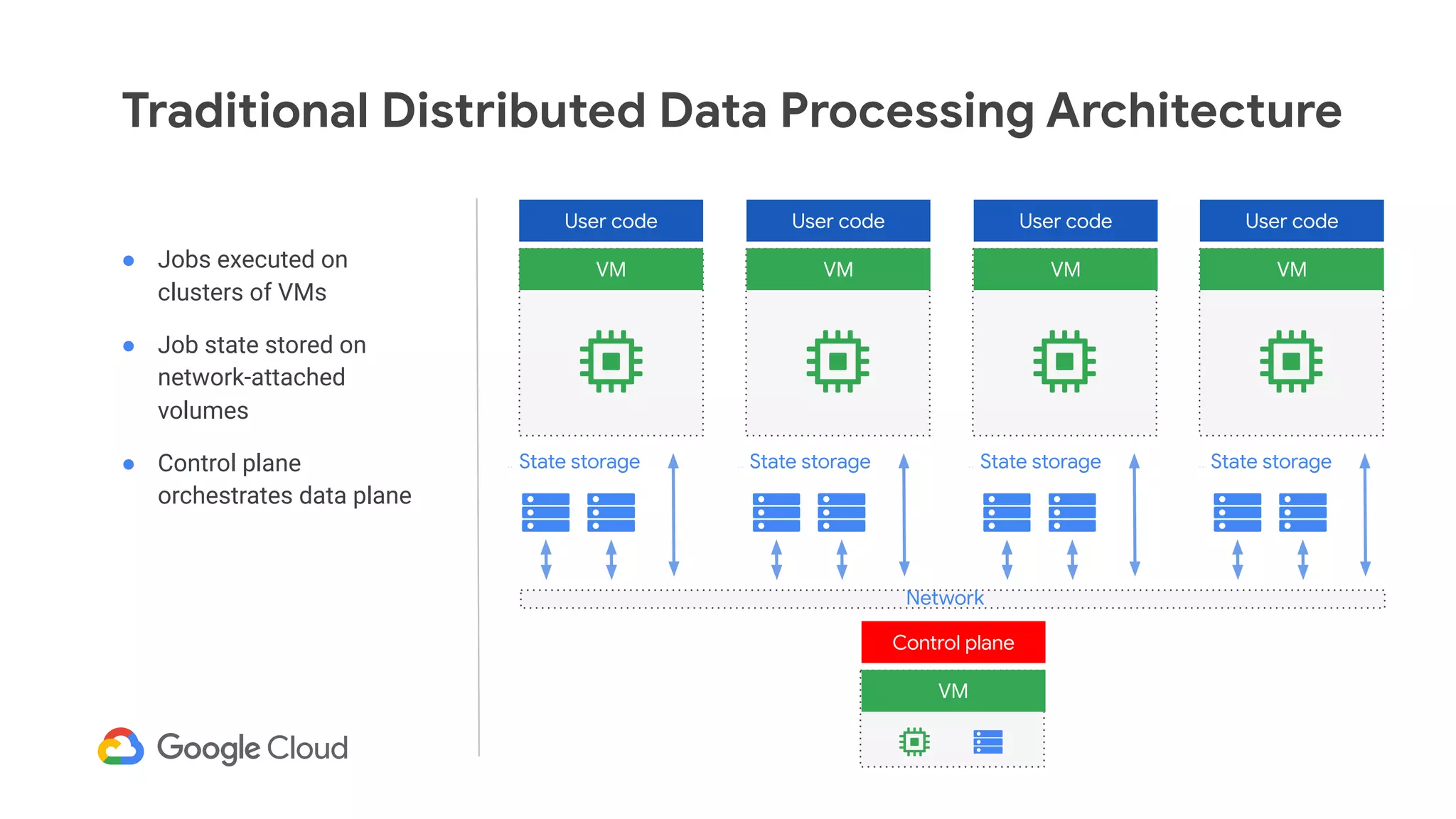
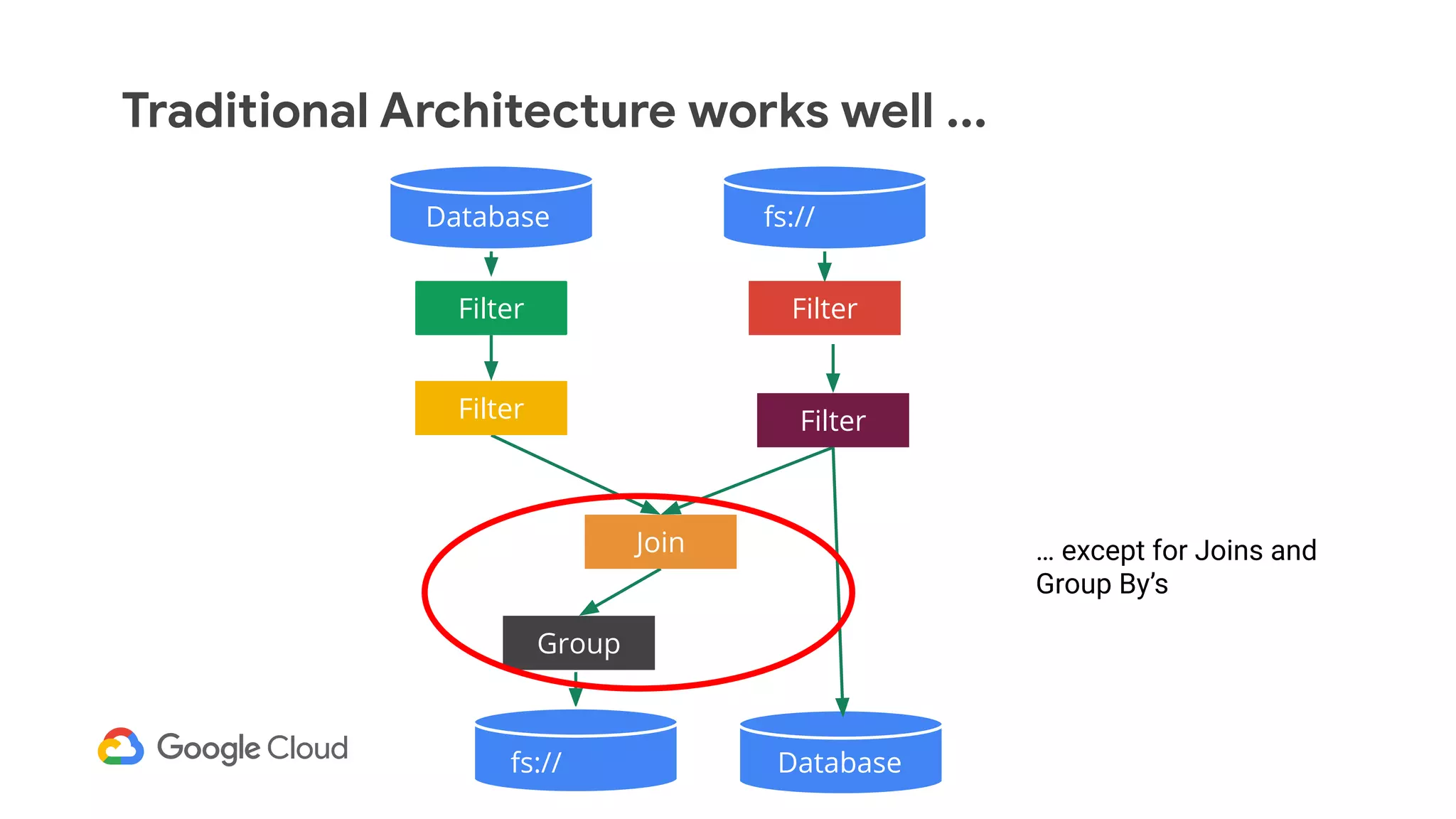
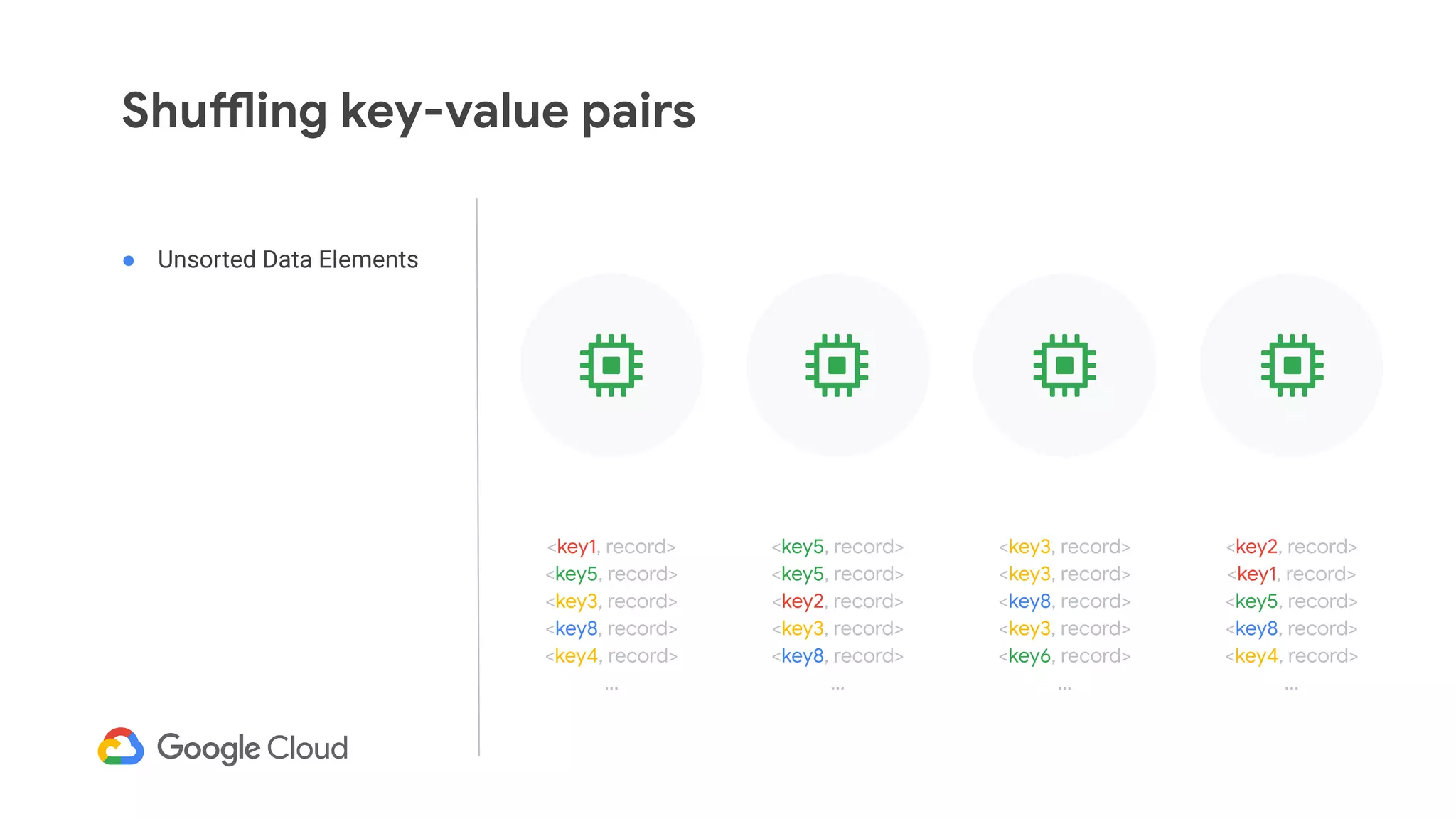
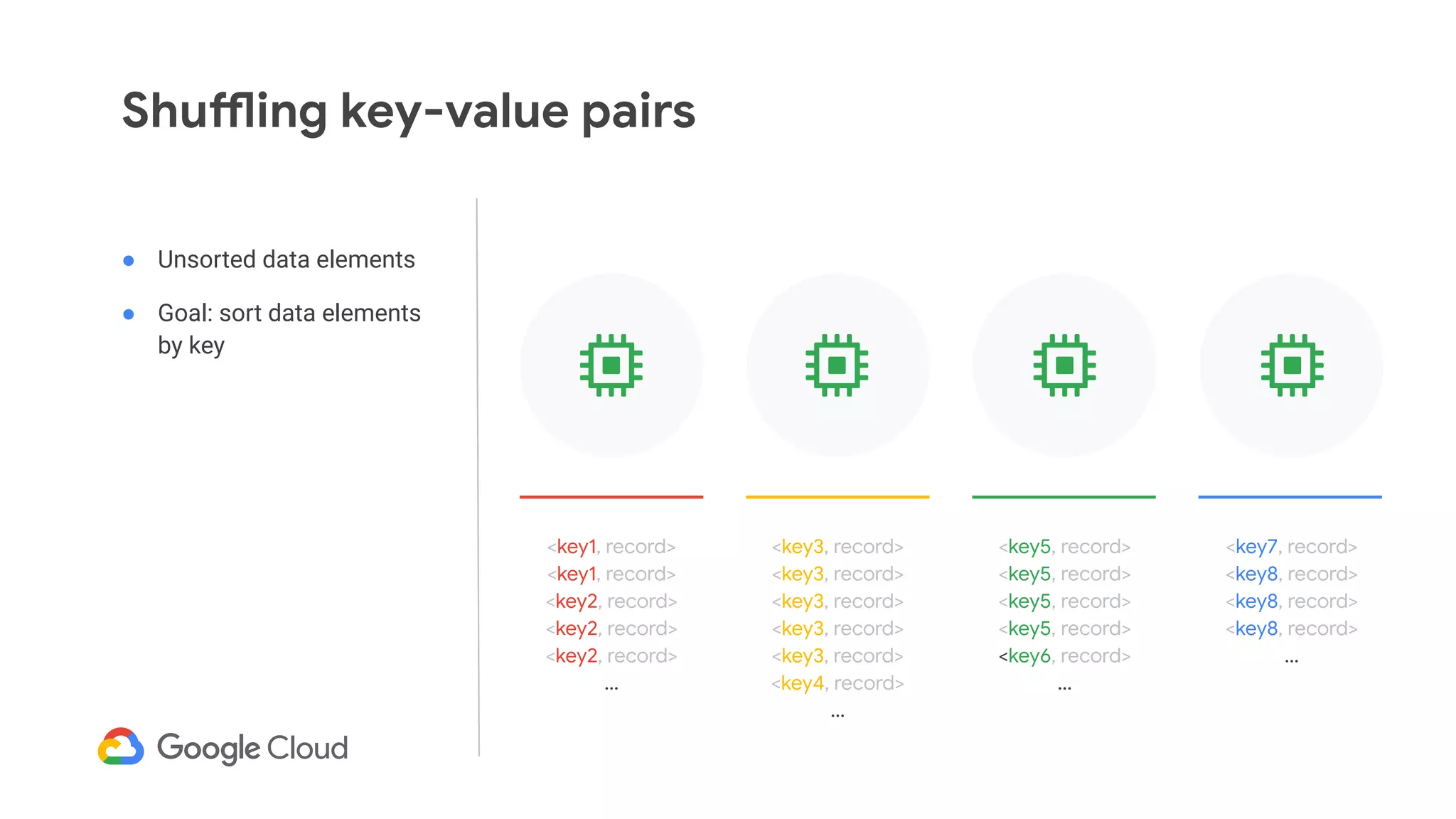
