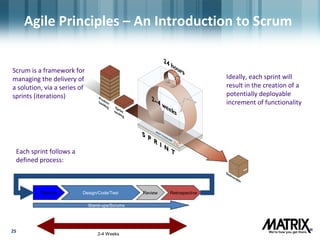
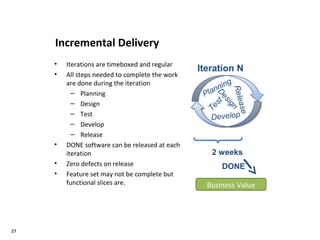
The document provides an overview of Matrix, an IT solutions company, and discusses key concepts of agile project management and how they can be applied to sales. Some key points:
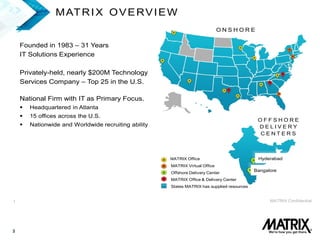
- Matrix is a 31-year-old, privately held IT services company with over 2,300 IT positions filled annually and 1,500 consultants. It has offices across the US and offshore delivery centers.
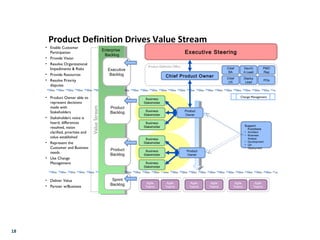
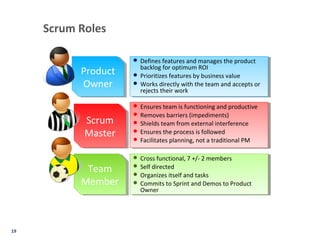
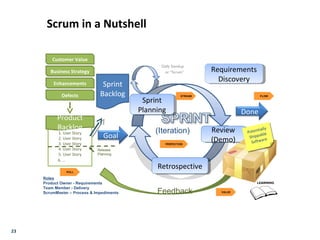
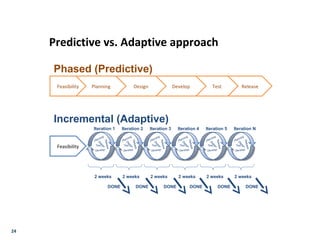
- Agile principles focus on individuals, interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change. For sales, these emphasize understanding customer value, tying it to company vision/initiatives, and ensuring quick delivery of value.
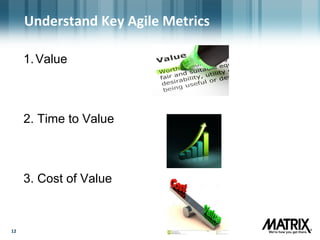
- Key agile metrics for sales include customer value, time to deliver value, and