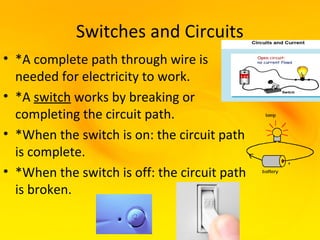
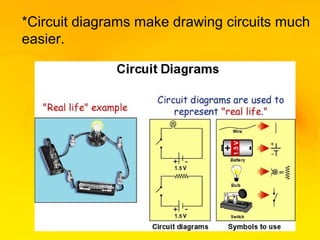
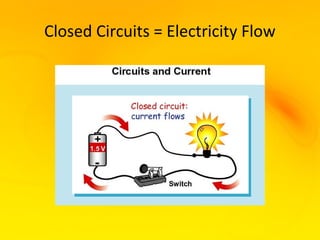
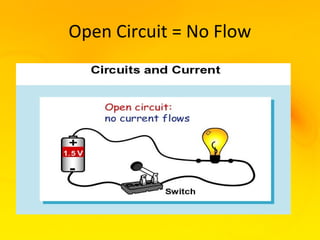
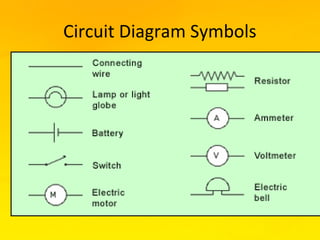
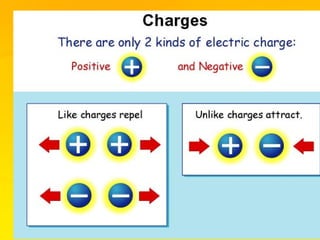
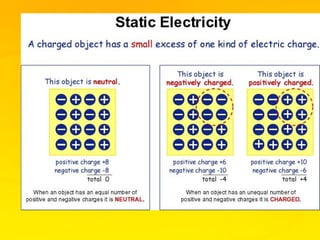
This document provides an overview of electricity and electrical circuits. It defines electricity as the flow of electric current and notes that electricity is caused by an imbalance of positive and negative charges. It then explains that an electrical circuit provides a complete path for electricity to flow through devices. Common examples of circuits include household wiring and car batteries. The document discusses the differences between open and closed circuits and how switches are used to open and close circuits to control the flow of electricity.




![2. Which of these is NOT
an electric circuit?
A. The wiring the lights your
house.
B. Lightning, clouds, planet Earth
C. Water flowing through pipes
[Default] a house.
in
[MC Any]
[MC All]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electricityandcircuitsemilyneistadtsconflictedcopy2011-10-27-121104225900-phpapp01/85/Electricity-and-circuits-7-320.jpg)
![3. When a current is
broken, where does
the electricity go?
A. It spills out onto the ground.
B. The current stops, electrical currents only
flow in closed circuits.
[Default]
[MC Any]
C. All] floats off into space.
[MC It](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electricityandcircuitsemilyneistadtsconflictedcopy2011-10-27-121104225900-phpapp01/85/Electricity-and-circuits-10-320.jpg)