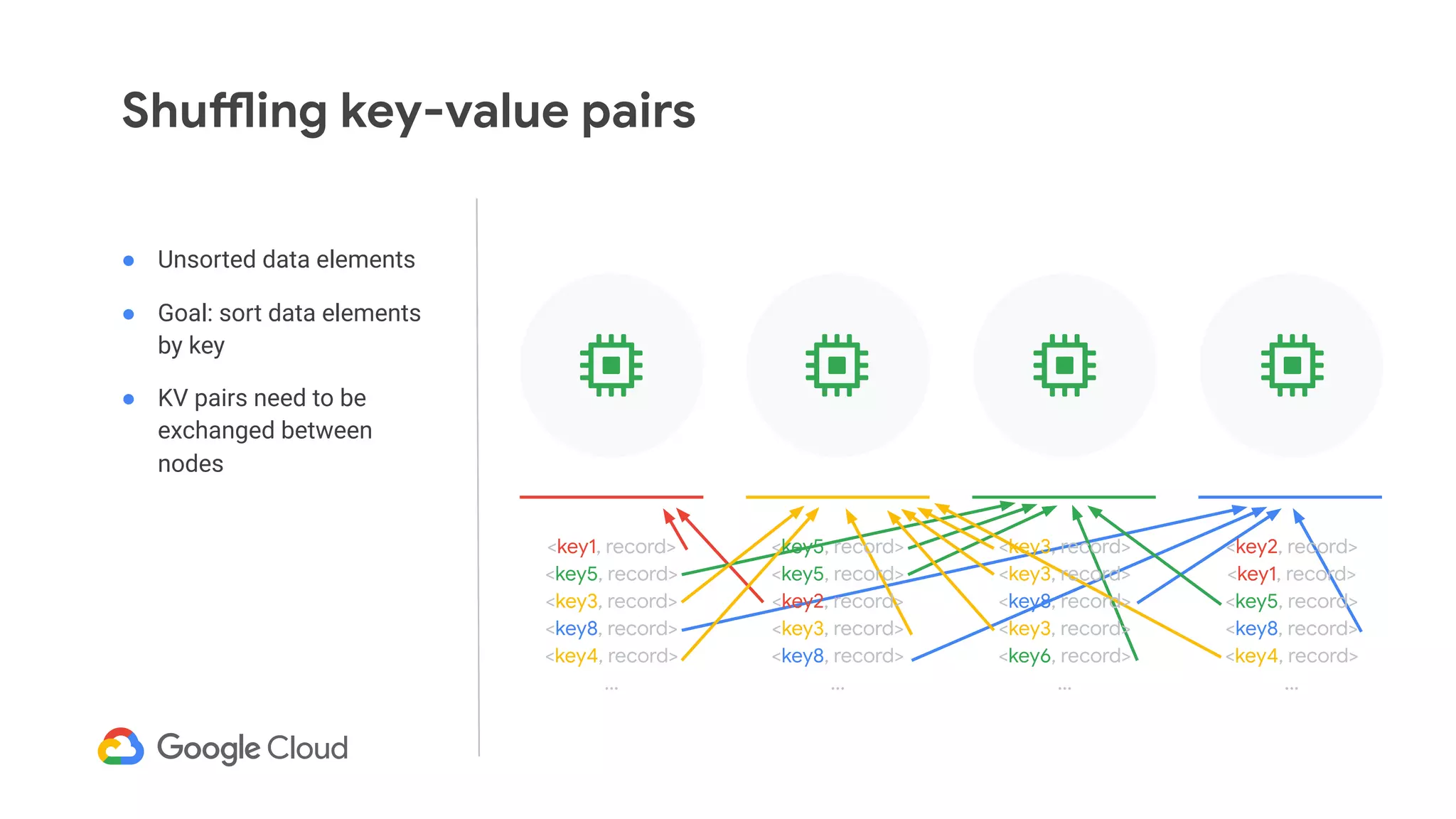
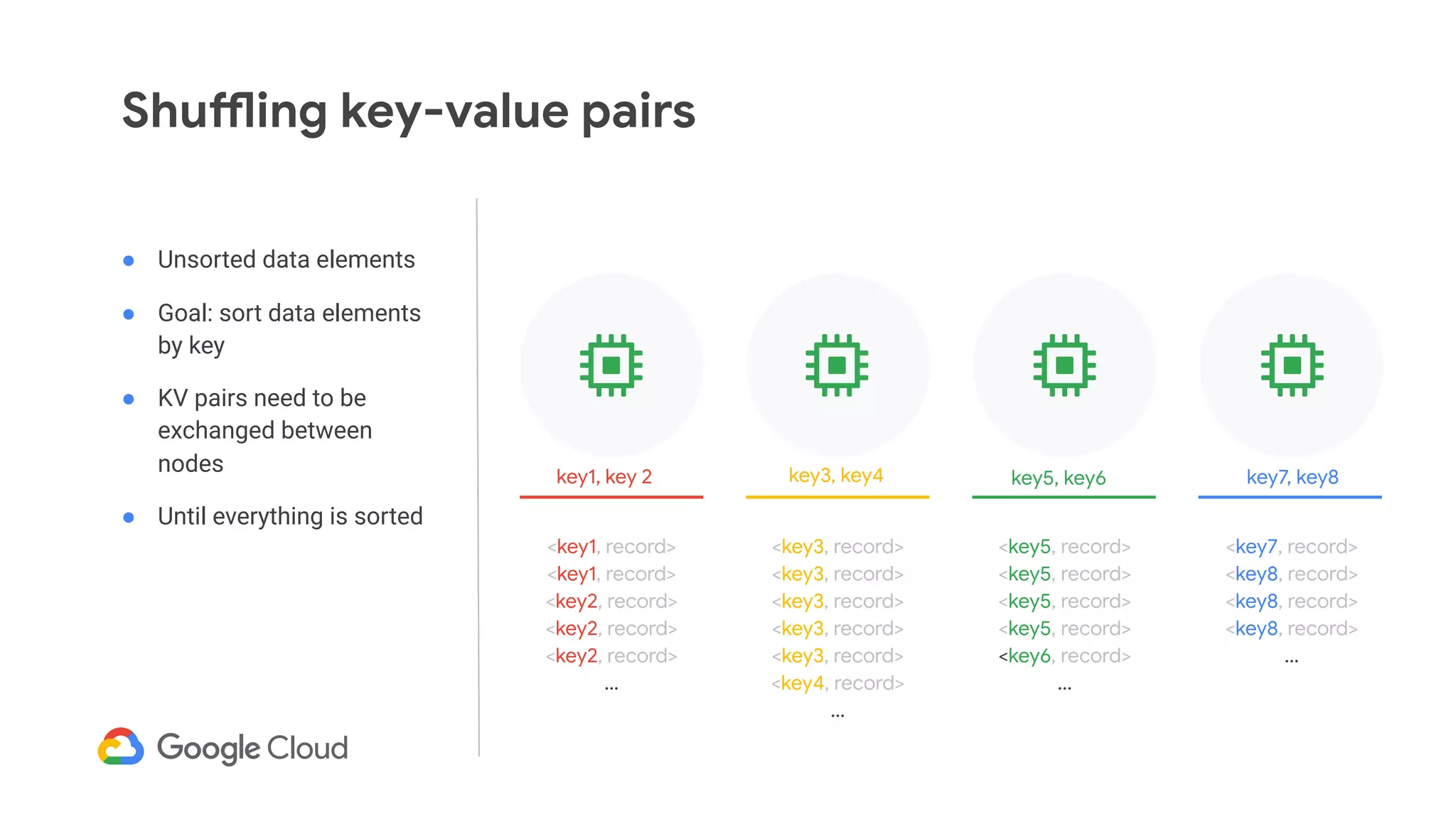
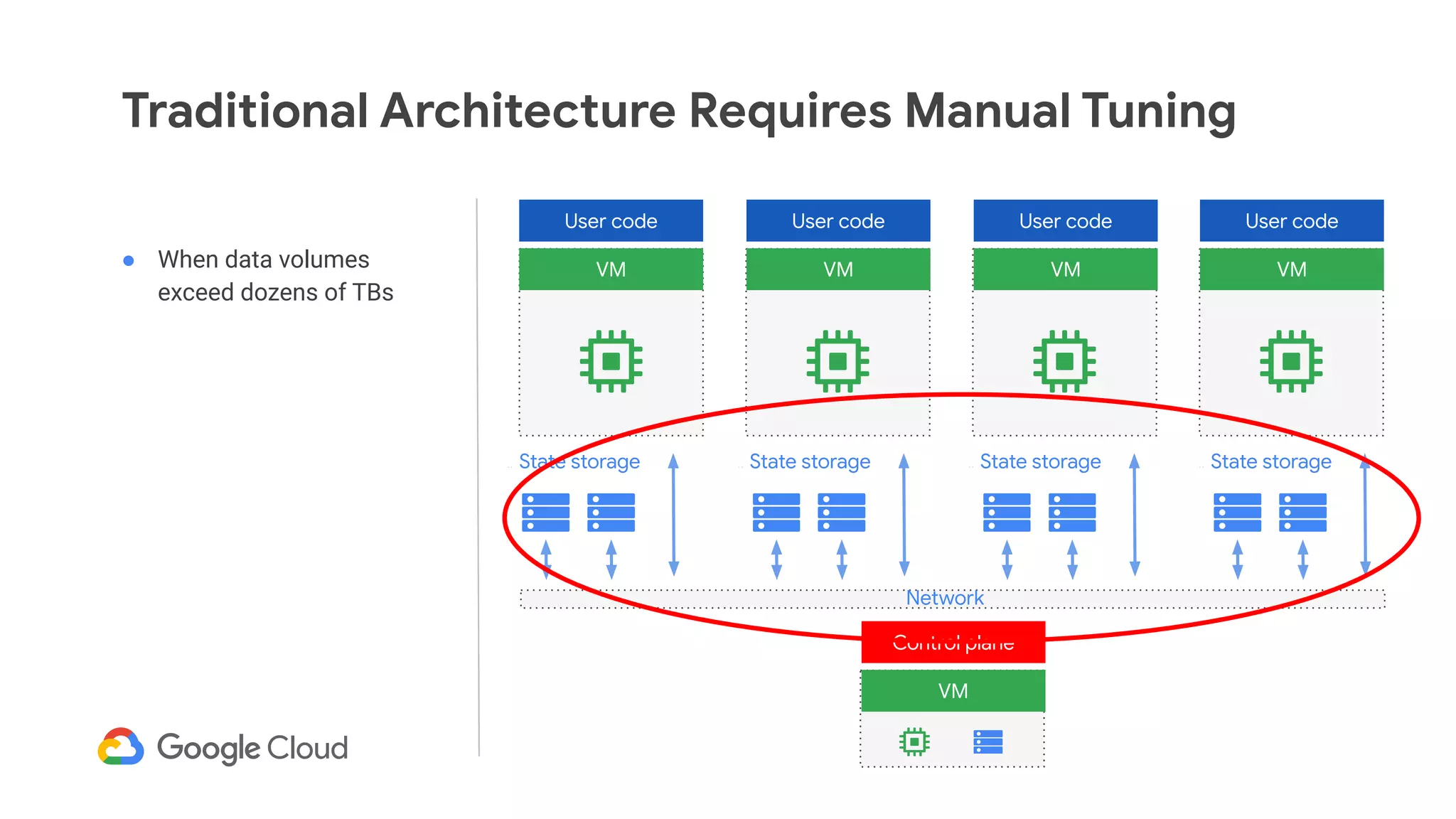
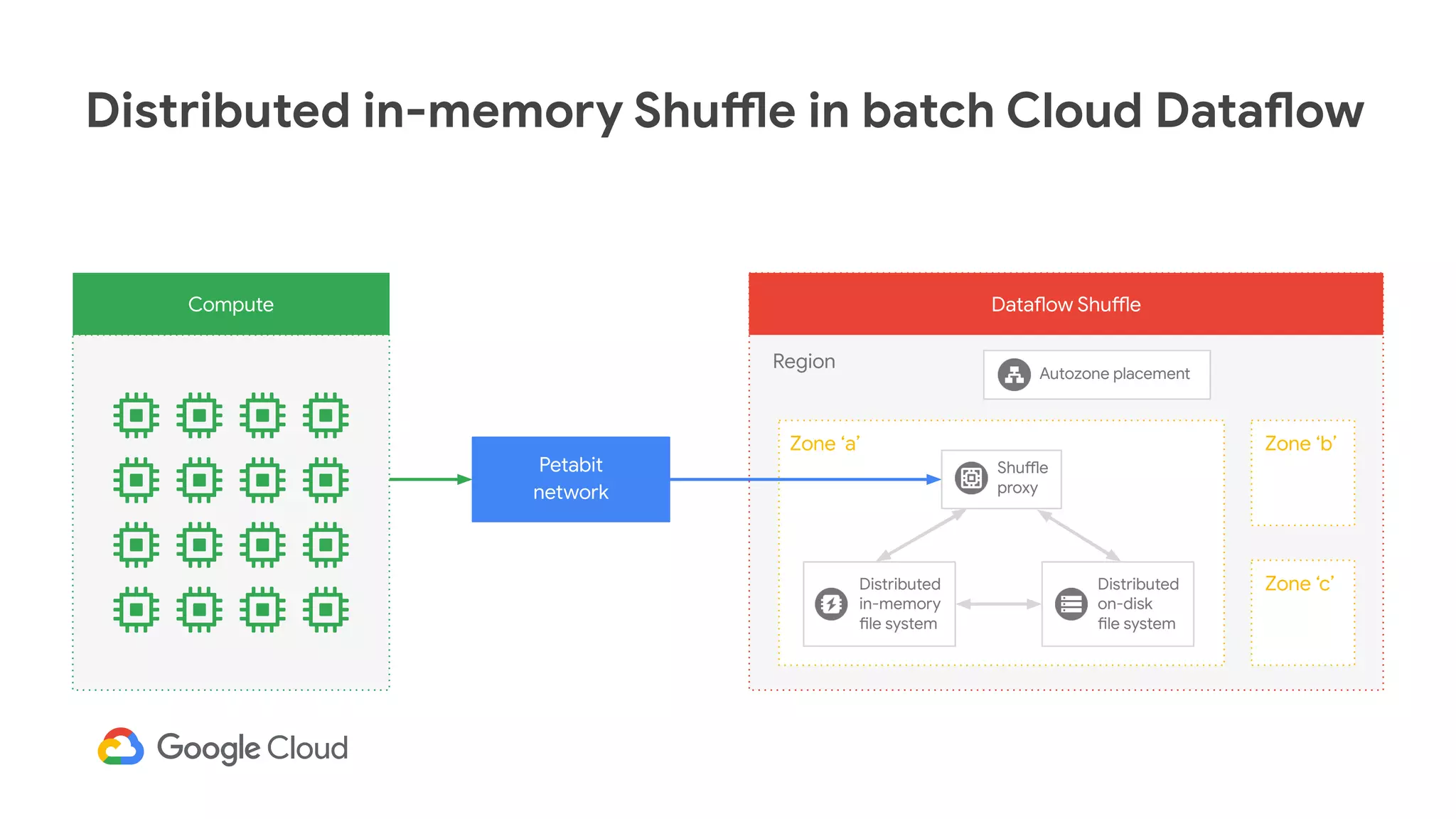
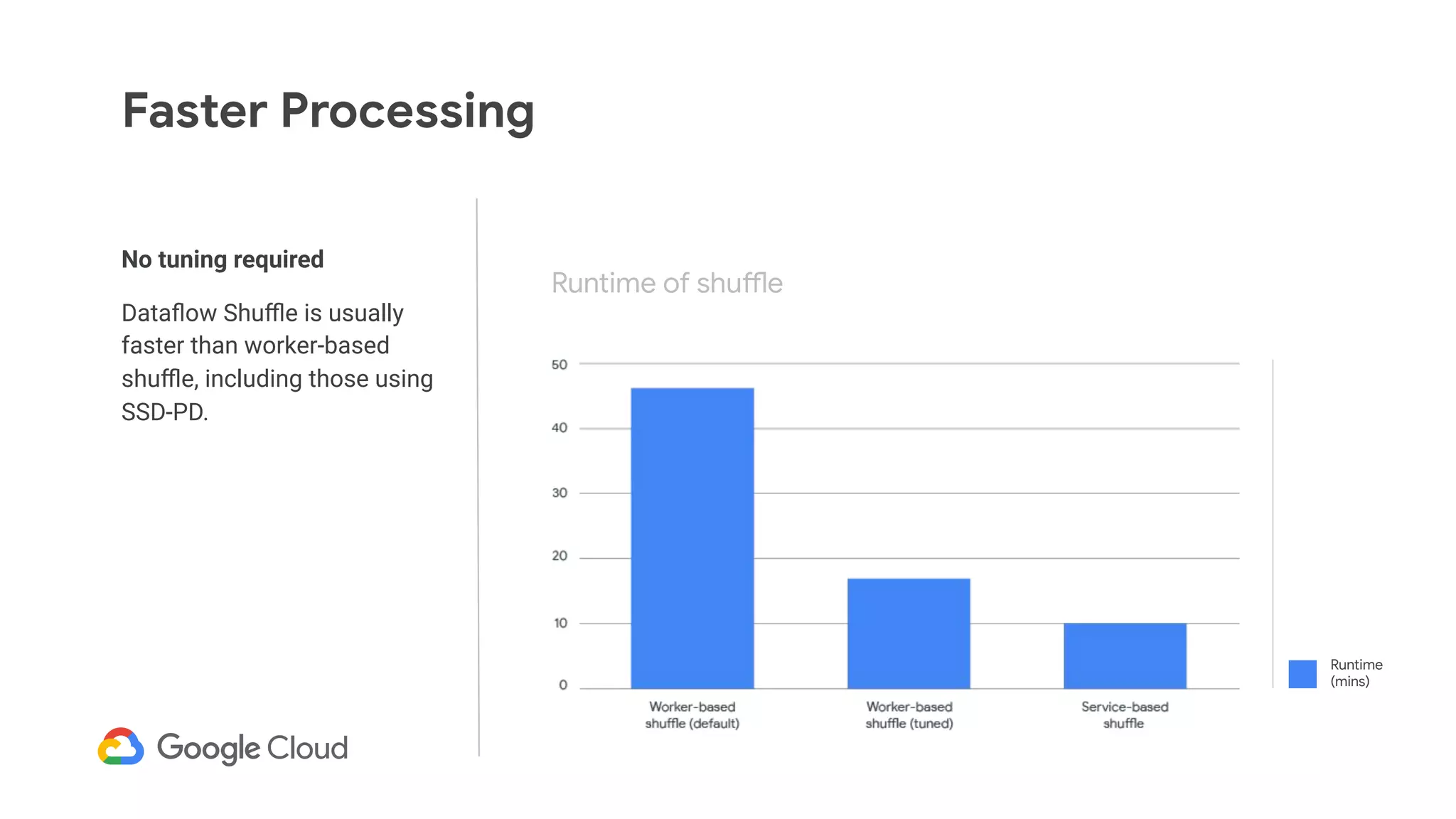
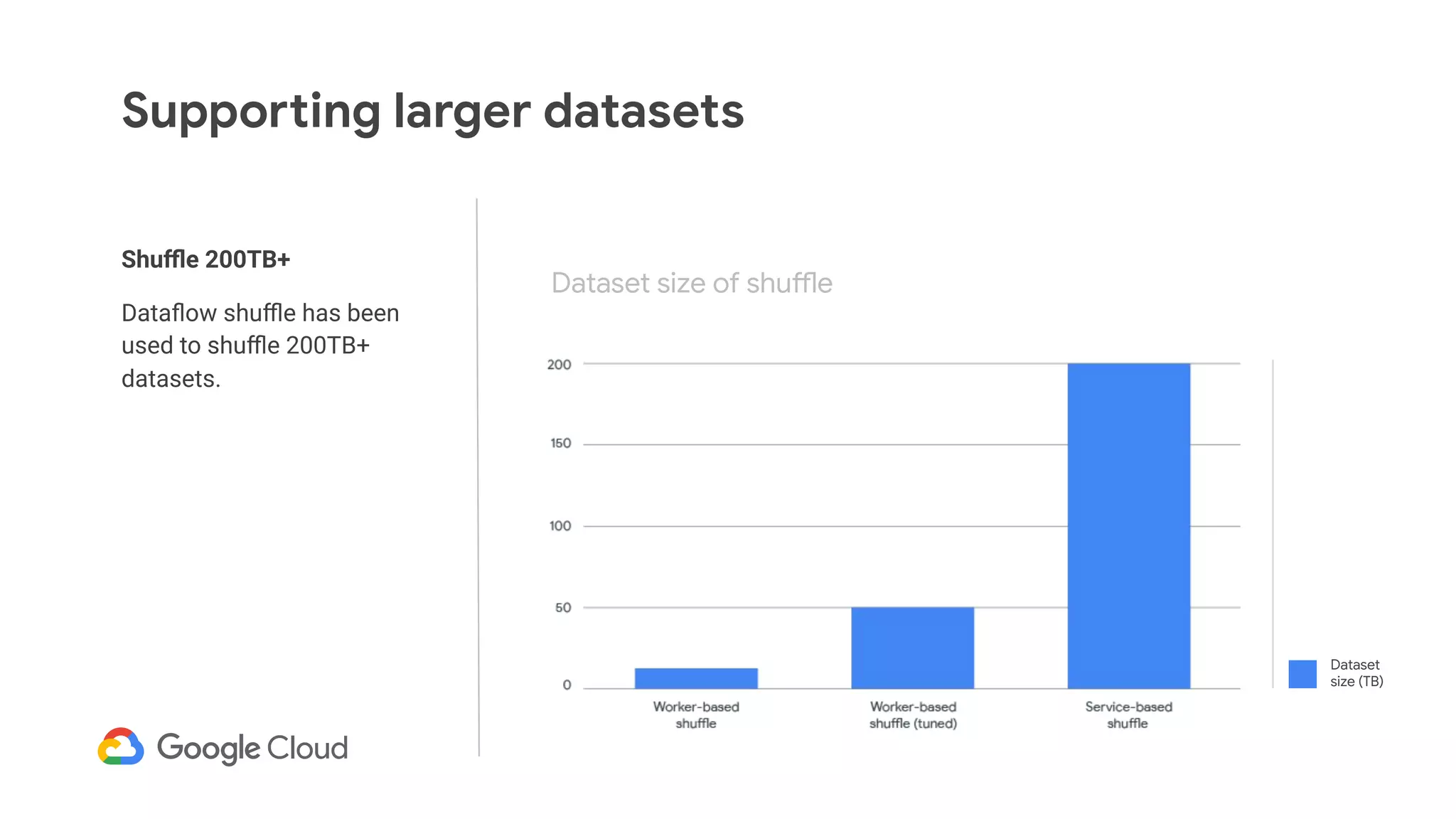
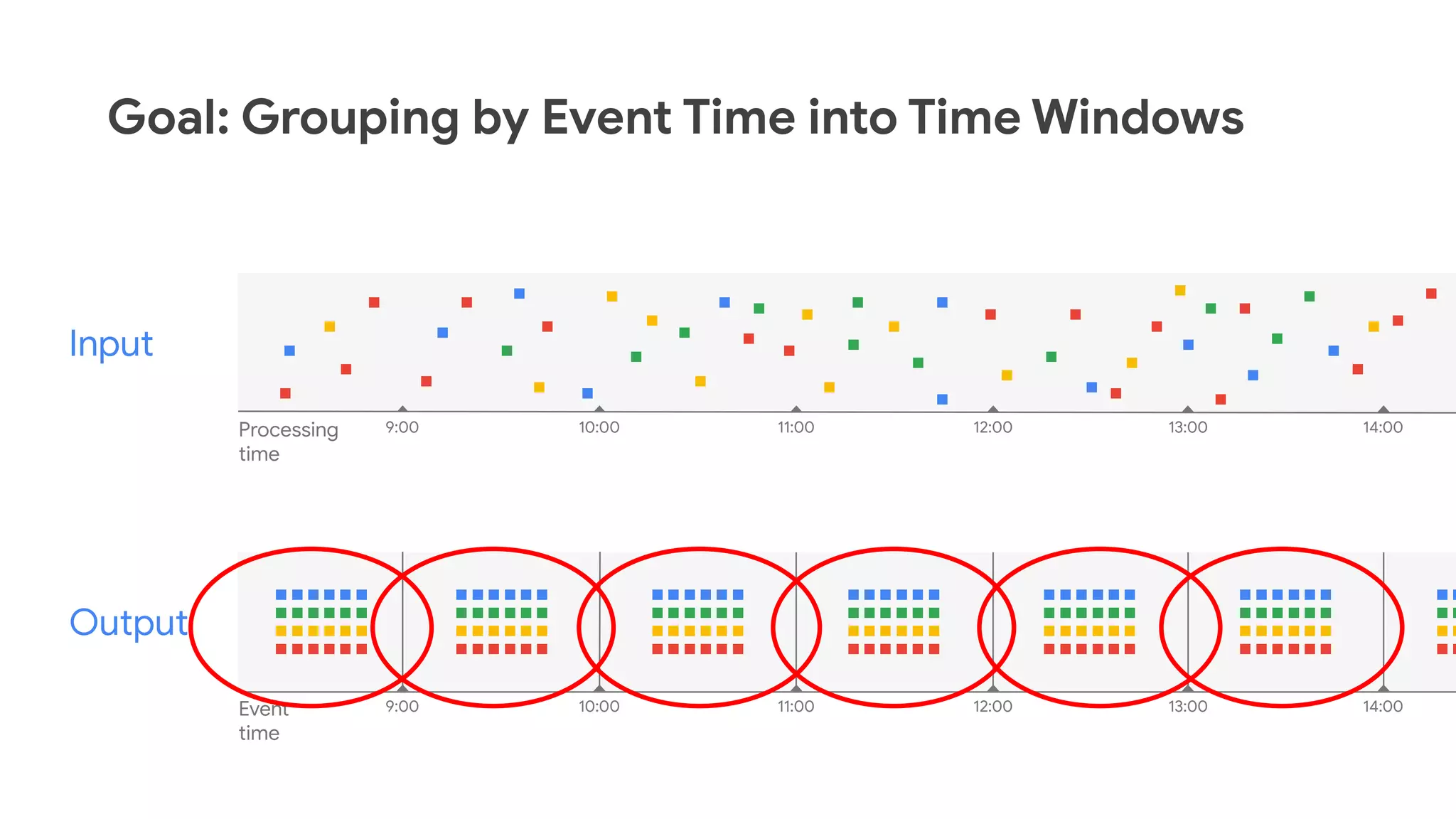
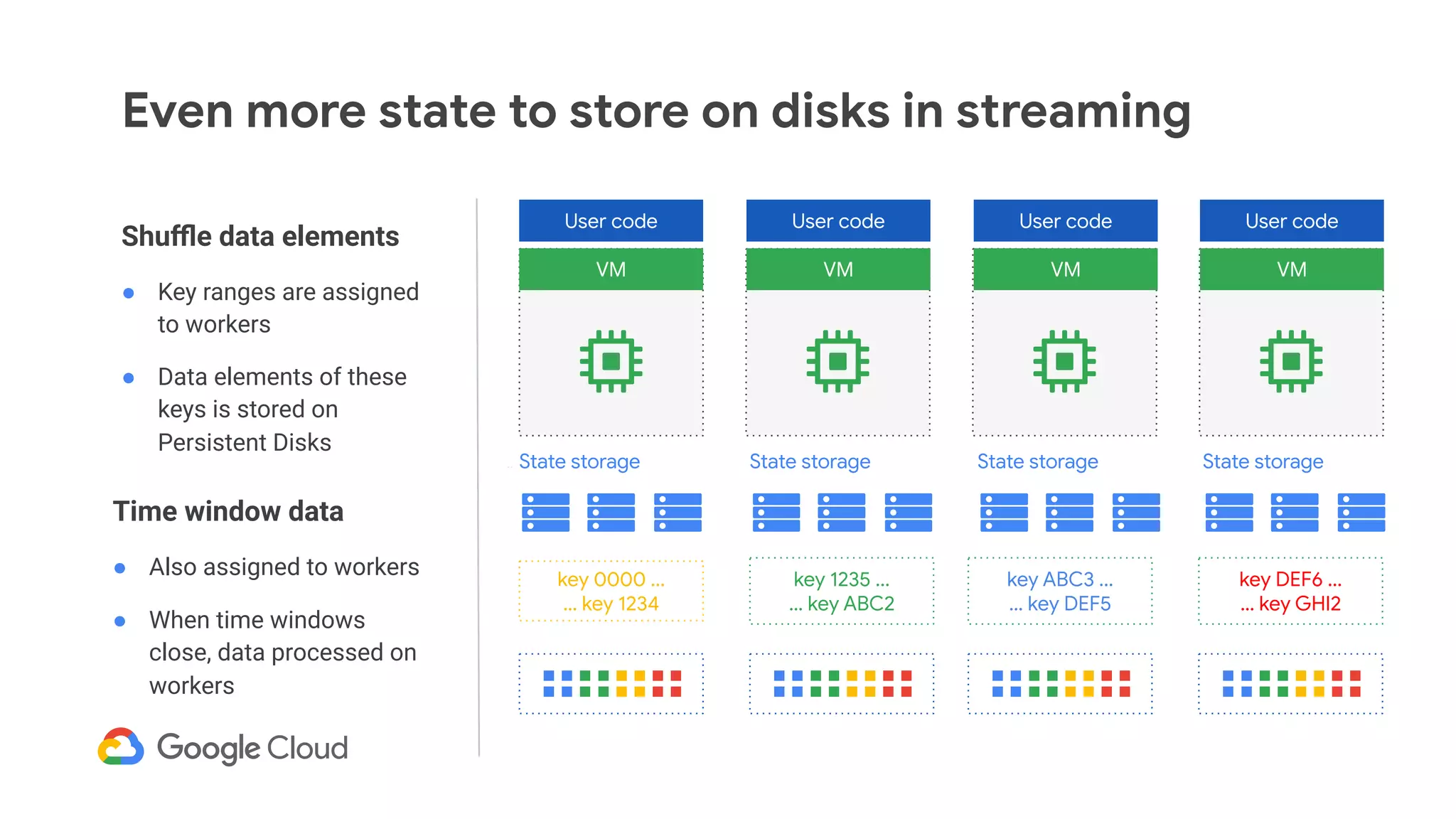
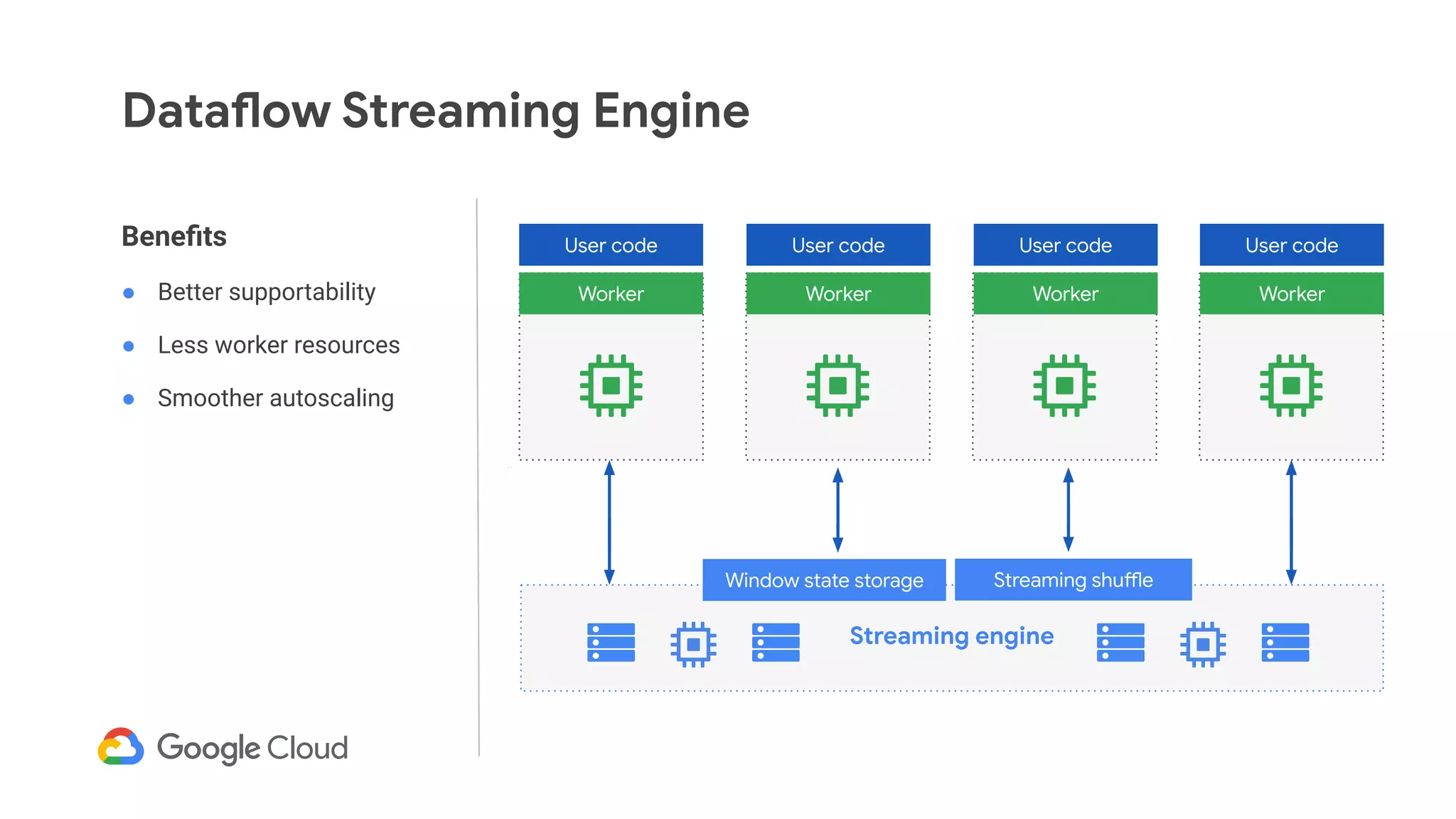
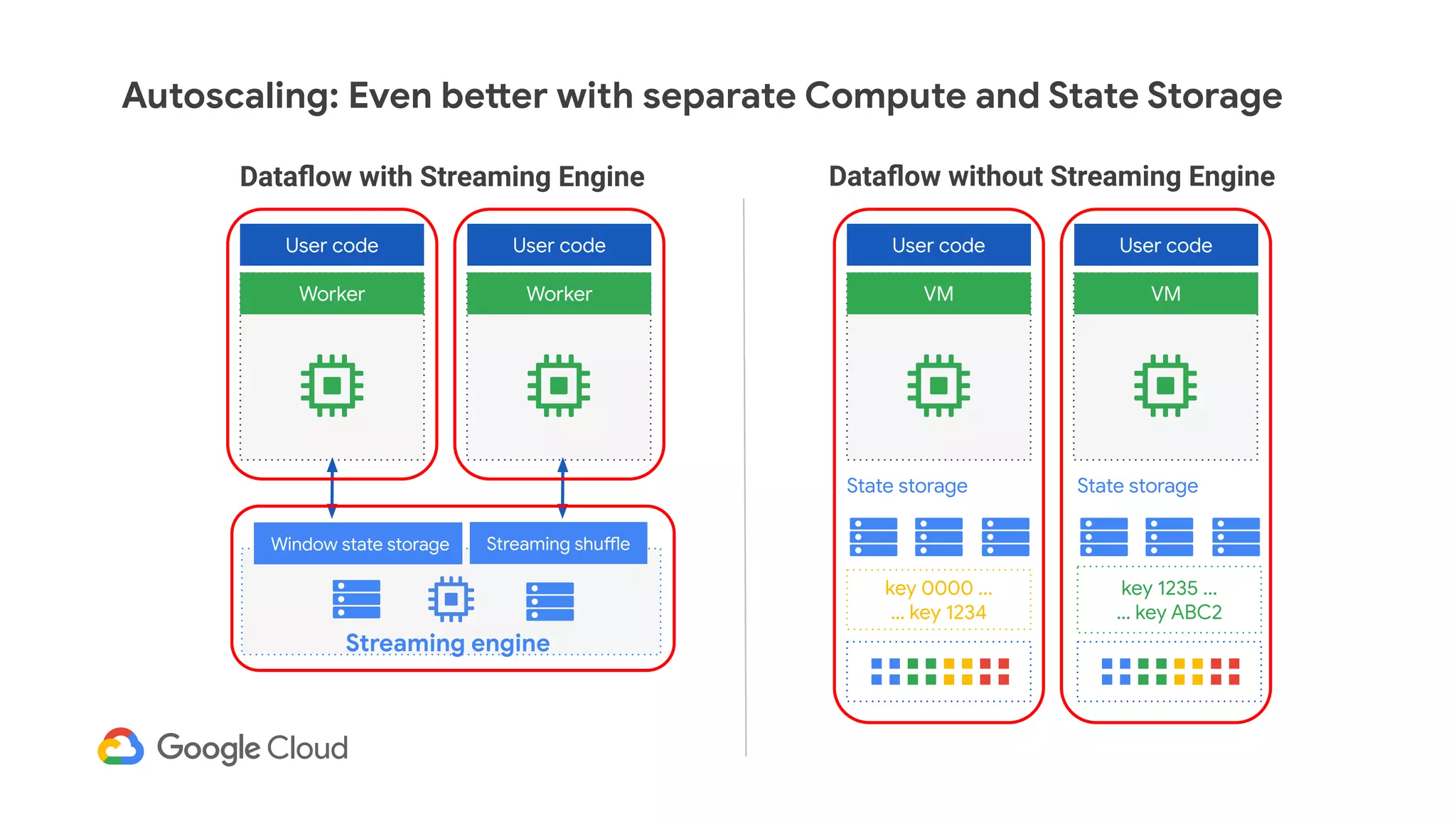
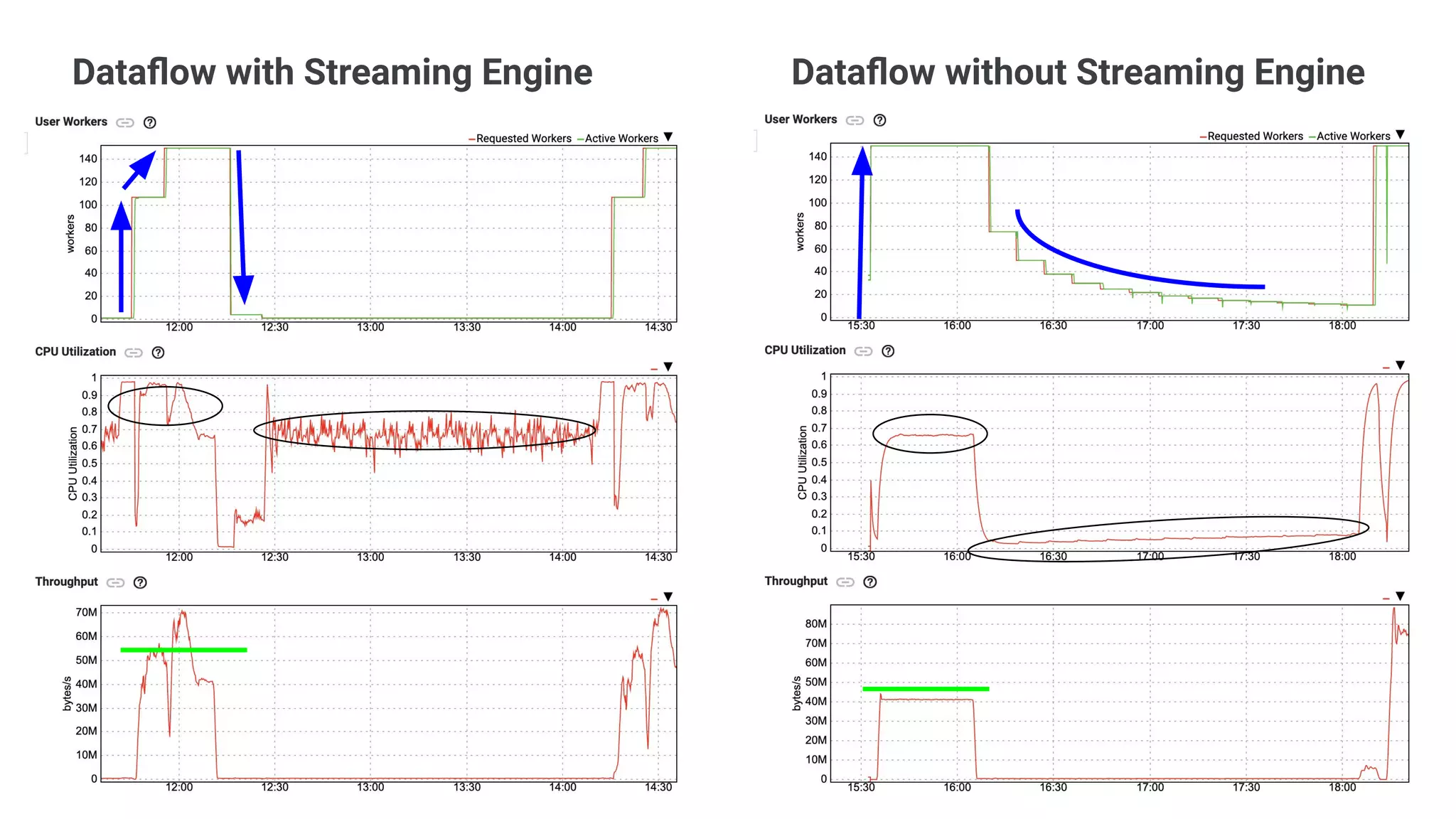
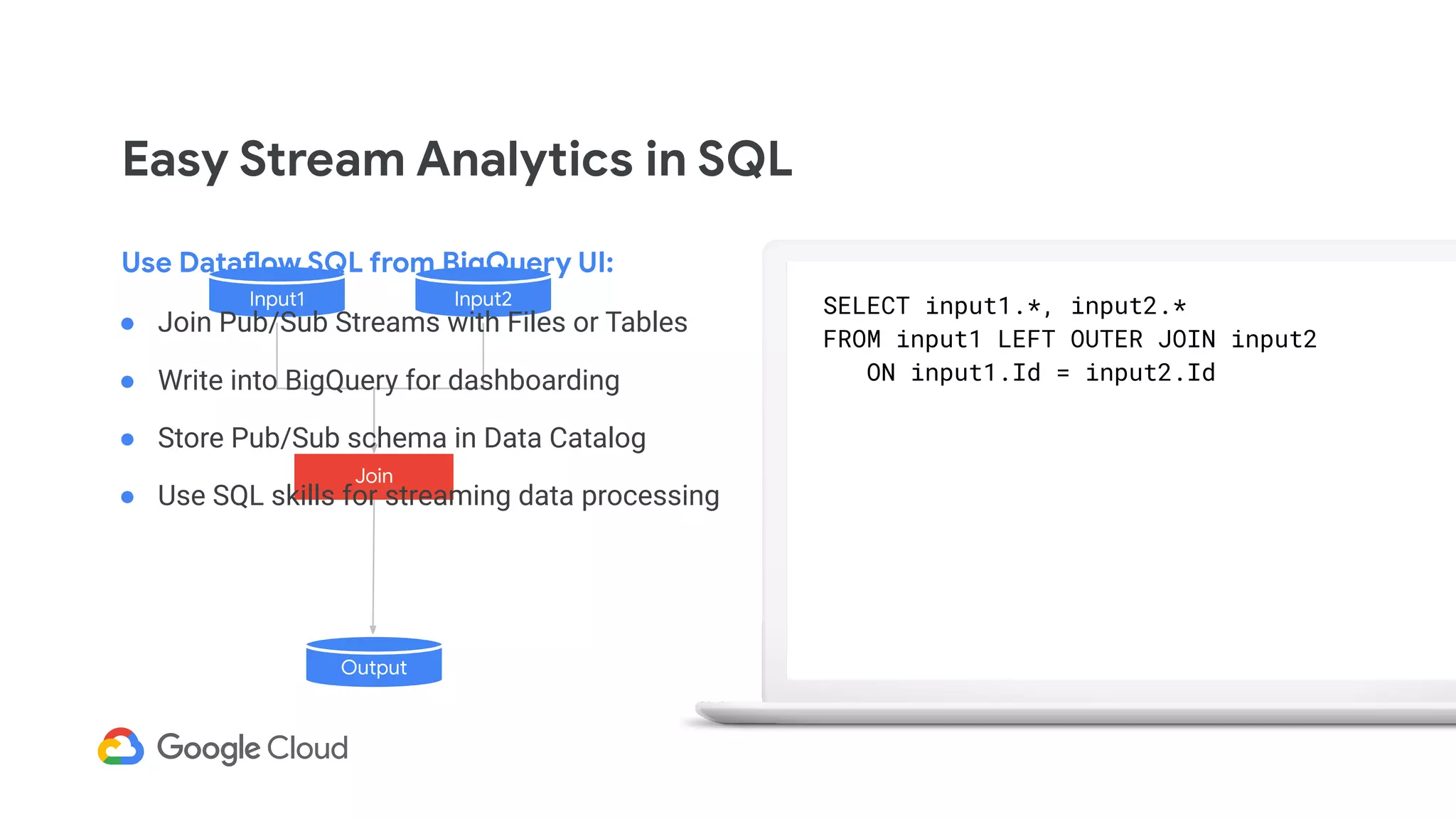
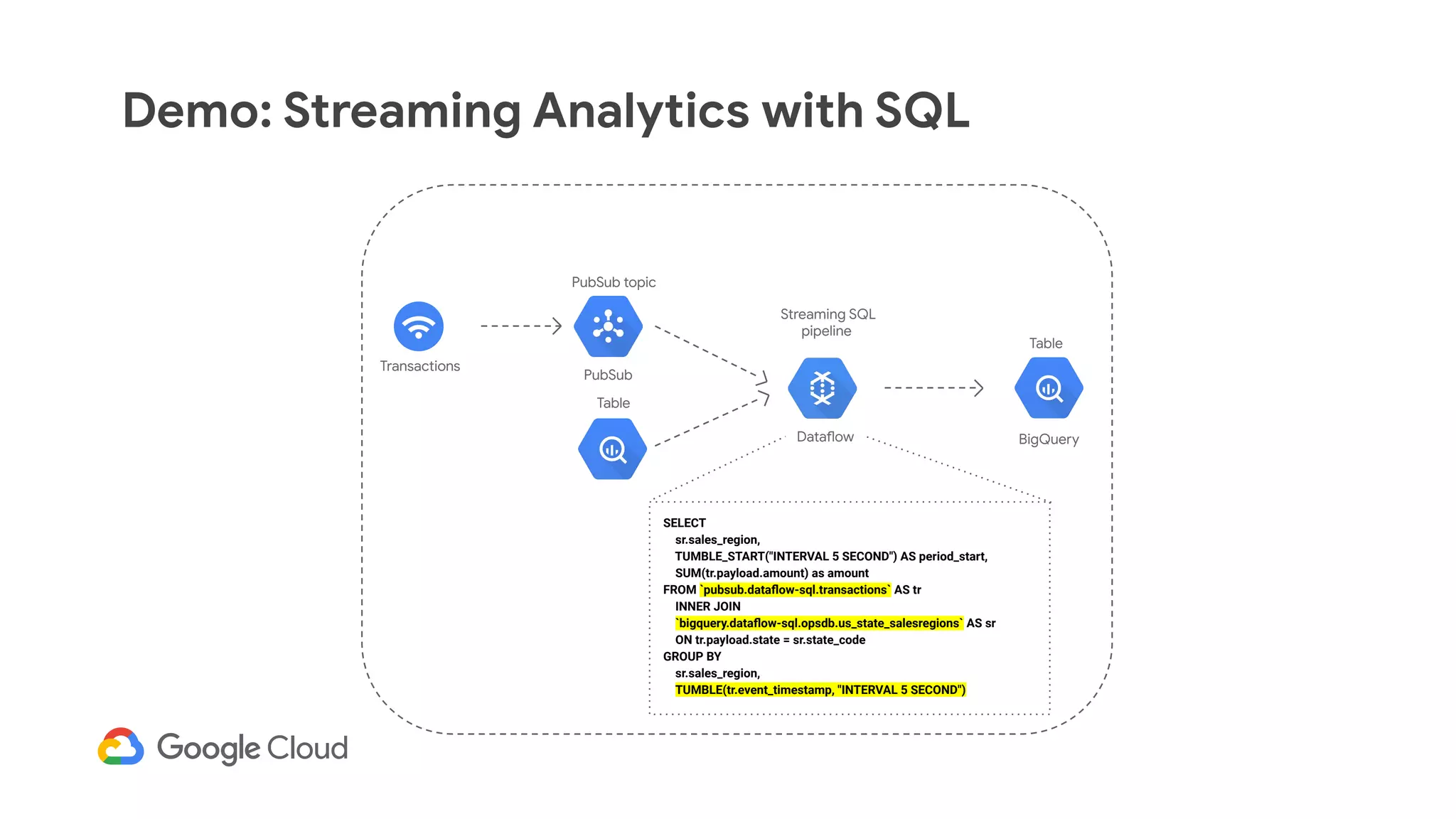
The document discusses advances in stream analytics utilizing Google Cloud Dataflow and Apache Beam, highlighting the benefits of separating state storage from compute for improved scalability and performance. It emphasizes the growing importance of real-time data processing and the tools available within Google Cloud for managing both batch and streaming data. Additionally, the document outlines various infrastructure components, architecture, and demonstrations of simplifying streaming analytics through SQL.